Introduction
Is a heart attack like a sudden storm, striking unexpectedly, or can we predict who might be in its path? 🌩️ This question is particularly crucial for busy Indian professionals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, who often juggle high-stress jobs and hectic lifestyles.
This blog is your roadmap to understanding the risk demographics of heart attacks. In India, heart disease is a major health concern, with studies indicating a rising trend in younger populations due to lifestyle factors.
We’ll dive into the various factors that determine who is most at risk of a heart attack. From age and gender to ethnicity and lifestyle habits, we’ll explore how each aspect contributes to the risk. It’s not just about the numbers; it’s about understanding your personal risk profile and taking proactive steps to safeguard your heart.
Join us on this journey of heart health awareness. Let’s navigate these waters together, learning how to steer clear of the heart attack storm and keep our hearts sailing smoothly. ❤️⚓
Resetting Priorities: From Code to Care
Part – 1
In the bustling heart of Bangalore, where the streets are alive with the symphony of daily commerce and the vibrant hues of city life, Nisha, a 38-year-old software developer, found herself caught in the relentless pace of her profession. From the moment the sun peeked over the horizon, she was immersed in code, her life a series of projects and deadlines that blurred the days into one another. Her family, a supportive husband and two spirited children, often dined without her, their laughter a distant melody amidst her focus on career advancement.
Nisha prided herself on her emotional intelligence, a skill that made her a beloved team leader and a problem solver. Yet, this same intelligence failed to convince her of the necessity of self-care. Caught in a mental trap that equated rest with laziness, she neglected her health, skipping meals, and substituting sleep with caffeine.
The Role of Age in Heart Attack Risk
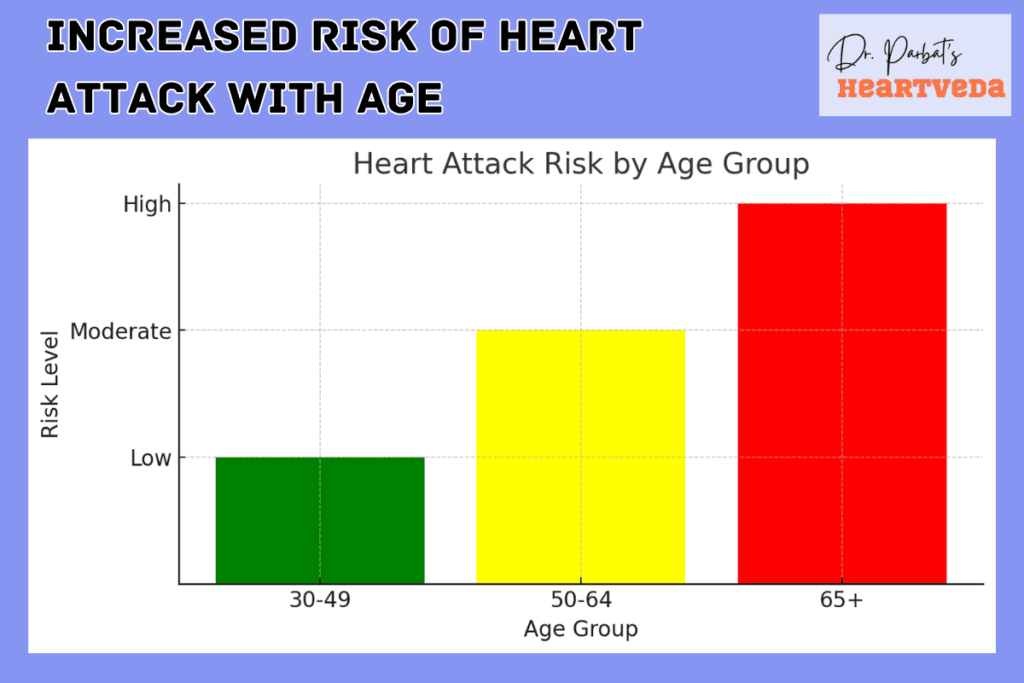
Age plays a significant role in determining the risk of heart attacks. Understanding how age influences the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack is crucial for taking appropriate preventive measures.
In general, the majority of people who die from coronary heart disease are 65 years or older, highlighting the increased risk associated with aging.
Furthermore, men are at a higher risk of heart attacks earlier in life compared to women. This can be attributed to factors such as hormonal differences and lifestyle habits.
By recognizing the impact of age on heart attack risk, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and managing other risk factors become essential as you age.
