
Introduction
High blood cholesterol can be a silent architect of a dangerous condition in your arteries. For busy Indian professionals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, understanding how to prevent atherosclerosis and arterial plaque buildup is like learning to steer clear of hidden roadblocks on the path to good health.
This blog serves as your roadmap in navigating the complex world of atherosclerosis, a condition where cholesterol, fats, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries, much like unwanted clutter in a vital pathway. We’ll explore the causes of arterial plaques, the role of LDL cholesterol in this process, and most importantly, effective strategies to prevent and manage this condition.
With simple language and a friendly tone, we aim to empower you with knowledge and practical tips to keep your arteries clear and your heart healthy. From lifestyle changes to medical interventions, this blog is your guide to maintaining smooth and healthy arterial highways for your blood flow.
Let’s embark on this journey to better heart health, understanding the importance of keeping our arterial pathways free from the clutter of cholesterol and plaque.
What Causes Arterial Plaques and Atherosclerosis
Cholesterol plaques develop in the walls of your arteries over time, primarily due to the accumulation of LDL cholesterol. This process is known as atherosclerosis, and it can have serious consequences for your cardiovascular health.
Atherosclerosis begins when the endothelium, the delicate lining of your blood vessels, becomes damaged. This damage allows LDL cholesterol to enter the artery walls, where it starts to build up. Over time, this buildup attracts white blood cells called macrophages, which engulf the cholesterol and create plaques.
Cholesterol plaques can take different forms within the artery walls. They may stay within the wall itself, causing the narrowing of the artery and restricting blood flow. In some cases, the plaques can grow, further obstructing the path of blood flow. In more severe situations, the plaques can rupture, leading to the formation of blood clots that can block the artery entirely.
Cholesterol plaques are the main factor behind heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral arterial disease. When a plaque fully blocks an artery in the heart, it can result in a heart attack. Blocked arteries in the brain can cause strokes, and when the arteries that supply the limbs are affected, it can lead to peripheral arterial disease.
To protect your cardiovascular health, it’s important to understand the role of cholesterol plaques and how they contribute to atherosclerosis. By addressing the underlying causes and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can reduce the risk of plaque formation and improve your overall well-being.
The Silent Battle: Conquering Cholesterol
Part – 1
In the pulsating heart of Mumbai, where the rhythm of local trains and the buzz of street vendors blend into the soundtrack of daily life, lived Anjali, a 45-year-old bank manager. Her life was a whirlwind of numbers, negotiations, and nurturing a team that looked up to her as a beacon of strength and wisdom.
Anjali’s home was a sanctuary she shared with her husband, a freelance graphic designer, and their two spirited children. Despite her demanding career, Anjali’s emotional intelligence shone through in her ability to maintain a delicate balance between her professional and personal life. However, this balance did not extend to her health, which she often placed on the back burner, dismissing the need for regular check-ups and exercise with a wave of her hand and a confident, “I feel fine.”
