
Introduction
Is the stress of your bustling professional life planting seeds for heart diseases or heart attacks? As Indian professionals in your 30s, 40s, and 50s, grappling with stress is like trying to navigate through a dense forest – you know the path is there, but it’s not always clear. Our blog sheds light on this pressing concern, exploring whether stress is merely a thorn in your side or a root cause of serious heart conditions.
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become a constant companion, especially for busy professionals. But how does this affect your heart health? This blog delves into the intricate relationship between stress and heart health, debunking myths and revealing truths. We’ll explore how chronic stress can contribute to heart disease, leading to an increased risk of heart attacks. With a focus on simple, friendly, and motivating language, we aim to guide you through understanding the impact of stress hormones like cortisol, which can lead to high blood pressure and weight gain, and how these factors intertwine with heart health.
Our goal is to empower you with knowledge and practical tips to manage stress and protect your heart. By the end of this blog, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how to navigate the forest of stress and keep your heart health on the right track.
Racing Heart, Pausing Life: Part 1
In the bustling city of Mumbai, where dreams soared as high as the skyscrapers, lived Vikram, a 42-year-old marketing executive. His life was a whirlwind of deadlines, meetings, and late-night client calls. Vikram’s family, his wife and two young daughters, often complained about his constant preoccupation with work.
Vikram, a man of ambition, believed in the mantra, “Work hard, party harder.” His diet was an afterthought, often consisting of fast food and high-calorie meals. Exercise was a word missing from his dictionary. Despite his wife’s repeated concerns about his health, Vikram brushed them off, believing stress was just part of the job.
The Relationship between Stress and Heart Health
Stress can have a profound impact on cardiovascular health, affecting both physical and mental well-being. While certain levels of stress are a normal part of life, chronic or excessive stress can negatively affect your heart and increase the risk of heart disease. Understanding the relationship between stress and heart health is crucial for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
Impact of Stress on Heart Health:
Acute stress, such as experiencing a sudden death or a catastrophic event, can trigger a cascade of physiological responses in the body, including the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormonal changes can lead to an increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and narrowed blood vessels, all of which strain the heart and increase the risk of a sudden cardiac event.
Additionally, the unhealthy coping mechanisms often associated with stress, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor eating habits, can further contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease. Smoking, in particular, damages the blood vessels, increases the formation of blood clots, and promotes the buildup of plaque in the arteries, all of which can lead to heart attacks.
Managing Stress for Heart Health:
Given the impact of stress on the heart, it is essential to adopt healthy strategies to manage stress effectively. Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercise and strength training, can help reduce stress levels and improve heart health. Exercise releases endorphins, which act as natural mood elevators and help alleviate stress and anxiety.
In addition to exercise, maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial for heart health. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide essential nutrients that support heart health and help manage stress. Avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption is also important, as these substances can exacerbate the negative effects of stress on the heart.
| Lifestyle Change | Impact on Stress | Effect on Heart Health |
| Regular Physical Activity | Reduces stress levels and promotes relaxation | Strengthens the heart, improves blood flow, and lowers blood pressure |
| Healthy Eating Habits | Provides essential nutrients for stress management | Supports heart health and helps maintain a healthy weight |
| Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques | Promotes stress reduction and emotional well-being | Reduces blood pressure and improves heart rate variability |
| Social Support and Connection | Provides emotional support and buffers the effects of stress | Improves overall mental well-being and reduces the risk of heart disease |
By adopting these lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage stress, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve your overall heart health. Remember, taking care of your mental and emotional well-being is just as important as taking care of your physical health when it comes to protecting your heart.
Stress as a Risk Factor for Heart Attacks
Studies suggest an association between chronic stress and heart disease, with work stress increasing the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke by 10%-40%.
Stress plays a significant role in the development of heart attacks. While stress itself may not directly cause a heart attack, its long-term effects on the body can increase the risk. Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy lifestyle habits and hormone changes that contribute to heart disease.
Individuals who use unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as smoking or overeating, to manage stress are more likely to develop heart disease. These behaviors can lead to high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart attacks. Additionally, stress can directly contribute to high blood pressure, further increasing the risk.