It is important to note that age is just one aspect of heart attack risk, and other factors such as lifestyle, family history, and overall health must also be taken into consideration.
“Age is just a number, but it is a crucial factor to consider when it comes to heart attack risk. As you get older, it becomes even more important to prioritize your cardiovascular health.” – Dr. Biprajit Parbat
Heart Attack Risk by Age
To better understand the relationship between age and heart attack risk, let’s take a look at a comparison between different age groups:
| Age Group | Heart Attack Risk |
| 30-49 | Relatively low, but not negligible, especially for men |
| 50-64 | Moderate risk, more significant for men than women |
| 65+ | Higher risk, especially for both men and women |
These figures demonstrate the increasing heart attack risk with age and emphasize the importance of adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and seeking regular medical advice as you grow older.
Gender and Heart Attack Risk
When it comes to heart attacks, gender plays a significant role in determining the risk level. Generally, men are more prone to heart attacks compared to women. However, this doesn’t mean that women should ignore their heart health, as their risk increases after menopause.
It is crucial for both men and women to be aware of their individual risk factors for heart attacks. By understanding the factors that contribute to heart disease, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk.
For men, it’s important to pay attention to their heart health at an earlier stage in life. Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress effectively, can significantly lower the risk of heart attacks.
“Heart health is a priority for everyone, regardless of gender. By taking care of your body and making conscious choices, you can protect yourself from the dangers of heart disease.”
Women, on the other hand, should be aware of the changes their bodies undergo during menopause. Hormonal fluctuations can increase the risk of heart disease. It is recommended that women focus on maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle by following a nutritious diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing their overall well-being during this phase of life.
Resetting Priorities: From Code to Care
Part – 2
The consequence of her choices became starkly evident one evening. As she pushed through another late-night coding session, a sudden, sharp pain radiated through her chest. The screen before her blurred, and the code she once mastered seemed like an indecipherable script. This was her body’s ultimatum, a stark warning of the toll her lifestyle had taken.
Her darkest moment came in the solitude of a hospital room, where the beeping monitors echoed her racing thoughts. The diagnosis was a mild heart attack, a jarring revelation for someone who believed youth was an impenetrable shield against such ailments. It was here, in the vulnerability of recovery, that Nisha encountered Dr. Komal, a cardiologist with a gentle demeanor and a wealth of knowledge about the lifestyle factors contributing to heart disease in young professionals.
Understanding Heart Disease Prevalence by Gender
Statistical data reveals a clear difference in heart disease prevalence between men and women. According to the American Heart Association, heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women in the United States, but men tend to experience heart attacks at a younger age.
It is essential for healthcare providers and individuals to acknowledge these gender differences and develop tailored prevention and treatment strategies accordingly.
| Heart Attack Risk | |
| Men | Higher risk compared to women |
| Women | Risk increases after menopause |
By addressing the unique risk factors associated with each gender, such as hormonal changes and lifestyle choices, we can create a society where heart attacks are less prevalent and everyone has the opportunity to live a healthier, heart-protected life.
Ethnicity and Heart Attack Risk
When it comes to heart disease, certain racial and ethnic groups face a higher risk compared to others. It is crucial to address the specific risk factors faced by different ethnicities in order to reduce the incidence of heart attacks and promote heart-healthy lifestyles.
Racial and Ethnic Groups at Higher Risk
Several racial and ethnic groups have been identified as having higher rates of heart disease, including:
- Black populations
- Mexican Americans
- American Indians
- Native Hawaiians
- Some Asian American populations
Possible Contributing Factors
The increased risk of heart disease in these ethnic groups can be attributed to various factors, such as:
- Higher rates of obesity
- Higher prevalence of diabetes
Reducing Heart Attack Risk in Ethnic Populations
Addressing the specific risk factors faced by these ethnic groups is essential for reducing the incidence of heart attacks. This includes:
- Implementing culturally sensitive education and outreach programs
- Promoting healthy lifestyle habits, including regular physical activity and a balanced diet
- Increasing access to healthcare and preventive services
| Ethnic Group | Heart Disease Risk Factors |
| Black populations | Higher rates of obesity and hypertension; greater prevalence of diabetes |
| Mexican Americans | Higher rates of obesity and diabetes; increased prevalence of high cholesterol |
| American Indians | Higher rates of obesity and diabetes; greater prevalence of smoking and high blood pressure |
| Native Hawaiians | Higher rates of obesity and diabetes; increased prevalence of smoking and hypertension |
| Some Asian American populations | Higher rates of diabetes and hypertension; increased prevalence of high cholesterol |
Identifying Risk Factors for Heart Attacks
Several risk factors contribute to the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack. By understanding these major risk factors for heart attacks, you can take proactive steps to reduce your risk and prioritize your heart health.
