
Introduction
Just like an eagle keenly observes its surroundings to avoid danger, busy Indian professionals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s need to be aware of the silent yet significant threats of heart attacks. This blog serves as your vigilant eye, offering a comprehensive understanding of the science behind heart attacks and their effects on health.
We delve into the real causes of heart attacks, focusing on coronary artery disease (CAD) and other less common causes like severe artery spasms. With heart disease being a leading cause of death globally, and considering that about 27.1 million people in India suffer from coronary artery disease, this blog is a crucial read for those seeking to safeguard their heart health.
The blog outlines the symptoms of a heart attack, emphasising the importance of recognizing these signs for prompt medical intervention. It also highlights key risk factors, including age, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and lifestyle choices like smoking and physical inactivity. Our goal is to empower you with knowledge, enabling you to identify risks and take proactive steps towards a healthier heart.
Written in simple English, this blog is designed to be accessible and motivating, encouraging you to take control of your heart health. By understanding the exact science behind heart attacks, you can be better prepared to prevent them and ensure a healthier future.
The Unseen Enemy: Part 1
In the heart of Gujrat, a city that never sleeps, lived Ayesha, a 45-year-old financial analyst. Her life was a tapestry of numbers and trends, woven with the threads of long hours and relentless dedication. Ayesha, a mother of two, balanced her demanding career with her family life, often at the cost of her own health.
Ayesha, known for her sharp intellect and emotional resilience, had always placed her health on the back burner. She believed that her busy lifestyle left no room for ailments. Her diet was sporadic, exercise was a forgotten word, and stress was her constant companion.
Symptoms and Signs of a Heart Attack
A heart attack can present with various symptoms and signs that should not be ignored. Recognizing these warning signs can help you seek immediate medical attention, potentially preventing further damage to your heart. Common symptoms of a heart attack include:
- Chest pain or discomfort: This can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the chest. It may last for a few minutes or come and go.
- Pain in the jaw, neck, back, or arm: The pain can radiate from the chest to these areas. It is not limited to the left side of the body.
- Shortness of breath: You may feel breathless or have difficulty breathing, even when resting or performing simple tasks.
- Feeling weak or light-headed: You may experience a sudden loss of strength or feel faint.
- Nausea: Some people may feel nauseous or vomit during a heart attack.
- Unusual tiredness: Fatigue or extreme exhaustion can occur without any apparent reason.
If you or someone around you experiences these symptoms, it is crucial to call 9-1-1 or your local emergency number immediately. Do not wait or try to tough it out. Prompt medical attention can greatly reduce the amount of damage to the heart muscle and improve your chances of recovery.
“Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack and seeking help promptly can save lives.”- American Heart Association
Remember, every minute matters during a heart attack. Don’t delay seeking medical assistance, as quick treatment can make a significant difference in your outcome.
Risk Factors for Heart Attack
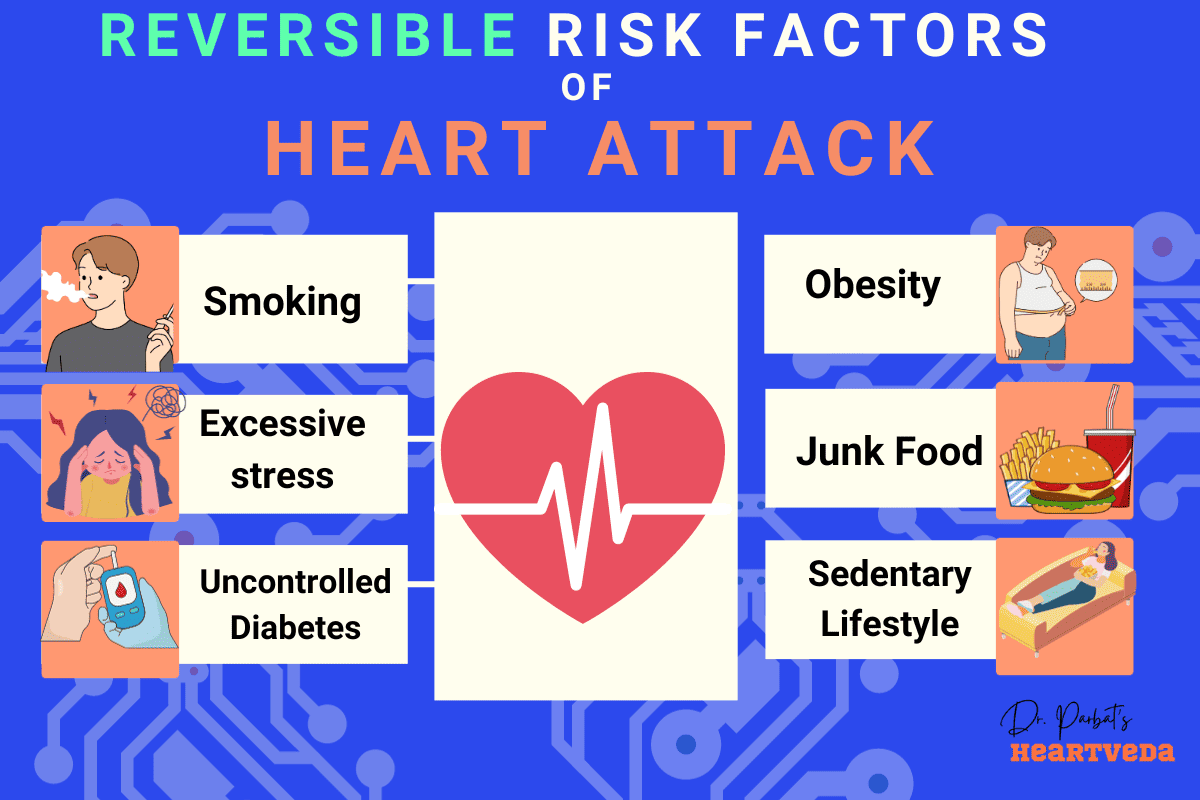
Several factors can increase the risk of a heart attack. It’s important to understand these risk factors and take steps to lower them through lifestyle changes, medication, or both.