To better understand the relationship between stress and heart attacks, it’s important to recognize stress as a risk factor and address it accordingly. By adopting healthier coping strategies and managing stress levels, individuals can reduce their risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Heart Attacks |
| Chronic Stress | Increases risk indirectly through lifestyle factors and hormone changes |
| Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms | Smoking, overeating, and other unhealthy habits can contribute to heart disease |
| High Blood Pressure | Stress can cause high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart attacks |
By recognizing stress as a risk factor for heart attacks and implementing strategies to manage stress effectively, individuals can take proactive steps towards protecting their heart health.
Racing Heart, Pausing Life: Part 2
One day, amidst a high-profile product launch, Vikram felt an unusual tightness in his chest. He dismissed it as indigestion from his hurried lunch. But as the pain intensified, he collapsed, clutching his chest. It was a heart attack.
In the sterile silence of the hospital room, Vikram’s world of relentless ambition came crashing down. He realized his constant stress and unhealthy lifestyle had nearly cost him his life. The doctors warned him: without a significant reduction in stress and a change in lifestyle, his heart would remain at risk.
Stress-Induced Cardiac Events: Not Just Heart Attacks
In addition to heart attacks, stress can also lead to other cardiac events such as broken heart syndrome and sudden spikes in blood pressure. Broken heart syndrome, also known as stress-induced cardiomyopathy, can occur after an emotionally stressful event and can cause symptoms similar to a heart attack. Although these events are not true heart attacks, they can still cause damage to the heart muscle.
Broken heart syndrome, or stress-induced cardiomyopathy, is a condition that mimics the symptoms of a heart attack. It is triggered by intense emotional stress, such as the loss of a loved one or a traumatic event. When exposed to high levels of stress, the heart’s function can be temporarily impaired, leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, and even heart failure.
“After my husband’s sudden passing, I experienced a sharp pain in my chest and difficulty breathing. I thought I was having a heart attack, but it turned out to be broken heart syndrome. It was a wake-up call for me to prioritize my emotional well-being along with my physical health.”
Unlike a heart attack, broken heart syndrome is not caused by blocked arteries. Instead, it is believed to be the result of a surge in stress hormones that temporarily disrupt the heart’s normal functioning. The good news is that most people with broken heart syndrome fully recover within a matter of weeks.
Here’s a comparison between heart attacks and broken heart syndrome:
| Heart Attack | Broken Heart Syndrome |
| Caused by blocked arteries | Caused by intense emotional stress |
| EKG and blood tests show evidence of heart damage | EKG and blood tests may show no evidence of heart damage or different results |
| Physical exertion or exercise may trigger symptoms | Emotional stress is the trigger |
| Recovery time can be longer | Most people make a full recovery within weeks |
If you experience symptoms of a heart attack or broken heart syndrome, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. While the symptoms may be similar, proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the best possible outcome.
Remember, managing stress is not just about preventing heart attacks, but also about protecting your overall cardiovascular health. Taking steps to reduce stress and prioritize your emotional well-being can have a positive impact on your heart and reduce the risk of stress-induced cardiac events.
The Impact of Stress on Other Body Systems
Stress doesn’t just affect your cardiovascular system; it can also have a profound impact on other systems in your body. When you experience chronic stress, it disrupts the normal functioning of various body systems, leading to a range of stress-related health conditions.
Musculoskeletal Conditions
One of the systems most affected by stress is your musculoskeletal system. Prolonged stress can cause muscle tension, stiffness, and pain, leading to conditions such as tension headaches, migraines, and even musculoskeletal disorders like fibromyalgia.
Endocrine System Imbalances
Your endocrine system, which includes hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, is closely connected to stress. Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to imbalances in the endocrine system. This can result in conditions such as adrenal fatigue, thyroid disorders, and reproductive hormone imbalances.
Respiratory System Issues
When you’re stressed, your breathing pattern may change, becoming more shallow or rapid. This can lead to respiratory issues such as shortness of breath, asthma attacks, or hyperventilation. Stress can also worsen existing respiratory conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Stress can take a toll on your digestive system, causing symptoms such as stomachaches, nausea, diarrhea, or constipation. It can worsen existing gastrointestinal conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or acid reflux disease.
Reproductive System Problems
Chronic stress can affect your reproductive system, leading to issues such as menstrual irregularities, fertility problems, or decreased libido. Stress can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance required for proper reproductive function.
“Stress disrupts the normal functioning of various body systems, leading to a range of stress-related health conditions.”
