Introduction
Did you know that heart attacks are not just a moment of crisis but a gateway to a series of health challenges that could be life-threatening? 🤔💔 In India, where the hustle of professional life often takes precedence, many in their 30s, 40s, and 50s find themselves at a crossroads between career ambitions and health priorities. This blog is your compass in navigating the aftermath of a heart attack, shedding light on the lesser-known paths that lead to increased mortality rates post-heart attack.
Imagine your heart as a bustling city, with blood vessels as its roads. A heart attack is akin to a major roadblock that disrupts the flow of life, causing significant damage to the city’s core. But what happens after the immediate crisis is averted? Our discussion delves into the primary causes of death following a heart attack, including cardiac arrest, arrhythmias, heart failure, and cardiogenic shock, alongside secondary complications like myocardial rupture and thromboembolism.
With a friendly and motivating tone, we aim to guide busy Indian professionals through the importance of understanding these risks, emphasizing simple lifestyle changes and preventive measures that can significantly lower their chances of severe complications. This blog is not just about the aftermath of a heart attack; it’s a roadmap to a healthier heart and a longer, fulfilling life. 🌈❤️
Let’s embark on this journey together, armed with knowledge and the power to change our health destiny.
Heartbreak in the Fast Lane
Part – 1
In the heart of Mumbai’s bustling streets, where the pace of life mirrors the rapid heartbeat of the city itself, lived Sameer, a high-flying stockbroker. His days were a blur of numbers, negotiations, and networking, a relentless pursuit of success that left little room for anything else. Sameer, a devoted husband and father of two, had always prided himself on his ability to handle stress, viewing it as just another challenge to overcome.
Despite his emotional intelligence, which allowed him to navigate the complexities of the stock market and family life with equal dexterity, Sameer’s approach to his health was one of denial. He lived in a mental frame that dismissed the importance of regular health check-ups and a balanced lifestyle, convinced that his youth and vitality were enough to ward off any serious health issues.
Types of Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases encompass a range of conditions that affect different parts of the body. Understanding these various diseases is essential in identifying their causes and symptoms for prevention and effective management. The major types of cardiovascular diseases include:
- Coronary Heart Disease: It affects the blood vessels supplying the heart, resulting in reduced blood flow and oxygen to the cardiac muscles. This condition can lead to heart attacks and heart failure.
- Cerebrovascular Disease: It affects the blood vessels supplying the brain, leading to conditions such as strokes and transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes).
- Peripheral Arterial Disease: It affects the blood vessels supplying the arms and legs, causing reduced blood flow and potential complications like pain, numbness, and even amputation in severe cases.
- Rheumatic Heart Disease: It is caused by streptococcal bacteria that lead to heart valve damage and inflammation, resulting in long-term complications.
- Congenital Heart Disease: This is a condition present at birth, impacting the structure and function of the heart. It requires medical intervention or surgery to correct, depending on the severity.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism: Deep vein thrombosis occurs when blood clots form in the deep veins of the legs, while pulmonary embolism refers to the dislodging of these clots, which can travel to the lungs and cause serious complications.
| Cardiovascular Disease | Affected Body Part | Main Complications |
| Coronary Heart Disease | Heart | Heart attacks, heart failure |
| Cerebrovascular Disease | Brain | Strokes, transient ischemic attacks |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease | Arms and Legs | Pain, numbness, amputation |
| Rheumatic Heart Disease | Heart Valves | Heart valve damage, inflammation |
| Congenital Heart Disease | Heart | Structural abnormalities, heart failure |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Legs | Blood clots in deep veins |
| Pulmonary Embolism | Lungs | Blood clots in the lungs |
Risk Factors for Heart Disease and Stroke
Unhealthy behaviors can significantly increase your risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke. Certain lifestyle choices and habits can disrupt the normal functioning of your cardiovascular system, leading to various complications. Here are some key risk factors that contribute to the development of these conditions:
Unhealthy Diet
An unhealthy diet, characterized by the excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary beverages, saturated fats, and high levels of salt, can raise your risk of heart disease and stroke. Consuming nutrient-poor foods and insufficient amounts of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can lead to an imbalance in your body’s essential nutrients and contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Physical Inactivity
Leading a sedentary lifestyle and not engaging in regular physical activity can have detrimental effects on your cardiovascular health. Lack of exercise weakens your heart muscles, affects blood circulation, increases the risk of high blood pressure, and can lead to the accumulation of unhealthy body weight. Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is essential for maintaining a healthy heart and preventing cardiovascular diseases.