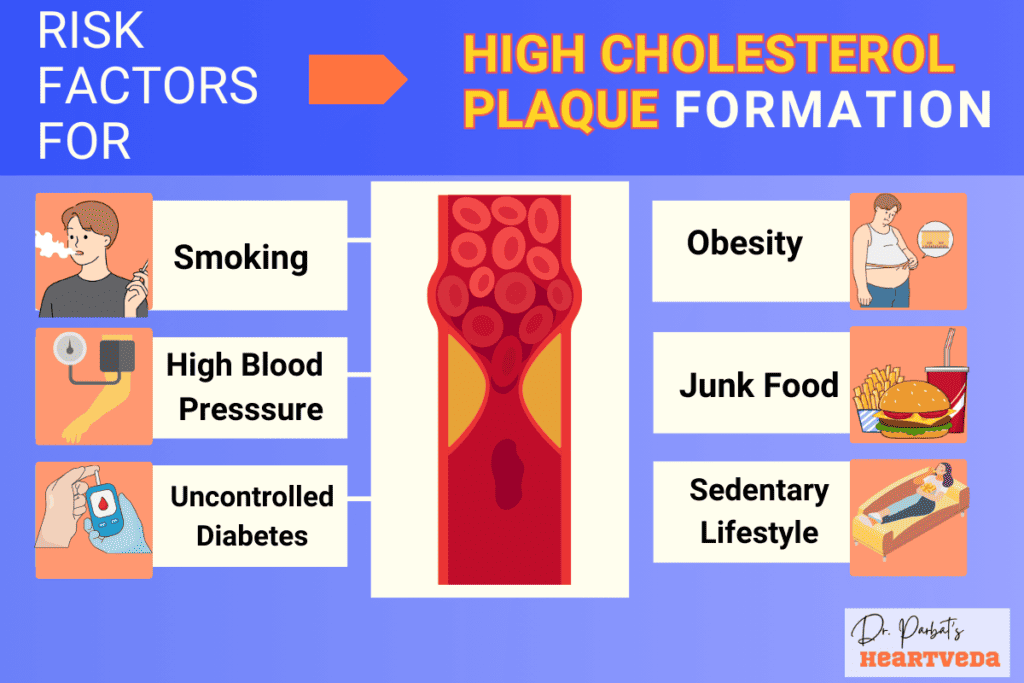
Risk for High Cholesterol Plaque Formation
How LDL forms arterial plaques – Flowchart
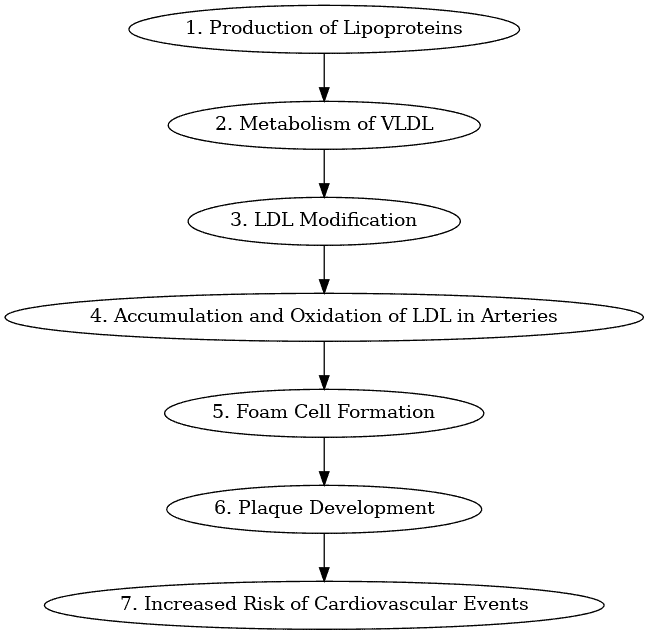
Cholesterol plaques can develop due to several risk factors that increase the likelihood of plaque formation. It is important to be aware of these risk factors in order to take appropriate measures to prevent and reduce plaque buildup. The main risk factors for cholesterol plaque formation include:
- High Cholesterol Levels: Elevated levels of cholesterol, particularly LDL cholesterol, contribute to plaque formation. LDL cholesterol can build up in artery walls and initiate the development of cholesterol plaques over time.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. This damage allows LDL cholesterol to enter the arterial walls, leading to plaque formation.
- Smoking: Smoking not only damages blood vessels but also reduces the level of HDL cholesterol, which helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. This combination increases the risk of plaque buildup.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes often have high blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels and accelerate plaque formation. Additionally, diabetes is often associated with other risk factors, such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure.
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the waist area, has been linked to increased cholesterol levels and the development of plaque. Obesity also contributes to other risk factors, such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels, all of which promote plaque formation. Engaging in regular exercise helps manage cholesterol levels and reduces the risk of plaque buildup.
It is worth noting that genetic factors and a family history of high cholesterol can also increase the risk of developing cholesterol plaques. If you have a family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular disease, it is especially important to monitor and manage your risk factors.