Managing stress is crucial not only for your cardiovascular health but also for maintaining overall well-being. Take steps to reduce stress in your life through techniques such as exercise, mindfulness, and healthy coping mechanisms. By prioritizing stress management, you can support the optimal functioning of all body systems and reduce the risk of stress-related health conditions.
| Body System | Stress-Related Conditions |
| Musculoskeletal | Tension headaches, migraines, fibromyalgia |
| Endocrine | Adrenal fatigue, thyroid disorders, hormone imbalances |
| Respiratory | Shortness of breath, asthma attacks, hyperventilation |
| Gastrointestinal | Stomachaches, nausea, diarrhea, constipation |
| Reproductive | Menstrual irregularities, fertility problems, decreased libido |
Heart Disease Risk Factors and Stress
Stress can have a significant impact on heart health and contribute to the development of heart disease. Chronic and excessive stress can lead to various risk factors that increase the likelihood of heart disease. By addressing and managing these risk factors, along with implementing stress management techniques, you can take proactive steps to prevent heart disease and maintain a healthy heart.
Risk Factors for Heart Diseases
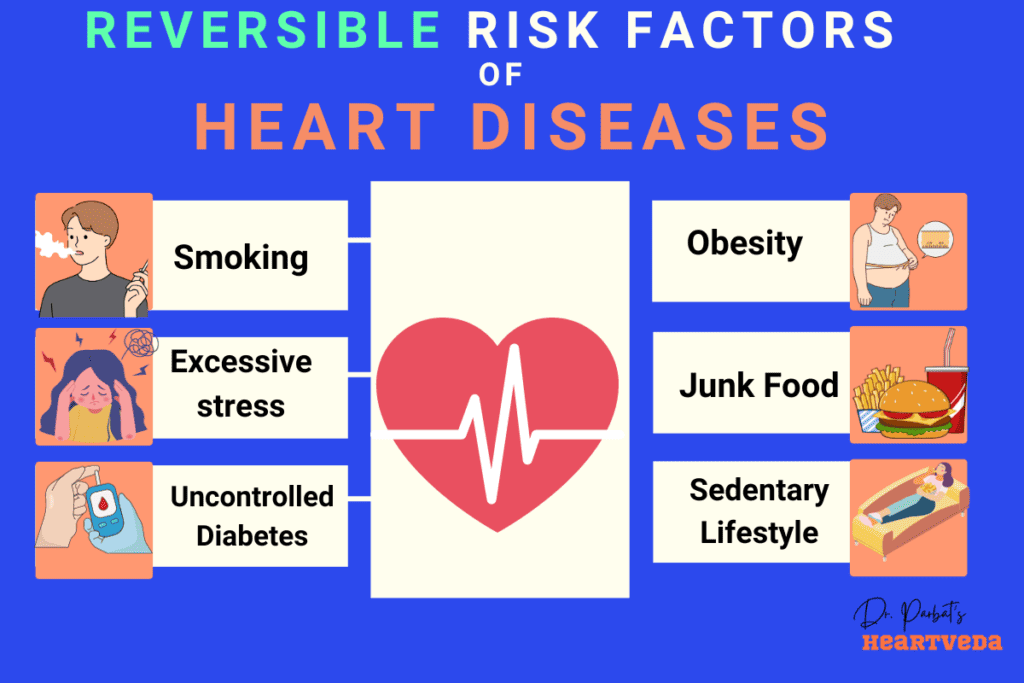
There are several risk factors for heart disease that can be influenced by stress. These include:
- Smoking: Stress can often trigger or worsen the habit of smoking, which is a known risk factor for heart disease.
- High blood pressure: Chronic stress can lead to an increase in blood pressure, which puts added strain on the heart.
- High cholesterol: Stress can contribute to unhealthy eating habits and a poor diet, leading to high cholesterol levels.
- Obesity: Stress can lead to emotional eating and weight gain, increasing the risk of obesity and heart disease.
- Physical inactivity: When under stress, individuals may neglect regular exercise, which is crucial for heart health.
- Diabetes: Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels, potentially leading to or worsening diabetes, which is a significant risk factor for heart disease.
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Some individuals turn to alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress, which can have adverse effects on heart health.
- Poor diet: Stress can lead to unhealthy eating patterns and the consumption of high-fat and high-sugar foods, contributing to heart disease.
Addressing these risk factors through lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing chronic health conditions, can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, implementing stress management techniques, such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in relaxation exercises, and seeking support from loved ones, can help mitigate the impact of stress on your heart.