1. Smoking:
Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart attacks. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage your blood vessels, reduce oxygen supply to the heart, and increase the formation of blood clots. Quitting smoking is one of the most beneficial actions you can take to reduce your risk of a heart attack.
2. High Blood Pressure:
Having high blood pressure puts strain on your heart and increases the risk of heart attacks. Over time, uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage your arteries and lead to the formation of cholesterol plaques. Regular monitoring, medication, and lifestyle changes can help keep your blood pressure within a healthy range.
3. High Cholesterol Levels:
Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood can contribute to the development of fatty deposits in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and increasing the risk of heart attacks. Managing your cholesterol levels through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication if necessary can help lower your risk.
4. Diabetes:
Diabetes, especially if poorly controlled, can damage blood vessels and nerves, raising the risk of heart attacks. People with diabetes should closely monitor their blood sugar levels, follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take prescribed medication as directed by their healthcare provider.
5. Obesity:
Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on your heart and increases the risk of heart attacks. It is important to maintain a healthy body weight through a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and lifestyle changes that promote sustainable weight loss.
6. Sedentary Lifestyle:
A lack of physical activity increases the risk of heart attacks. Engaging in regular exercise, at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, can help strengthen your heart, lower blood pressure, and maintain a healthy weight.
| Risk Factors | Description |
| Smoking | Significantly increases the risk of heart attacks by damaging blood vessels and promoting blood clot formation. |
| High Blood Pressure | Puts strain on the heart and contributes to the development of heart attacks by damaging arteries. |
| High Cholesterol Levels | Elevated cholesterol levels lead to the formation of plaque in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks. |
| Diabetes | Damaged blood vessels and elevated blood sugar levels raise the risk of heart attacks. |
| Obesity | Excess body weight puts strain on the heart and increases the likelihood of heart attacks. |
| Sedentary Lifestyle | A lack of physical activity weakens the heart and raises the risk of heart attacks. |
Take Action to Protect Your Heart
Identifying these major risk factors for heart attacks is the first step towards prevention. By making meaningful lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, managing blood pressure and cholesterol, controlling diabetes, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying physically active, you can significantly reduce your heart attack risk and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
The Impact of Uncontrollable Risk Factors
While there are modifiable risk factors for heart attacks, such as smoking and high blood pressure, there are also uncontrollable risk factors that you may inherit or develop over time. These include increasing age, male gender, and a family history of heart disease.
Age is a significant risk factor for heart attacks, with the majority of people who die from coronary heart disease being 65 years or older. As you age, your risk of experiencing a heart attack increases. It is important to be aware of the age-related risk and take appropriate preventive measures.
Heredity also plays a role in heart attack risk. If you have a family history of heart disease, especially if a close relative had a heart attack at a young age, your risk may be higher. Understanding your family history and discussing it with your healthcare provider can help you develop strategies to manage your risk.
“By addressing modifiable risk factors and managing uncontrollable ones, you can significantly reduce your likelihood of experiencing a heart attack.”
Modifiable Risk Factors for Heart Attacks

When it comes to reducing the risk of heart attacks, certain behaviors and lifestyle choices can be modified to make a significant difference. By addressing these modifiable risk factors, individuals can take control of their heart health and lower their chances of experiencing a heart attack.
Smoking and Heart Attack Risk
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart attacks. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage the blood vessels and lead to the buildup of plaque, increasing the likelihood of a heart attack. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do to protect your heart.
High Blood Pressure and Heart Attack Risk
High blood pressure puts extra strain on your heart and increases the risk of a heart attack. By managing your blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication if needed, you can significantly reduce your risk.
High Cholesterol and Heart Attack Risk
High levels of cholesterol can clog your arteries and hinder blood flow to the heart. This can increase the risk of a heart attack. By adopting a heart-healthy diet and taking prescribed medications, you can lower your cholesterol levels and decrease your risk.
Physical Inactivity and Heart Attack Risk
A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to various heart-related problems, including an increased risk of heart attacks. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can strengthen your heart and lower the risk.