By addressing these risk factors through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, it is possible to prevent and reduce the formation of cholesterol plaques. Making healthy choices and managing these risk factors can significantly improve your cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
The Silent Battle: Conquering Cholesterol
Part – 2
Her daily routine was a testament to her dedication—early mornings, late nights, and meals often skipped or replaced with whatever was quickest and most convenient. This relentless pace was a badge of honor until the day it wasn’t.
The consequence of her neglect came subtly at first—a persistent fatigue, breathlessness on her daily commute, and a discomfort in her chest she attributed to stress. It was during a routine health check-up, insisted upon by her concerned husband, that the truth emerged: Anjali had high blood cholesterol, a silent architect of atherosclerosis, laying the groundwork for heart disease.
Anjali’s darkest moment came with the realization that her lifestyle could lead her down a path from which there was no return. The thought of not being there for her children’s milestones, of leaving her husband too soon, and of dreams unfulfilled because of preventable health issues was a wake-up call louder than any alarm.
Identifying the Symptoms and Complications of Cholesterol Plaques
Cholesterol plaques can cause various symptoms and complications depending on their location. It is essential to recognize and address these symptoms promptly to prevent further complications.
1. Angina
One of the primary symptoms of cholesterol plaque buildup in the heart is angina. Angina is characterized by chest pain or discomfort, often a result of inadequate blood flow to the heart muscle. It can feel like pressure, squeezing, or a burning sensation in the chest. Angina typically occurs during physical exertion or high-stress situations and subsides with rest or medication.
2. Heart Attack
A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, occurs when a cholesterol plaque in a coronary artery ruptures, leading to a complete blockage of blood flow. This sudden blockage can cause irreversible damage to the heart muscle, and prompt medical attention is crucial. Common symptoms of a heart attack include severe chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, dizziness, and pain or discomfort in the arms, jaw, neck, or back.
3. Stroke
When a cholesterol plaque in the brain’s arteries ruptures or blocks blood flow, it can result in a stroke. Stroke symptoms include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side), difficulty speaking or understanding speech, sudden confusion, severe headache, and trouble walking or maintaining balance. Immediate medical intervention is vital in minimizing brain damage and maximizing chances of recovery.
4. Peripheral Arterial Disease
Cholesterol plaque buildup in the arteries of the limbs can cause peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Symptoms of PAD include leg pain or cramping during physical activity (claudication), slow wound healing, coldness or numbness in the legs or feet, and the development of sores or ulcers. In severe cases, PAD can lead to tissue death (gangrene) and the need for amputation.
By recognizing these symptoms and seeking appropriate medical attention, individuals can prevent complications and effectively manage cholesterol plaques. Regular check-ups, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to prescribed treatments are vital in combating the effects of cholesterol plaques.
Diagnosis and Screening for Cholesterol Plaques
To effectively combat cholesterol plaques and mitigate their health hazards, timely diagnosis and screening are crucial. There are various methods and tests available that can accurately assess and evaluate the presence of cholesterol plaques and associated risk factors.
Cholesterol Screening and Lipid Profile Tests
Cholesterol screenings and lipid profile tests are commonly used to measure cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood. These tests provide valuable insights into your lipid profile and help determine your risk of developing cholesterol plaques and related complications.
During a cholesterol screening, a small blood sample is taken, typically from your finger or arm. The sample is then analyzed to assess your total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol), HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol), and triglyceride levels. Based on these measurements, healthcare professionals can evaluate your cholesterol levels and identify any abnormalities or imbalances.
A lipid profile test provides more comprehensive information about your lipid profile, encompassing various cholesterol subtypes, such as LDL particle size and density. This test offers a detailed analysis of your cholesterol composition, enabling a more accurate assessment of your heart disease risk and potential plaque formation.
These screenings and tests are typically accessible through healthcare facilities, clinics, and laboratories. They are quick, non-invasive, and provide critical information enabling healthcare professionals to tailor preventive and treatment strategies specifically to you.