- Age: Men over the age of 45 and women over the age of 55 are at higher risk of a heart attack.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a significant risk factor for heart disease and heart attacks.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood can contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of a heart attack.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease, including heart attacks.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing heart disease and are more likely to have a heart attack.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
Half of all Americans have at least one of these key risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking. It is crucial to address these risk factors and make lifestyle changes to lower the risk of a heart attack.
Take control of your heart health
“Understanding your risk factors is the first step towards prevention. By making healthier choices and managing these factors, you can significantly reduce your chances of a heart attack.”
| Risk Factors | Prevalence |
| Age | Men over 45 Women over 55 |
| High Blood Pressure | Approximately 45% of adults in India have hypertension. |
| High Cholesterol | About 15% of adults in India have high cholesterol levels. |
| Smoking | Approximately 10% of adults in India are smokers. |
| Diabetes | Around 9.3% of adults in India have diabetes. |
| Obesity | Roughly 30% of adults in India are obese. |
By addressing these risk factors and prioritizing your heart health, you can take control of your well-being and reduce the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack.
The Unseen Enemy: Part 2
One day, while analyzing a complex financial report, Ayesha felt a sudden, intense pain in her chest. She paused, attributing it to stress and overwork. But the pain persisted, accompanied by a feeling of tightness and breathlessness. Ayesha tried to push through, but her body refused to cooperate.
Her husband, Amit, noticing her discomfort, suggested they visit the hospital. Ayesha reluctantly agreed, thinking it was just a precaution. At the hospital, the doctors performed several tests and revealed a shocking diagnosis – Ayesha had suffered a minor heart attack.
Recovery After a Heart Attack
After a heart attack, it’s important to take steps to lower the risk of future health problems. The heart may be damaged, which can affect its rhythm and ability to pump blood effectively. To support your recovery and promote heart health, incorporating physical activity, making lifestyle changes, and participating in cardiac rehabilitation can significantly benefit you.
Physical Activity for Heart Health
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. As you recover from a heart attack, it’s essential to start with low-intensity exercises, gradually increasing the intensity and duration over time. Activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling are ideal for enhancing cardiovascular fitness, strengthening the heart muscle, and improving overall circulation.
Lifestyle Changes for Heart Health
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is essential for preventing further damage and reducing the risk of future heart problems. Making changes to your diet, such as consuming a balanced and nutritious meal plan that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and limiting unhealthy fats and sodium, can significantly benefit your heart health. Additionally, quitting smoking and managing stress levels through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga are vital for promoting a healthy recovery.
Cardiac Rehabilitation Program
Participating in a cardiac rehabilitation program can provide comprehensive support for your recovery journey. These programs are designed to offer physical activity guidance, education on healthy living, counseling, and emotional support from a team of healthcare professionals. The structured exercise sessions, combined with personalized education and ongoing monitoring, can help you regain strength, enhance cardiovascular fitness, and improve your overall quality of life.