Remember, taking care of your heart involves not only managing stress but also addressing other risk factors that contribute to heart disease. By making conscious choices and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can promote heart health and reduce the likelihood of heart disease.
| Risk Factors | Impact of Stress |
| Smoking | Stress can trigger or worsen smoking habits, increasing the risk of heart disease. |
| High blood pressure | Chronic stress can lead to elevated blood pressure levels, putting strain on the heart. |
| High cholesterol | Stress can contribute to unhealthy eating habits and a poor diet, leading to increased cholesterol levels. |
| Obesity | Stress can lead to emotional eating and weight gain, increasing the risk of obesity and heart disease. |
| Physical inactivity | Under stress, individuals may neglect regular exercise, which is crucial for heart health. |
| Diabetes | Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels, potentially leading to or worsening diabetes, a significant risk factor for heart disease. |
| Excessive alcohol consumption | Some individuals turn to alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress, which can have adverse effects on heart health. |
| Poor diet | Stress can lead to unhealthy eating patterns, including the consumption of high-fat and high-sugar foods, contributing to heart disease. |
Preventing Heart Attacks: Healthy Lifestyle Practices
Prevention is key when it comes to protecting yourself against heart attacks. By adopting healthy lifestyle practices and effectively managing existing health conditions, you can significantly reduce your risk of experiencing a heart attack. Here are some essential steps to take:
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise every week. Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing can help keep your heart strong and reduce the chances of a heart attack.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese can increase the strain on your heart and elevate the risk of heart disease and heart attacks. Maintain a healthy weight by consuming a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise. Consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized guidance.
Eat a Nutritious Diet
A well-balanced and nutritious diet is essential for maintaining heart health. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars. Prioritize foods that are rich in essential nutrients and antioxidants to support heart health.
Limit Alcohol Intake
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to high blood pressure, obesity, and an increased risk of heart disease. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For men, this means a maximum of two alcoholic beverages per day, and for women, a maximum of one alcoholic beverage per day.
Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease and heart attacks. It damages blood vessels, reduces oxygen supply to the heart, and increases the likelihood of blood clots. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to protect your heart and improve overall health.
Manage Health Conditions
If you have underlying health conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes, it is crucial to manage them effectively. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations, take prescribed medications as directed, and attend regular check-ups to monitor your condition and minimize the risk of heart attacks.
| Healthy Lifestyle Practices | Benefits |
| Regular physical activity | – Strengthens the heart- Improves circulation- Helps maintain a healthy weight |
| Maintaining a healthy weight | – Reduces strain on the heart- Minimizes the risk of heart disease |
| Eating a nutritious diet | – Provides essential nutrients- Supports heart health |
| Limiting alcohol intake | – Reduces the risk of heart disease- Prevents high blood pressure |
| Quitting smoking | – Lowers the risk of heart attacks- Improves overall health |
| Managing health conditions | – Minimizes complications- Reduces the risk of heart attacks |
By adopting these healthy lifestyle practices, you can take control of your heart health and reduce the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack. Remember, prevention is key, and every positive step you take towards a healthier lifestyle matters!
Racing Heart, Pausing Life: Part 3
During his recovery, Vikram met Dr. Ayesha, a cardiologist who emphasized the lethal combination of stress and poor lifestyle choices. She guided him towards a path of recovery, focusing on stress management, a balanced diet, and regular exercise.
Vikram’s journey to recovery was not easy. He struggled to balance his demanding career with his new lifestyle. But with his family’s support, he started making small yet significant changes. He began practicing yoga and meditation to manage stress, and home-cooked meals replaced late-night takeouts.
Broken Heart Syndrome: When Your Heart Breaks… Literally
Have you ever experienced a situation so emotionally intense that it felt like your heart was breaking? It turns out, there’s a medical condition that reflects this exact sentiment – broken heart syndrome, also known as stress-induced cardiomyopathy.
This condition can occur even in individuals who are otherwise healthy, and it is often triggered by emotionally stressful events such as the loss of a loved one, a devastating breakup, or a severe betrayal. When the heart experiences intense emotional stress, it can temporarily weaken, leading to symptoms that resemble a heart attack.
While the symptoms of broken heart syndrome, such as angina (chest pain) and shortness of breath, may mimic those of a heart attack, there is one crucial difference – there is no evidence of blocked heart arteries. In other words, the cause of broken heart syndrome lies in stress rather than a physical blockage.