Assessment for Risk Factors of Heart Disease
Alongside cholesterol screenings, a thorough heart disease risk assessment may be conducted to evaluate other risk factors associated with cholesterol plaques and cardiovascular diseases. This assessment takes into account various factors that contribute to plaque formation and the overall risk of developing heart-related complications.
Risk factors considered during this assessment may include:
- High cholesterol levels
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
By assessing these risk factors, healthcare professionals can identify individuals who may be at higher risk of developing cholesterol plaques and implement appropriate preventive measures accordingly.
Imaging Tests for Visualization and Detection
Imaging tests are invaluable tools for visualizing arteries and detecting the presence of cholesterol plaques. These non-invasive procedures provide detailed information about the extent and location of plaque buildup, allowing healthcare professionals to establish the most effective course of action.
Commonly used imaging tests include:
- Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to create images of the arteries and identify plaque formation.
- CT Scans: Computerized tomography scans analyze cross-sectional images of the arteries, providing detailed insights into plaque buildup.
- Angiograms: Angiograms involve the injection of contrast dye into the arteries, enabling clear visualization of plaque presence and arterial blockages.
| Imaging Test | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, painless, and safe; provides real-time imaging | May have limitations in visualizing certain areas |
| CT Scans | Offers detailed images; useful for detecting calcified plaques | Exposure to radiation; potential allergies to contrast dye |
| Angiograms | Highly accurate; allows for simultaneous intervention or treatment if required | Invasive procedure with potential risks; requires contrast dye |
Regular screenings, evaluations, and imaging tests play a pivotal role in the early detection and management of cholesterol plaques. These diagnostic tools empower healthcare professionals to closely monitor plaque formation, assess associated risks, and intervene promptly to prevent complications.
The Silent Battle: Conquering Cholesterol
Part – 3
The path to recovery was illuminated by Dr. Shah, a cardiologist who became her guide in navigating the complexities of heart health. Alongside medication prescribed to combat her high cholesterol, Anjali embraced lifestyle changes with the support of her family. Together, they embarked on a journey of transformation—incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and finding joy in evening walks that became a cherished family ritual.
Anjali’s journey from denial to proactive health management became a message of hope and resilience. She shared her story with colleagues, friends, and anyone willing to listen, emphasizing the importance of regular health screenings, the power of medication in managing conditions like high cholesterol, and the transformative impact of lifestyle changes.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent and Manage Your Cholesterol

To combat cholesterol plaques and reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral arterial disease, it is essential to make positive lifestyle changes. By adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight, you can actively prevent and manage cholesterol plaques.
1. Healthy Diet:
Avoiding saturated fats and incorporating a variety of nutritious foods into your diet can help lower cholesterol levels and promote cardiovascular health. Consider the following dietary recommendations:
- Include plenty of fruits and vegetables in your meals.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Opt for lean proteins, such as fish, poultry, and legumes.
- Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages.
Eating a balanced and wholesome diet can significantly contribute to plaque prevention and overall well-being.
2. Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for managing weight, improving cardiovascular health, and reducing the risk of cholesterol plaques. Incorporate both aerobic exercises and strength training into your routine for optimal results. Some exercise recommendations include:
- Brisk walking, jogging, or cycling for at least 30 minutes a day.
- Strength training exercises to build muscle and boost metabolism.
- Practicing yoga or other forms of stress-reducing activities.
By making exercise a part of your daily routine, you can significantly decrease the chances of plaque formation and maintain a healthy heart.
3. Smoking Cessation:
Smoking damages the blood vessels and contributes to plaque build-up, increasing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular complications. Quitting smoking is crucial for managing and preventing cholesterol plaques. Seek support from healthcare professionals, join smoking cessation programs, and explore nicotine replacement therapies to successfully quit smoking.
4. Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for overall well-being and plaque prevention. Excess weight puts strain on the heart and increases the likelihood of plaque formation. Focus on achieving a healthy weight through a combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized weight management strategies and guidance.