Obesity and Heart Attack Risk
Obesity is a significant risk factor for heart attacks. Excess weight puts extra strain on your heart and increases the likelihood of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. By maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, you can reduce your risk of a heart attack.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Heart Attack Risk | |
| 1 | Smoking | Significantly increases the risk |
| 2 | High Blood Pressure | Increases the risk |
| 3 | High Cholesterol | Increases the risk |
| 4 | Physical Inactivity | Increases the risk |
| 5 | Obesity | Significantly increases the risk |
Resetting Priorities: From Code to Care
END
Dr. Komal became Nisha’s beacon of hope, guiding her through the murky waters of recovery with advice that extended beyond medication. She introduced Nisha to the concept of holistic wellness, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and, crucially, mental rest. Encouraged by her family’s unwavering support, Nisha embarked on a journey of transformation. She rediscovered the joy of morning walks, the peace found in meditation, and the bonding over family meals.
Nisha’s story is a testament to the power of awareness and change. It serves as a reminder that age and lifestyle habits are silent contributors to our health’s decline, urging us to listen to our bodies and prioritize our well-being. The question that lingers is, will we wait for a wake-up call, or can we preempt the alarm and steer our lives towards a healthier horizon?
The Role of Stress in Heart Attack Risk
Chronic stress can have a significant impact on your risk of experiencing a heart attack. When you’re under constant stress, your body releases stress hormones like cortisol, which can increase your blood pressure and heart rate, putting additional strain on your cardiovascular system. In the long term, this can contribute to the development of heart disease and increase the chances of a heart attack.
Furthermore, in response to stress, many people engage in unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as overeating or smoking, which further exacerbate the risk of heart attacks. Overeating can lead to weight gain and obesity, while smoking damages blood vessels and decreases the amount of oxygen available to the heart. These behaviors can have detrimental effects on your heart health.
Managing stress effectively is crucial for reducing the risk of heart attacks. By implementing stress management techniques, you can protect your cardiovascular health and improve overall well-being. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress levels and promote heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, each week.
- Meditation and deep breathing: Practice deep breathing exercises and mindfulness meditation to relax your body and mind, reducing stress and promoting calmness.
- Seek social support: Surround yourself with supportive friends and family members who can provide emotional support during stressful times. Sharing your feelings and seeking advice can help alleviate stress.
- Engage in hobbies: Pursue activities that bring you joy and help you relax, such as reading, gardening, or painting. These hobbies can serve as a form of stress relief and help you unwind.
Remember, managing stress is not only beneficial for your heart health but also for your overall well-being. Incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine to reduce the risk of heart attacks and improve the quality of your life.
The Importance of Sleep for Heart Health
Adequate sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health. Lack of sleep can increase the risk of heart attacks and other heart-related conditions. Prioritizing good sleep habits and ensuring sufficient rest can help reduce the risk of heart attacks.
Alcohol Consumption and Heart Attack Risk
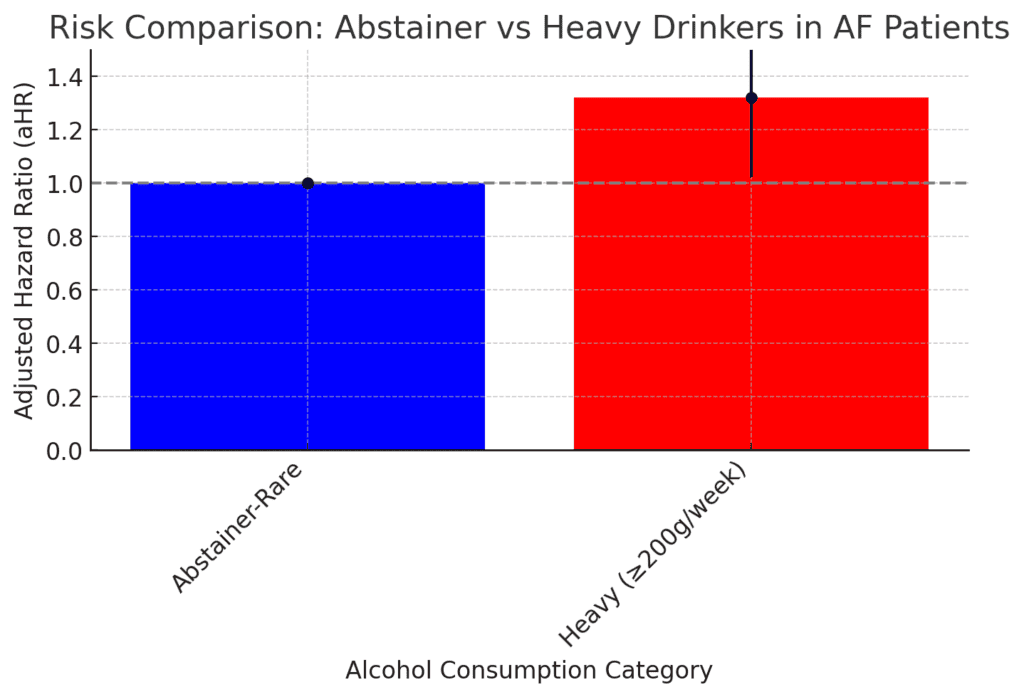
The chart compares the risk between people who rarely or never drink alcohol (“Abstainer-Rare”) and those who drink heavily (more than 200 grams of alcohol per week). The risk of having problems like a stroke or needing hospital care for heart issues is set to 1 for people who don’t drink much. For heavy drinkers, the risk increases by 32% (shown as 1.32 on the chart). This means heavy drinkers have a higher chance of facing these health issues compared to those who abstain or drink rarely. The line across the chart at 1 shows the baseline risk for abstainers, making it easier to see the increased risk for heavy drinkers.