Tobacco Use
Smoking and tobacco use are major risk factors for heart disease and stroke. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco can damage your blood vessels, reduce blood flow, and increase the risk of blood clots. Both active smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly impact your cardiovascular health. Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco use is crucial for reducing your risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol consumption can elevate your blood pressure, increase the levels of triglycerides (a type of fat) in your blood, and contribute to the development of various cardiovascular conditions. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some health benefits, excessive drinking can be detrimental to your heart health. It is important to consume alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether to lower your risk of heart disease and stroke.
High Blood Pressure
Having high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. When your blood pressure remains consistently high, it puts extra stress on your heart and blood vessels, leading to their damage over time. Managing and controlling your blood pressure through lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medication is vital for reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
High Blood Glucose
High levels of blood glucose, a condition known as hyperglycemia, are commonly associated with diabetes. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to damage to your blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Maintaining healthy blood glucose levels through proper diabetes management is crucial for preventing cardiovascular complications.
High Blood Lipids
Abnormal levels of blood lipids, including high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases. These lipids can accumulate in your arteries, forming plaque and narrowing the blood vessels. This reduces blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and, if necessary, taking medication can help manage your lipid levels and reduce your risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Overweight and Obesity
Being overweight or obese significantly increases your risk of heart disease and stroke. Excess weight puts strain on your heart, causes hormonal imbalances, and contributes to the development of other risk factors such as high blood pressure and high blood lipids. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity is essential for preventing cardiovascular diseases.
Addressing these risk factors and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk of developing heart disease and stroke. However, it is important to remember that individual risk factors interact with each other, and comprehensive prevention efforts should address the collective impact of these factors on cardiovascular health.
Heartbreak in the Fast Lane
Part – 2
The consequence of his relentless pace and disregard for his health came without warning. One evening, after a particularly stressful day at the stock exchange, Sameer felt an intense pressure in his chest, a pain unlike anything he had experienced before. Brushing it off as indigestion, he chose to ignore it, not wanting to worry his family or admit that he might be vulnerable.
Sameer’s darkest moment came silently, in the quiet of his study, where he collapsed, alone. The heart attack was swift, and the complications that followed were unforgiving. Cardiac arrest took him from his family in a matter of minutes, leaving behind a world of ‘what ifs.’
In the aftermath, Sameer’s family was left to navigate the pain of their loss, grappling with the harsh reality that his death could have been prevented. His wife, Sweta, found herself reflecting on the signs that had been overlooked, the opportunities for intervention that were missed. She became determined to ensure that Sameer’s story would serve as a wake-up call for others.
Symptoms of a Heart Attack
If you suspect you or someone around you may be having a heart attack, it’s crucial to recognize the symptoms and take immediate action. The signs of a heart attack can vary from person to person, but there are common indications to look out for:
- Chest pain or discomfort: This is one of the most recognizable symptoms of a heart attack. The pain can feel like tightness, pressure, or a squeezing sensation in the center of the chest.
- Pain or discomfort in other areas: Heart attack pain may also radiate to the arms, left shoulder, elbows, jaw, or back.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or a feeling of being unable to catch your breath can accompany a heart attack.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea, indigestion, or vomiting during a heart attack.
- Light-headedness and cold sweat: Feeling lightheaded, dizzy, or breaking out in a cold sweat can be warning signs of a heart attack.
- Paleness: The skin may become pale or take on a grayish hue during a heart attack.