“Broken heart syndrome reflects the profound impact that emotional stress can have on our physical well-being,” says Dr. Catherine Smith, cardiologist at the Heart Wellness Center.
During a typical case of broken heart syndrome, the left ventricle, which is responsible for pumping blood to the body, temporarily weakens, and its shape may appear distorted on imaging tests. However, unlike a heart attack, where permanent damage occurs due to blocked arteries, the heart muscle in broken heart syndrome typically recovers within a few weeks or months.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may be experiencing broken heart syndrome, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention to properly diagnose and manage the condition. Treatment options may include medications to manage symptoms, stress reduction techniques, and counseling to help address emotional distress.
“Recognizing the signs of broken heart syndrome and seeking medical help is crucial for a timely and appropriate diagnosis. A comprehensive evaluation is necessary to distinguish between broken heart syndrome and a heart attack, as their management and recovery processes differ.”
Signs of Broken Heart Syndrome:
- Angina (chest pain)
- Shortness of breath
- Fainting
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Low blood pressure
Remember, broken heart syndrome is a temporary condition that can be managed with proper medical care and a focus on stress reduction. Taking steps to nurture your emotional well-being and seeking support from loved ones can also contribute to a smoother recovery.
The Difference Between Heart Attack and Broken Heart Syndrome
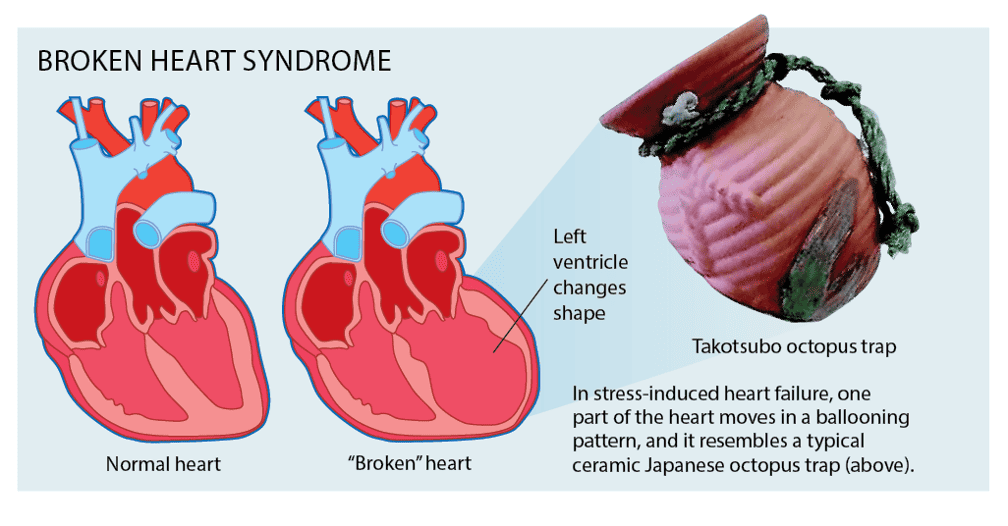
Photo Credit: https://www.discovermagazine.com/health/the-broken-heart-syndrome
Heart attack and broken heart syndrome may share some similar symptoms, but they have distinct differences in terms of diagnostic test results and recovery time. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnostic Test Results
Diagnostic tests play a vital role in differentiating between a heart attack and broken heart syndrome. Electrocardiogram (EKG) results and blood tests for heart damage can provide valuable insights.
“In broken heart syndrome, the EKG results may show temporary changes that are different from those observed in a heart attack.”
In a heart attack, the EKG often shows specific changes indicating damage to the heart muscle. Blood tests may also reveal elevated levels of cardiac enzymes, indicating heart tissue damage.
On the other hand, in broken heart syndrome, the EKG results may show transient abnormalities that can differ from those seen in a heart attack. Additionally, blood tests may not show the same levels of cardiac enzymes as observed in a typical heart attack.
Unusual Heart Chamber Movement
Another differentiating factor is the movement of the heart chamber, which can be observed through imaging tests.
“Imaging tests such as echocardiography or cardiac MRI can help identify the unusual movement of the heart chamber in broken heart syndrome.”
In a heart attack, the heart muscle experiences decreased blood flow due to the blockage of coronary arteries. In broken heart syndrome, however, there is no evidence of blocked arteries. Imaging tests can reveal abnormal contractions in the heart chamber, particularly in the left ventricle, which is characteristic of broken heart syndrome.