Heart Damage and Heart Rhythm
A heart attack can cause damage to the heart muscle, affecting its rhythm and ability to pump blood efficiently. The damaged tissue may need time to heal, and during this period, maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle and following medical guidelines are crucial to prevent further complications.
Benefits of Cardiac Rehabilitation
| Benefits | Description |
| Improved physical fitness | Structured exercise sessions tailored to your needs can enhance cardiovascular fitness, improving endurance and strength. |
| Healthy lifestyle education | Receive guidance on nutrition, stress management, medication management, and strategies to quit smoking. |
| Emotional support | Counseling and emotional support from healthcare professionals and fellow participants can help address any concerns or anxieties regarding your recovery. |
| Reduced risk of future events | By actively participating in a cardiac rehabilitation program, you can lower the chances of experiencing future heart problems and improve long-term outcomes. |
In summary, prioritizing your recovery after a heart attack involves engaging in physical activity, making lifestyle changes, and considering cardiac rehabilitation. By taking proactive steps to maintain heart health, you can reduce the risk of further complications and promote a healthy, fulfilling life.
Understanding a Heart Attack
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of blood to the heart is severely reduced or blocked. This can result in the damage or destruction of part of the heart muscle, leading to various symptoms and complications. To truly comprehend what happens during a heart attack, it is essential to understand the underlying causes and processes involved.
Plaque Buildup and Blocked Arteries
One of the most common causes of a heart attack is the buildup of plaques in the coronary arteries. These plaques consist of fatty deposits that gradually accumulate on the artery walls. Over time, the plaques can become thick and hardened, causing the arteries to narrow and restrict blood flow to the heart. In some cases, these plaques can rupture, resulting in the formation of a blood clot that further obstructs the artery, leading to a heart attack.
Coronary Artery Spasm
In addition to plaque buildup, a heart attack can also occur due to a severe spasm of a coronary artery. This spasm causes the artery to constrict and narrow abruptly, reducing or completely cutting off blood flow to the heart muscle. Although less common than plaque buildup, coronary artery spasms can still result in a heart attack and require immediate medical attention.
The Resulting Myocardial Infarction
Regardless of the specific cause, a heart attack, or myocardial infarction, results from a lack of blood flow to the heart muscle. This deprivation of oxygen and nutrients can lead to the death of heart tissue, causing significant damage to the overall heart function. The severity of the myocardial infarction depends on various factors, including the size and location of the affected area.
Understanding the mechanisms behind a heart attack can help individuals recognize the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors. By controlling conditions that contribute to plaque buildup and promoting heart health, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing a heart attack.
| Causes of a Heart Attack | How it affects the heart |
| Plaque buildup | Restricts blood flow and can lead to the formation of blood clots, causing a heart attack. |
| Coronary artery spasm | Constricts and narrows the artery, cutting off blood flow to the heart muscle, resulting in a heart attack. |
The Unseen Enemy: Part 3
Ayesha was stunned. She had always associated heart attacks with more dramatic symptoms. The doctors explained the science behind heart attacks, emphasizing how stress, diet, and lifestyle play significant roles. Ayesha realized her ignorance had nearly cost her life.
During her recovery, Ayesha reflected on her choices. She remembered her colleague, Dr. Rhea, a cardiologist who had once offered a seminar on heart health, which she had skipped. Ayesha decided it was time to change.
Causes of a Heart Attack
Impact of LDL-C Levels on Heart-Related Risks
| LDL-C Level | Heart Attack (MI) Risk | Cardiovascular Disease Risk |
| Higher LDL-C (38.7 mg/dL ↑) | 28% Increased Risk | 14% Increased Risk |
| Very High LDL-C (≥193 mg/dL) | 134% Increased Risk | 54% Increased Risk |
The main cause of a heart attack is coronary artery disease, which is the buildup of plaques in the coronary arteries. These plaques can rupture and form a blood clot, leading to a blockage of blood flow. Another cause is a severe coronary artery spasm, which can stop blood flow to the heart muscle. Infections, such as COVID-19, can also damage the heart muscle and cause a heart attack. Spontaneous coronary artery dissection, a tear inside a heart artery, is another life-threatening condition that can cause a heart attack.
Risk Factors for a Heart Attack
There are several risk factors that can increase your chances of developing coronary artery disease and experiencing a heart attack. It’s important to be aware of these risk factors and take steps to manage and reduce them to lower your risk. Here are the key risk factors to consider:
1. Age
As you get older, your risk of heart disease and heart attacks increases. Men over the age of 45 and women over the age of 55 are at higher risk.