It’s important to note that women may experience different symptoms compared to men. In addition to the symptoms mentioned, women may also have:
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Back pain
- Jaw pain
If you or someone around you is experiencing any of these symptoms, call emergency services immediately. Acting quickly can potentially save a life.
Primary Causes of Death During a Heart Attack

- Cardiac Arrest: The most immediate threat during a heart attack is cardiac arrest. This occurs when the heart’s electrical system malfunctions, causing it to stop beating effectively. Cardiac arrest can lead to sudden death if not treated immediately.
- Arrhythmias: Heart attacks can cause irregular heartbeats, known as arrhythmias. Some, like ventricular fibrillation, can be fatal if not promptly corrected.
- Heart Failure: If a large portion of the heart muscle is damaged, it can lead to heart failure. The heart becomes unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, which can be fatal.
- Cardiogenic Shock: This is a severe form of heart failure where the heart suddenly can’t pump enough blood. It’s a medical emergency and can be lethal if not treated immediately.
Secondary Complications Leading to Mortality
- Myocardial Rupture: Occurring usually within the first few weeks after a heart attack, this involves the tearing of the heart muscle or its structures. It can lead to rapid death.
- Pericarditis: This is inflammation of the pericardium, the sac-like covering of the heart. While not always fatal, it can complicate recovery from a heart attack.
- Thromboembolism: Blood clots formed in the heart can travel to other parts of the body, like the brain or lungs, causing strokes or pulmonary embolism, both of which can be fatal.
Predictors of 1 Year Mortality Rate in Heart Attack Patients
| Predictor | Association with 1-Year Mortality | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Pump Failure on Admission | Strongly predicts | Independent of other factors; significantly impacts survival. |
| LVEF Dysfunction | Strongly predicts | Low LVEF (<40%) is a significant independent predictor. |
| Age | Increases risk | Older age is linked to higher mortality; mean age difference between survivors and non-survivors is about 10 years (75.5 vs. 63). |
| History of Diabetes | Increases risk | Doubles post-MI mortality rates; effect equivalent to aging 15 years. |
| Elevated Heart Rate at Admission | Increases risk | Indicates higher physiologic stress and is an independent predictor of mortality. |
| Coronary Artery Disease Severity | Initially considered | Not an independent predictor after adjusting for baseline variables. |
| Bleeding Complications | Initially considered | Not an independent predictor after adjusting for baseline variables. |
Heartbreak in the Fast Lane
Part – 3
Guided by her resolve, Sweta embarked on a mission to raise awareness about heart health, especially among busy professionals like Sameer. She partnered with local health organizations to organize workshops and screenings, emphasizing the importance of recognizing the signs of a heart attack and the critical need for prompt action to prevent complications like cardiac arrest and heart failure.
Sameer’s story, though tragic, sparked a movement within his community. It became a powerful reminder that success and ambition must not come at the cost of health. It challenged busy professionals to reevaluate their priorities, to find balance, and to remember that taking care of their heart is the most important investment they can make.
Symptoms of a Stroke
A stroke occurs when there is a disruption in the blood flow to the brain, leading to potential brain damage and other severe complications. Recognizing the symptoms of a stroke is crucial for immediate medical intervention, as early treatment can minimize the damage caused. Here are the key symptoms to watch out for:
1. Weakness, Numbness, or Paralysis
One of the most common signs of a stroke is sudden weakness, numbness, or paralysis on one side of the face, arm, or leg. If you notice any asymmetry in your limbs or face, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
2. Confusion and Difficulty Speaking
Another characteristic symptom of a stroke is confusion, difficulty finding the right words, slurred speech, or an inability to comprehend spoken language. If you or someone around you experiences sudden confusion or speech difficulties, it could be a sign of a stroke.
3. Difficulty Seeing
Vision problems can also indicate a stroke. Some individuals may experience blurred vision, sudden blindness in one or both eyes, or difficulty focusing. If you notice any abrupt changes in your vision, it is essential to seek medical help promptly.
4. Difficulty Walking, Dizziness, or Loss of Balance
Strokes can affect your motor skills and balance. If you suddenly have trouble walking, feel dizzy, or experience a loss of coordination, this could be a sign of a stroke. It is crucial to take these symptoms seriously and seek immediate medical attention.