Recovery Time
Recovery time is another distinguishing factor between a heart attack and broken heart syndrome.
“Recovery from broken heart syndrome is typically faster compared to recovery from a heart attack.”
Most people who experience broken heart syndrome recover within weeks, with a low risk of recurrence. The heart muscle tends to regain its normal function without significant long-term damage. In contrast, recovery from a heart attack may take longer, depending on the extent of heart muscle damage. Rehabilitation and lifestyle changes are often necessary to optimize recovery and prevent future heart events.
| Heart Attack | Broken Heart Syndrome | |
| EKG Results | Specific changes indicating heart muscle damage | Temporary changes differing from a heart attack |
| Blood Tests | Elevated levels of cardiac enzymes | May not show same levels as in a heart attack |
| Heart Chamber Movement | Heart chamber movement affected by blocked arteries | Unusual movement of the heart chamber |
| Recovery Time | Varies, often longer | Usually shorter |
Understanding the Recovery from Broken Heart Syndrome
Recovering from broken heart syndrome is a gradual process that varies from person to person. However, most individuals who experience this condition can expect to make a full recovery within weeks. The good news is that the risk of recurrence is generally low, giving patients peace of mind as they navigate the healing journey.
To ensure an effective recovery, treatment options for broken heart syndrome may include various diagnostic tests and procedures. These can help healthcare professionals assess the extent of the damage caused by the syndrome and monitor the progress of the healing process. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Coronary Angiography: This test uses X-rays and contrast dye to examine the blood vessels in the heart. It helps determine if there are any blockages or abnormalities that may have contributed to the syndrome.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can provide valuable insights into the overall health of the heart. They can detect any enzyme abnormalities or other markers that indicate heart muscle damage.
- EKG: An electrocardiogram (EKG) is a non-invasive test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. It helps evaluate the heart’s rhythm and identify any irregularities.
- Echocardiography: This test uses sound waves to create images of the heart. It provides detailed information about the structure and function of the heart, helping healthcare providers assess any abnormalities.
- Cardiac MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide detailed images of the heart and its blood vessels. It helps healthcare professionals assess the extent of damage caused by broken heart syndrome.
Regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring heart health and ensuring ongoing recovery from broken heart syndrome. These visits allow for the evaluation of progress, adjustment of treatment plans if necessary, and the development of strategies to maintain heart health in the long term.
Diagnosis for Broken Heart Syndrome
| Diagnostic Tools | Description |
| Coronary Angiography | An X-ray procedure used to examine the blood vessels in the heart and identify any blockages or abnormalities. |
| Blood Tests | Laboratory tests that assess enzyme levels and other markers to detect heart muscle damage. |
| EKG | A non-invasive test that measures the electrical activity of the heart to evaluate its rhythm and detect irregularities. |
| Echocardiography | A test that uses sound waves to create images of the heart, providing detailed information about its structure and function. |
| Cardiac MRI | An imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the heart and its blood vessels. |
Managing Stress and Heart Health
In today’s fast-paced world, managing stress is essential for maintaining a healthy heart. Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on cardiovascular health, increasing the risk of heart attacks and other cardiac events. By implementing stress reduction techniques and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can protect your heart and enhance overall well-being.
Stress Reduction Techniques:
- Exercise: Physical activity is a powerful stress reliever. Engaging in regular exercise releases endorphins, improves mood, and reduces anxiety. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, every day.
- Mindfulness: Practicing mindfulness techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can calm the mind and reduce stress. Allocate time each day to focus on your breath, thoughts, and sensations to promote relaxation and clarity.
- Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Avoid relying on unhealthy coping mechanisms such as excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, or overeating. Instead, find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as talking to a trusted friend or family member, journaling, or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy.
A Healthy Lifestyle for Heart Health:
Managing stress goes hand in hand with maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle. By following these practices, you can support your cardiovascular health:
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, swimming, or dancing to keep your heart strong and reduce stress.
- Nutritious Diet: Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive salt, sugar, and processed foods.
- Manage Existing Health Conditions: If you have high blood pressure, diabetes, or other health conditions, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively. Following your prescribed treatment plan and attending regular check-ups is crucial.