Remember, lifestyle changes play a significant role in preventing and managing cholesterol plaques. By adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight, you can actively reduce the risk of heart disease and promote overall cardiovascular health.
| Benefits of Lifestyle Changes for Cholesterol Plaque Prevention | Actions to Take |
| Lowering cholesterol levels | Adopt a healthy, low-cholesterol diet |
| Improving cardiovascular health | Engage in regular aerobic and strength training exercises |
| Reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes | Quit smoking and maintain a healthy weight |
| Promoting overall well-being | Foster a healthy lifestyle and prioritize self-care |
Medications for Treating Cholesterol Plaques
When it comes to combating cholesterol plaques, medications can play a vital role in supplementing lifestyle changes. Several cholesterol-lowering medications have proven effective in managing cholesterol levels and stabilizing plaques. Here are some common medications used in the treatment of cholesterol plaques:
1. Statins
Statins are the most commonly prescribed medication for lowering LDL cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. They work by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for producing cholesterol in the liver. By lowering LDL cholesterol, statins help prevent the formation of new plaques and can even reduce the size of existing ones.
2. Fibrates
Fibrates are another class of medications used in conjunction with statins to manage cholesterol levels. They primarily target triglyceride levels and increase HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol). By reducing triglycerides, fibrates contribute to plaque stabilization and overall cardiovascular health.
3. Niacin
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is a medication that can raise HDL cholesterol levels and lower LDL and triglyceride levels. By improving the lipid profile, niacin aids in plaque stabilization and prevention. However, niacin may cause side effects such as flushing and liver abnormalities, so it should be used under medical supervision.
4. Bile Acid Sequestrants
Bile acid sequestrants work by binding to bile acids in the intestines, preventing their reabsorption and promoting their excretion. This process indirectly lowers LDL cholesterol levels by increasing the liver’s uptake of cholesterol to produce new bile acids. Bile acid sequestrants are often used in combination with statins to further decrease LDL levels.
It is essential to follow your healthcare provider’s prescribed medication regimen and regularly consult with them for check-ups and adjustments. While these medications have proven benefits, they may also have side effects and interactions with other medications. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures personalized treatment options tailored to your specific needs and health conditions.
Surgical and Interventional Procedures for Cholesterol Plaques
In severe cases of cholesterol plaques, surgical and interventional procedures may be necessary to restore blood flow. There are several options available to address arterial blockages and coronary artery disease:
- Angioplasty: This procedure involves inserting a catheter with a deflated balloon into the blocked artery. The balloon is then inflated to compress the plaque against the artery walls, widening the passage for better blood flow.
- Stenting: In conjunction with angioplasty, a stent, which is a small mesh-like tube, is placed in the artery to keep it open. The stent remains permanently in place, providing support and preventing future blockages.
- Bypass surgery: In cases where multiple arteries are affected or the blockage is severe, bypass surgery may be recommended. This procedure involves using a healthy blood vessel, often from the leg or chest, to create a detour around the blocked artery, restoring proper blood flow.
These surgical and interventional procedures are effective in managing arterial blockages and coronary artery disease, providing relief and improving overall heart health. However, the choice of procedure will depend on the individual’s condition, the severity of the blockage, and the doctor’s assessment.
| Procedure | Main Purpose | Advantages |
| Angioplasty | Clear arterial blockages, improve blood flow | Minimally invasiveShort recovery timeCan be done on an outpatient basis |
| Stenting | Keep the artery open, prevent future blockages | Provides long-term supportReduces the risk of restenosis (re-narrowing)Improves blood flow dynamics |
| Bypass surgery | Create a detour around the blocked artery | Allows blood to bypass the blocked areaImproves blood flow to the heart muscleCan be used for multiple blockages |
These procedures require the expertise of a cardiovascular surgeon and a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s condition. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate procedure and to discuss the potential risks and benefits.
The Silent Battle: Conquering Cholesterol
END
As she reflected on her journey, Anjali pondered a question that resonated deeply with her audience: “If not now, when?” It was an invitation to prioritize health, to recognize the signs our bodies give us, and to understand that fighting conditions like atherosclerosis is not just possible but imperative for a life filled with moments worth living for.