2. Tobacco Use
Smoking or using tobacco products can damage your blood vessels and increase the risk of a heart attack. It’s important to quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
3. High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, forces your heart to work harder, increasing the risk of a heart attack. Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure are crucial.
4. High Cholesterol
Elevated levels of cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in your arteries, increasing the risk of a heart attack. It’s essential to monitor your cholesterol levels and take steps to keep them within a healthy range.
5. Diabetes
Diabetes can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks. Managing blood sugar levels and adopting a healthy lifestyle is vital for preventing complications.
6. Obesity
Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on your heart and increases the risk of heart disease and heart attacks. Maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and regular exercise is essential.
7. Family History
If you have a close family member who has experienced a heart attack or has a history of heart disease, your risk may be higher. Genetic factors can influence your susceptibility to heart problems.
8. Physical Inactivity
Lack of physical activity can contribute to obesity, high blood pressure, and other risk factors for heart disease. Regular exercise helps keep your heart healthy and reduces the risk of a heart attack.
Managing these risk factors through lifestyle changes, medication, or a combination of both is crucial for reducing your risk of a heart attack. Consult with your healthcare provider to assess your personal risk and develop a plan to protect your heart health.
Complications of a Heart Attack
A heart attack can have serious complications that can affect the overall functioning of the heart. These complications include:
- Irregular Heart Rhythms: After a heart attack, irregular heart rhythms, also known as arrhythmias, can occur. This can disrupt the normal electrical signals in the heart and cause the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or in an irregular pattern.
- Cardiogenic Shock: In some cases, a heart attack can cause the heart to be unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This condition, known as cardiogenic shock, can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
- Heart Failure: Heart failure can occur when the heart is unable to pump blood adequately. This can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention.
- Pericarditis: Pericarditis refers to inflammation of the sac that surrounds the heart. It can cause chest pain and discomfort, and in severe cases, can lead to complications such as fluid accumulation around the heart.
- Cardiac Arrest: Cardiac arrest is a sudden, unexpected loss of heart function. It occurs when the heart stops beating effectively, and immediate medical intervention is required to restore normal heart rhythm.
To reduce the risk of these complications, it’s important to seek prompt medical treatment after a heart attack and follow a comprehensive rehabilitation plan. This may include medication, lifestyle changes, and cardiac rehabilitation programs to improve heart health and reduce the chances of further complications.
Prevention of Heart Attack

To prevent a heart attack and promote a healthy heart, it is essential to adopt a balanced and healthy lifestyle while effectively managing risk factors. By incorporating the following practices into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing coronary artery disease and experiencing a heart attack:
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Eating a nutritious and well-balanced diet is crucial for maintaining heart health. Focus on consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars. A healthy diet can help manage blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and body weight, lowering the risk of heart disease.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise plays a vital role in preventing heart disease. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity each week. Additionally, incorporate strength training exercises at least two days a week. Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, manages blood pressure, and improves overall cardiovascular health.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can contribute to the development of heart disease. Implement stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. Prioritizing self-care and finding healthy outlets to cope with stress can significantly reduce the impact on your heart health.
Get Enough Sleep
Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining heart health. Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep patterns and sleep disorders have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Establish a regular sleep routine and create a sleep-friendly environment to ensure optimal rest and rejuvenation for your body.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption
While moderate alcohol consumption may have some cardiovascular benefits, excessive drinking can lead to serious health problems. It is recommended to limit alcohol intake to moderate levels, which means up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. However, it is important to note that it is best to avoid alcohol altogether if you have certain health conditions or take specific medications.
Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to improve your heart health. Seek support from healthcare professionals, join smoking cessation programs, or utilize nicotine replacement therapies to quit smoking for good.
By implementing these healthy lifestyle practices, effectively managing risk factors, and seeking medical guidance when necessary, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing coronary artery disease and experiencing a heart attack.
| Heart Attack Prevention Strategies | Description |
| Maintain a Healthy Diet | Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your diet while limiting saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars. |
| Engage in Regular Physical Activity | Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity each week, coupled with strength training exercises at least two days a week. |
| Manage Stress | Implement stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies to reduce the impact of chronic stress on your heart health. |
| Get Enough Sleep | Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night to support optimal cardiovascular health. |
| Moderate Alcohol Consumption | Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels, such as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. |
| Quit Smoking | Seek support and resources to quit smoking, as smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease. |
The Unseen Enemy: END
With Dr. Rhea’s help, Ayesha embarked on a journey of learning and lifestyle change. She educated herself about heart health, adopted a balanced diet, and incorporated exercise into her daily routine. She also learned stress management techniques to maintain her mental well-being.