By prioritizing stress reduction techniques and maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can safeguard your heart and reduce the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular diseases.
| Heart Health Tips | Benefits |
| Exercise regularly | Improved cardiovascular function, reduced stress levels |
| Eat a balanced diet | Lowered cholesterol levels, reduced risk of obesity |
| Practice mindfulness | Relief from stress and anxiety, improved mental well-being |
| Avoid unhealthy coping mechanisms | Reduced risk of heart disease, improved overall health |
Remember, a healthy heart starts with effective stress management and adopting heart-healthy habits. Take care of your heart today to enjoy a long and fulfilling life.
Racing Heart, Pausing Life: END
As Vikram embraced his new lifestyle, he realized the importance of listening to his body and mind. He learned that stress, often an ignored aspect of health, was as harmful as any physical ailment. His heart attack was a wake-up call to prioritize his health over his work.
Vikram’s story is a reminder that in the race for success, we often overlook our health, the very essence of our being. It’s not just about achieving career goals but about nurturing the heart that beats for those dreams. As Vikram now often reflects, “Success is not just about the accolades and achievements; it’s about being healthy enough to enjoy them.”
Conclusion
While stress is not the sole cause of heart attacks, it is a significant risk factor that should not be overlooked. Chronic stress can contribute to the development of heart disease and increase the likelihood of experiencing cardiac events. It is crucial to manage stress effectively through healthy habits and lifestyle practices in order to reduce the risk and protect heart health.
Recognizing the impact of stress on the body, including the cardiovascular system, is an important step in preventing heart attacks. Lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, a nutritious diet, and proper stress management techniques can play a vital role in mitigating the negative effects of stress on heart health.
In addition to stress management, it is crucial to address other risk factors for heart disease such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and diabetes. By taking a comprehensive approach to heart health, individuals can better protect themselves against stress-induced heart attacks and promote overall well-being.
In conclusion, while stress may not directly cause heart attacks, its impact on the body’s physiological processes is undeniable. By prioritizing stress management and adopting healthy habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing heart-related complications. Remember to address stress alongside other preventive measures to safeguard your heart and enhance your overall quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Stress alone does not directly cause heart attacks.
- Chronic stress can contribute to the development or worsening of heart disease.
- Unhealthy coping mechanisms often associated with stress, such as smoking and poor diet, can increase the risk of heart attacks.
- By managing stress through healthy lifestyle practices, we can protect our heart health.
- Adopting effective stress reduction techniques is crucial in reducing the risk of heart attacks.
FAQ Section on Effect of Psychological Stress on Heart Health
A: Chronic stress has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke.
A: Chronic stress can elevate the risk of developing conditions such as hypertension, which in turn increases the risk of a heart attack or stroke.
A: Psychological stress can contribute to the risk of developing coronary heart disease, which in turn increases the risk of having a heart attack.
A: Ongoing or chronic psychological stress has been associated with a higher risk of heart disease and stroke.
A: Yes, stress can contribute to the development and progression of coronary artery disease, which in turn increases the risk of cardiovascular events.
A: Psychological stress, as well as mental health conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder, can increase the risk for heart disease and stroke.
A: The American Heart Association recognizes the impact of psychological stress on the risk of heart disease and advocates for maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle to mitigate these risks.
A: Chronic psychological stress can lead to physiological changes in the body, such as increased amygdalar activity, which can elevate the risk for developing heart disease.
A: Proactively managing stress through strategies such as exercise, meditation, and seeking support can help lower the risk of developing heart disease and experiencing cardiovascular events.
A: Chronic stress can elevate the risk of developing hypertension, coronary heart disease, and other conditions that increase the risk of a heart attack.
A: Psychological stress can lead to elevated levels of amygdalar activity, which is associated with a higher risk of heart disease and stroke.
A: Adopting stress-reducing practices and leading a heart-healthy lifestyle, as recommended by the American Heart Association, can help mitigate the risk of developing heart disease and experiencing cardiovascular events due to stress.
A: Managing stress through activities like exercise, meditation, and maintaining a heart-healthy diet can help reduce the risk of developing heart disease and experiencing cardiovascular events, even in the presence of ongoing stress.
A: Stress may contribute to the development of coronary artery disease and increase the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack or stroke.
A: The American Heart Association conducts research and provides education about the impact of stress on heart health, offering valuable insights into managing stress-related risk factors for heart disease and stroke.
A: Ongoing stress can increase amygdalar activity, potentially leading to adverse effects on heart health and a higher risk of experiencing cardiovascular events.
A: Recognizing the connection between stress and heart disease is essential for adopting heart-healthy lifestyles and effectively managing factors that elevate the risk of heart attacks and stroke.