The message was clear: high blood cholesterol is a formidable foe, but with medication, lifestyle changes, and a dose of awareness, it’s a battle that can be won, ensuring the heart’s rhythm beats strong and steady amidst the hustle and bustle of life.
Conclusion
Cholesterol plaque and atherosclerosis are serious health concerns that can have devastating consequences. The good news is that there are steps you can take to prevent and manage these conditions. By making simple lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and quitting smoking, you can significantly reduce your risk of plaque formation. Managing other risk factors like high cholesterol and high blood pressure is also crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health.
In addition to lifestyle modifications, medication and surgical interventions can be effective in treating existing cholesterol plaques. Prescription medications, such as statins, fibrates, niacin, and bile acid sequestrants, can help lower cholesterol levels and stabilize plaques. For more advanced cases, surgical procedures like angioplasty, stenting, and bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow and reduce the risk of complications.
Remember to work closely with your healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive prevention and treatment plan tailored to your individual needs. By taking control of your health and making necessary lifestyle changes, you can prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques and improve your overall well-being. Start today and prioritize your cardiovascular health for a healthier future.
Key Takeaways:
- Cholesterol plaques can cause heart disease, heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral arterial disease.
- Atherosclerosis, the process behind cholesterol plaque formation, can be prevented and managed.
- Risk factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and sedentary lifestyle contribute to plaque development.
- Symptoms of cholesterol plaques include angina, heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral arterial disease.
- Diagnosis and screening methods, such as cholesterol screenings, lipid profile tests, and imaging tests, help detect plaques.
Q: What is atherosclerosis and how is it related to high cholesterol?
A: Atherosclerosis is the buildup of plaque in the arteries, and high cholesterol, especially high LDL cholesterol, is a major contributor to this condition.
Q: How does high cholesterol lead to artery plaque buildup?
A: High levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Q: What are the common causes of arterial plaque buildup from high cholesterol?
A: Arterial plaque buildup is primarily caused by high levels of LDL cholesterol, along with other factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Q: How can I manage my cholesterol to prevent plaque buildup in my arteries?
A: You can manage your cholesterol by making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and, if necessary, taking medication prescribed by your doctor.
Q: Can artery plaque buildup from high cholesterol cause any symptoms?
A: In the early stages, arterial plaque buildup may not cause any symptoms, but as it progresses, it can lead to conditions such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or leg pain while walking.
Q: How can I lower my cholesterol levels to reduce the risk of plaque buildup in my arteries?
A: You can lower your cholesterol levels by adopting a healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, increasing physical activity, and, if needed, taking cholesterol-lowering medications.
Q: What medical conditions are associated with high cholesterol and arterial plaque buildup?
A: High cholesterol and arterial plaque buildup are associated with conditions such as peripheral artery disease, carotid artery disease, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
Q: How often should I get my cholesterol checked to monitor plaque buildup in my arteries?
A: The frequency of cholesterol checks depends on your age, overall health, and risk factors for high cholesterol. Your doctor can advise you on how often you should get tested.
Q: What lifestyle changes can help improve my cholesterol levels and prevent plaque buildup?
A: Making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and managing stress can all help improve cholesterol levels and prevent arterial plaque buildup.
Q: Does high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol play a role in preventing arterial plaque buildup?
A: Yes, HDL cholesterol is known as “good” cholesterol and helps remove LDL cholesterol from the arteries, which can reduce the risk of plaque buildup and atherosclerosis.
Q: What is atherosclerosis and how is it related to cholesterol?
A: Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis where plaque builds up in the arteries. Cholesterol plays a significant role in the formation of this arterial plaque, particularly LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol.
Q: What are the causes of arterial plaque buildup and high cholesterol?
A: Arterial plaque buildup is primarily caused by high levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. These can lead to reduced blood flow and increase the risk for heart-related complications.
Q: How can I manage my cholesterol levels to prevent atherosclerosis?