Months later, Ayesha was a transformed woman. She was still a brilliant financial analyst, but now, she was also an advocate for heart health awareness in her workplace. She shared her story, hoping to inspire others to understand the science of heart attacks and prioritize their health.
Ayesha’s story highlights the critical importance of understanding the science behind heart attacks. Awareness and knowledge can lead to healthier choices and potentially save lives.
Conclusion
Protecting your heart health is essential, and understanding the real causes of heart attacks and managing your risk factors is key. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking prompt medical treatment, you can greatly reduce the risk of developing coronary artery disease and experiencing a heart attack.
Make heart attack prevention a priority by taking proactive steps to promote a healthy heart. This includes maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress effectively, getting enough sleep, moderating alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking.
Remember, prevention is always better than cure. By prioritizing your heart health and implementing these lifestyle changes, alongside any necessary medications, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of heart disease and live a long, healthy life.
Are you, like Ayesha, aware of the silent signs your body might be sending you, or will you wait until it’s too late?
Key Takeaways:
- Heart attacks are caused by coronary artery disease or a severe spasm of a coronary artery.
- Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain, shortness of breath, jaw pain, arm pain, and fatigue.
- Risk factors for heart attacks include age, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and obesity.
- Recovery after a heart attack involves lifestyle changes, physical activity, and cardiac rehabilitation.
- Preventing heart attacks requires a healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and seeking medical treatment.
FAQ Section on Real Causes of Heart Attack in Early Age
A: The symptoms of a heart attack can include chest pain, discomfort in other areas of the upper body, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness, and cold sweats.
A: Several factors can increase your risk of a heart attack, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a family history of heart disease.
A: A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, often by a buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. This blockage can lead to damage or death of the heart muscle.
A: Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical activity, managing stress, controlling risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
A: Diagnosis involves analyzing symptoms, carrying out electrocardiograms (ECG), blood tests, and imaging tests. Treatment may involve medications, angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery, depending on the severity of the situation.
A: Recognizing symptoms early and seeking immediate medical attention is crucial. Rapid response can improve the chances of survival and minimize damage to the heart muscle.
A: Heart attacks are a leading cause of death globally and can occur suddenly without warning, emphasizing the importance of understanding the risks, symptoms, and preventive measures associated with heart health.
A: Heart disease can lead to a heart attack by causing a buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can eventually block blood flow to the heart, leading to a heart attack.
A: You can lower your risk of a heart attack by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco smoke.
A: Coronary heart disease is a condition in which plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart. This condition significantly increases the risk of a heart attack.
A: Treatment for a heart attack may include medications, such as clot-busting drugs, and medical procedures, such as angioplasty and stent placement, to restore blood flow to the heart. Cardiac rehabilitation and lifestyle changes are also important parts of the treatment plan.
A: A family history of heart disease can increase your risk of experiencing a heart attack, as it may indicate a genetic predisposition to certain risk factors for heart disease and heart attacks.
A: A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, usually due to a blood clot formed in a narrowed coronary artery. This blockage leads to damage or death of the heart muscle tissue.
A: A heart attack is diagnosed based on symptoms, medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, and imaging tests, like a coronary angiogram or cardiac MRI.
A: Some important facts about heart attacks include that they can occur suddenly, can be life-threatening, and require prompt medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the risk factors are essential for prevention and early intervention.
A: Treatments for a heart attack may include medications, such as clot-busting drugs, and procedures like angioplasty and stent placement to restore blood flow to the heart.
A: A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle becomes blocked, often due to the formation of a blood clot in a coronary artery, leading to oxygen deprivation and damage to the heart tissue.
A: Yes, there is a connection between heart disease and stroke, as both conditions can result from similar risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
A: The development of heart diseases can vary from person to person. It can be influenced by factors such as lifestyle, genetics, and overall health. It’s important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and undergo regular medical check-ups to monitor heart health.
A: The pain experienced during a heart attack can vary for different individuals. It may start as mild discomfort and escalate into severe pain. If you suspect a heart attack, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical assistance regardless of the intensity of the pain.
A: The pain associated with a heart attack can begin gradually or suddenly and may manifest as discomfort, pressure, or pain in the chest, arms, neck, jaw, or back. It’s essential to recognize these symptoms and seek medical help promptly.