Excessive alcohol consumption can significantly increase the risk of heart attacks. It has been found that alcohol can raise blood pressure, increase triglyceride levels, and promote irregular heartbeats, all of which contribute to a higher likelihood of experiencing a heart attack.
Understanding and adhering to recommended guidelines for alcohol consumption is crucial for maintaining heart health and reducing the associated risks. The American Heart Association suggests the following alcohol consumption guidelines:
- For men: Limit alcohol intake to no more than two standard drinks per day.
- For women: Limit alcohol intake to no more than one standard drink per day.
It is important to note that these guidelines are general recommendations and may vary depending on individual health conditions and medications. It is always best to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice regarding alcohol consumption and its impact on your heart health.
“Excessive alcohol consumption can significantly increase the risk of heart attacks.”
Nutrition and Heart Attack Risk
An unhealthy diet high in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium can significantly increase the risk of heart attacks. On the other hand, adopting a heart-healthy diet can greatly reduce the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack. A heart-healthy diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are beneficial for heart health. They can help lower blood pressure, decrease inflammation, and improve overall cardiovascular function. Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your diet not only adds flavor to your meals but also provides a wide range of heart-protective nutrients.
Whole grains, such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oats, are excellent sources of fiber, which can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Including whole grains in your meals can also stabilize blood sugar levels and promote feelings of fullness, aiding in weight management.
| Heart-Healthy Foods | Benefits |
| Fruits and vegetables | Provide essential nutrients and antioxidants; lower blood pressure and inflammation |
| Whole grains | Lower cholesterol levels; reduce the risk of heart disease; stabilize blood sugar levels |
| Lean proteins | Good sources of protein without the saturated fat; support muscle growth and repair |
| Healthy fats | Improve cholesterol levels; reduce inflammation; support brain function |
Lean proteins, such as fish, skinless poultry, legumes, and tofu, are excellent options to incorporate into a heart-healthy diet. They provide essential protein without the high levels of saturated fat found in red meat. Protein is vital for muscle growth and repair, and can assist in maintaining a healthy weight.
Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are crucial for heart health. These fats improve cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and support brain function. Including small portions of these healthy fats in your diet can have a positive impact on your cardiovascular health.
It is important to note that while a heart-healthy diet can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks, it should be combined with other healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, for optimal heart health.
Conclusion
Understanding the demographics and risk factors associated with heart attacks is crucial for individuals to take proactive measures to reduce their risk. By addressing modifiable risk factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, physical inactivity, and obesity, you can significantly decrease your likelihood of experiencing a heart attack.
It is important to prioritize heart health and adopt healthy habits to mitigate the risk factors associated with heart attacks. This includes making positive lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
By being aware of these risk factors and taking steps to address them, you can safeguard your cardiovascular health and reduce the probability of a heart attack. Remember, your actions today can have a significant impact on your future heart health. Take charge of your well-being and make heart-healthy choices for a long and healthy life.
Key Takeaways:
- Age is a significant factor in heart attack risk, with the majority of heart attack-related deaths occurring in people aged 65 and older.
- Men have a higher risk of heart attacks earlier in life compared to women.
- Certain ethnic groups, such as Black, Mexican American, American Indian, native Hawaiian, and some Asian American populations, have higher rates of heart disease.