A: You can manage your cholesterol levels by making lifestyle changes, such as following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and, if necessary, taking medication prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Q: What are the risks associated with high cholesterol and atherosclerosis?
A: High cholesterol and atherosclerosis can increase the risk of heart attacks, as the plaque may restrict blood flow and cause a heart attack if it ruptures. Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of death globally.
Q: What is the role of LDL in the development of atherosclerosis?
A: LDL, also known as “bad” cholesterol, can deposit cholesterol in the walls of the arteries, leading to the formation of plaque and the progression of atherosclerosis.
Q: How can I improve my cholesterol and reduce the risk of high cholesterol?
A: You can improve your cholesterol levels by adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking. These lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of high cholesterol.
Q: What happens when plaque builds up in the arteries?
A: When plaque builds up in the arteries, it can limit the flow of oxygen-rich blood to vital organs and tissues, increasing the risk of coronary artery disease and other cardiovascular complications.
Q: What are triglycerides, and how do they contribute to atherosclerosis?
A: Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood. High levels of triglycerides can contribute to atherosclerosis by causing plaque to form in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart-related issues.
Q: How does high cholesterol contribute to the risk of heart disease?
A: High levels of cholesterol in the blood can cause the arteries to narrow and harden, reducing blood flow. This can increase the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular problems.
Q: Why is it important to reduce the risk of high cholesterol and manage cholesterol levels?
A: It is crucial to reduce the risk of high cholesterol and manage cholesterol levels to lower the risk of atherosclerosis and its associated complications, including heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases.
Q: What is atherosclerosis and how is it related to cholesterol?
A: Atherosclerosis, often called hardening of the arteries, is caused by plaque buildup inside the arteries. Cholesterol, especially unhealthy cholesterol levels, plays a crucial role in the development of arterial plaque.
Q: What are the main causes of arterial plaque buildup?
A: Arterial plaque is primarily caused by high cholesterol levels, particularly unhealthy cholesterol, and triglyceride levels in the blood. It can also be made up of cholesterol, leading to the narrowing and hardening of the arteries over time.
Q: How does high cholesterol lead to atherosclerosis?
A: When there is too much cholesterol in your blood, it can cause plaque to form in the arteries, which can restrict or block blood flow, increasing the risk for atherosclerosis.
Q: What are the risks associated with high cholesterol and atherosclerosis?
A: High cholesterol levels can lead to atherosclerosis, which in turn increases the risk for heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. Managing your cholesterol is essential to prevent these risks.
Q: How can I manage my cholesterol to prevent atherosclerosis?
A: Managing your cholesterol involves maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and, if necessary, taking medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Monitoring and managing your cholesterol levels can help prevent atherosclerosis.
Q: Can atherosclerosis be prevented by controlling cholesterol levels?
A: Yes, by monitoring and maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, you can reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis and prevent the progression of plaque buildup in the arteries.
Q: How can I limit cholesterol intake?
A: Limiting cholesterol intake involves choosing healthier fats, such as unsaturated fats, and reducing consumption of saturated and trans fats. Additionally, focusing on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help in managing cholesterol levels.
Q: Are there different types of cholesterol that contribute to atherosclerosis?
A: Yes, there are different types of cholesterol, including LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein). High levels of LDL cholesterol, often referred to as unhealthy cholesterol, are particularly associated with atherosclerosis.
Q: What are some ways to prevent high cholesterol and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis?
A: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can help prevent high cholesterol and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
Q: How does a healthy diet help in preventing atherosclerosis?
A: A healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and plaque buildup in the arteries.Q: Can I test cholesterol at home?
Q: Can I test cholesterol at home?
A: Yes, there are at-home cholesterol testing kits available. These kits provide a convenient way to monitor your cholesterol levels, but it’s important to follow up with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment and interpretation of the results.
Q: Is atherosclerosis reversible with cholesterol management?
A: While managing cholesterol can help slow the progression of atherosclerosis and prevent further plaque buildup, advanced cases of arterial plaque may require medical intervention. It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers to address individual needs and determine the best course of action.