- Modifiable risk factors, such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle, can significantly increase the risk of heart attacks.
- Uncontrollable risk factors, including increasing age, male gender, and family history of heart disease, also contribute to the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack.
Q: Who is at risk of developing heart disease (cardiovascular disease)?
A: People at risk of developing heart disease include those with a family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, smoking, and leading a sedentary lifestyle. Additionally, aging, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and high levels of stress can increase the risk of developing heart disease.
Q: What are the common risk factors for heart disease?
A: The common risk factors for heart disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity, excessive alcohol consumption, family history of heart disease, and high levels of stress. These factors can increase the risk of developing heart disease or experiencing a cardiovascular event.
Q: How to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease?
A: To reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, individuals should adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, managing stress, and controlling conditions such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes. Regular medical check-ups and screenings also play a crucial role in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Q: What is the relationship between rheumatic heart disease and the risk of heart disease?
A: Rheumatic heart disease is a condition that can lead to damaged heart valves, causing an increased risk for heart disease and related cardiovascular events. Individuals with rheumatic heart disease should be particularly mindful of managing their condition and addressing the associated risk factors for heart disease.
Q: How does age influence the risk of developing heart disease?
A: As people age, the risk of developing heart disease increases. The prevalence of heart disease and related conditions tends to rise with age, highlighting the importance of adopting preventive measures and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, especially as one grows older.
Q: Are women more likely to develop heart disease?
A: Yes, women are at an increased risk of developing heart disease. It’s crucial for women to be aware of their risk factors, as they may experience symptoms of heart disease differently than men. Prevention and early detection are key in addressing the risk of heart disease in women.
Q: What are the chronic diseases related to heart disease?
A: Chronic diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity are closely related to heart disease. Managing these conditions effectively is essential in reducing the overall risk of heart disease and related cardiovascular events.
Q: How does smoking increase the risk of heart disease?
A: Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease as it damages the heart and blood vessels, increases the risk of blood clots and atherosclerosis, reduces the oxygen in the blood, and contributes to the development of other risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Q: What should individuals do to know their risk of developing heart disease?
A: Individuals can assess their risk of developing heart disease by consulting with healthcare professionals for comprehensive risk assessments. This may involve evaluating personal and family medical histories, undergoing physical examinations, and conducting tests for cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and other relevant indicators of cardiovascular health.
Q: How can stress impact the risk of cardiovascular disease?
A: High levels of stress can contribute to the risk of cardiovascular disease by triggering unhealthy coping behaviors, such as overeating, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking. Additionally, stress can directly affect heart health by elevating blood pressure and impacting overall cardiovascular function, further increasing the risk of heart disease.
Q: Who is at risk of developing heart disease?
A: People with risk factors for cardiovascular disease such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle are at increased risk for heart disease. It’s important to know your risk and take steps to reduce it.
Q: What are the common risk factors for heart disease?
A: Common risk factors for heart disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, family history of heart disease, and a sedentary lifestyle. Identifying and managing these risk factors is crucial for preventing heart disease.
Q: Does my gender affect my risk for heart disease?
A: Yes, women are more likely to develop heart disease after menopause. It’s important for women to be aware of their increased risk and take proactive measures to maintain heart health.
Q: How does stress impact the risk of heart disease?
A: Chronic stress can contribute to an increased risk for heart disease. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and positive coping strategies can help reduce this risk.
Q: What are the warning signs of a heart attack?
A: The warning signs of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, upper body pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, shortness of breath, cold sweats, nausea, and lightheadedness. It’s essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience these symptoms.
Q: How can I reduce my risk of developing heart disease?
A: Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, quitting smoking, and controlling underlying health conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Q: Is family history a significant contributing factor for heart disease?
A: Yes, a family history of heart disease can increase a person’s risk of developing it. It’s important for individuals with a family history of heart disease to be vigilant about managing their risk factors and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Q: What impact does obesity have on cardiovascular risk?
A: Obesity is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. It is associated with other risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial for reducing this risk.
Q: Can diabetes increase the risk of heart disease?
A: Yes, diabetes is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. People with diabetes have an increased chance of having a heart attack or stroke. Proper management of diabetes through medication, diet, and exercise is vital for reducing the risk of heart disease.
Q: How prevalent is heart disease and stroke?
A: Heart disease and stroke are leading causes of death worldwide. They are prevalent and pose a significant health burden. Understanding the risk factors and taking preventive measures is essential for combating these conditions.