5. Severe Headache without a Known Cause
A severe headache without a known cause, often described as the worst headache of one’s life, can be a warning sign of a stroke. If you experience an intense headache that comes on suddenly and is accompanied by other stroke symptoms, it is crucial to seek urgent medical assistance.
6. Fainting or Unconsciousness
In some cases, a stroke can cause fainting or loss of consciousness. If you witness someone fainting or becoming unresponsive, it could be a medical emergency, and immediate medical attention is necessary.
Remember, prompt action is vital when it comes to strokes. If you or someone around you exhibits any of these symptoms, do not wait to see if they improve; instead, call emergency services right away. Quick medical intervention can make a significant difference in the outcome and recovery process after a stroke.
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic heart disease is a condition that occurs due to the damage to the heart valves and heart muscle, caused by the inflammation and scarring resulting from rheumatic fever. This fever is triggered by an infection caused by streptococcal bacteria. Rheumatic heart disease primarily affects children in developing countries and is responsible for 2% of cardiovascular disease-related deaths globally.
Symptoms of Rheumatic Heart Disease:
The symptoms of rheumatic heart disease can vary, but common signs include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Irregular heartbeats
- Chest pain
- Fainting
Routine screenings and prompt medical attention are crucial in identifying and managing the condition, especially in regions with a high prevalence of rheumatic fever.
“Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential in preventing further damage to the heart valves and heart muscle in individuals with rheumatic heart disease.”
Effective management of streptococcal bacterial infections, such as timely administration of appropriate antibiotics, can help prevent the onset of rheumatic fever and subsequently reduce the risk of rheumatic heart disease.
Global Impact of Cardiovascular Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases have a significant global impact, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where access to healthcare is limited and poverty rates are high. In these countries, individuals with noncommunicable diseases like cardiovascular diseases often face challenges in early detection and lack access to effective healthcare services.
This unfortunate situation leads to premature deaths, robbing individuals of their productive years and placing a substantial economic burden on these countries.
Impact on Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries
Low-income and middle-income countries bear the brunt of cardiovascular diseases due to various factors:
- Lack of Access to Healthcare: Limited healthcare infrastructure and resources make it difficult for individuals in these countries to receive timely and adequate medical attention for cardiovascular conditions.
- Poverty: High poverty rates often mean that individuals cannot afford the cost of healthcare services, medications, or preventive measures necessary to address and manage cardiovascular diseases.
- Delayed Detection: Without accessible and affordable healthcare, illnesses often go undiagnosed until they reach advanced stages, leaving individuals with limited treatment options and poorer prognoses.
The Consequences
The consequences of the lack of access to healthcare and late detection in low- and middle-income countries are severe:
- Increased mortality rates: Individuals with cardiovascular diseases are more likely to die prematurely due to the lack of early detection and timely intervention.
- Reduced productivity: Premature deaths resulting from cardiovascular diseases lead to a loss of productive years, preventing individuals from contributing to their communities and countries’ economic growth.
- Economic burden: The burden of cardiovascular diseases placed on low- and middle-income countries is not solely a health concern but also an economic challenge, straining already limited resources.
Addressing the Issue
“Improving access to healthcare and early detection of cardiovascular diseases is crucial in reducing mortality rates and alleviating the economic burden on low- and middle-income countries.”
Efforts focused on improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing funding for healthcare systems, and implementing preventive strategies are essential for addressing the global impact of cardiovascular diseases.
By prioritizing access to healthcare services, especially for individuals in low- and middle-income countries, early detection of cardiovascular diseases can be enhanced, allowing for timely interventions and improved health outcomes.
Raising awareness, providing affordable treatment options, and implementing prevention programs are vital steps towards reducing the burden of cardiovascular diseases globally.
| Impact on Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries | Consequences |
| Lack of Access to Healthcare | Increased mortality rates |
| Poverty | Reduced productivity |
| Delayed Detection | Economic burden |
Modifying Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
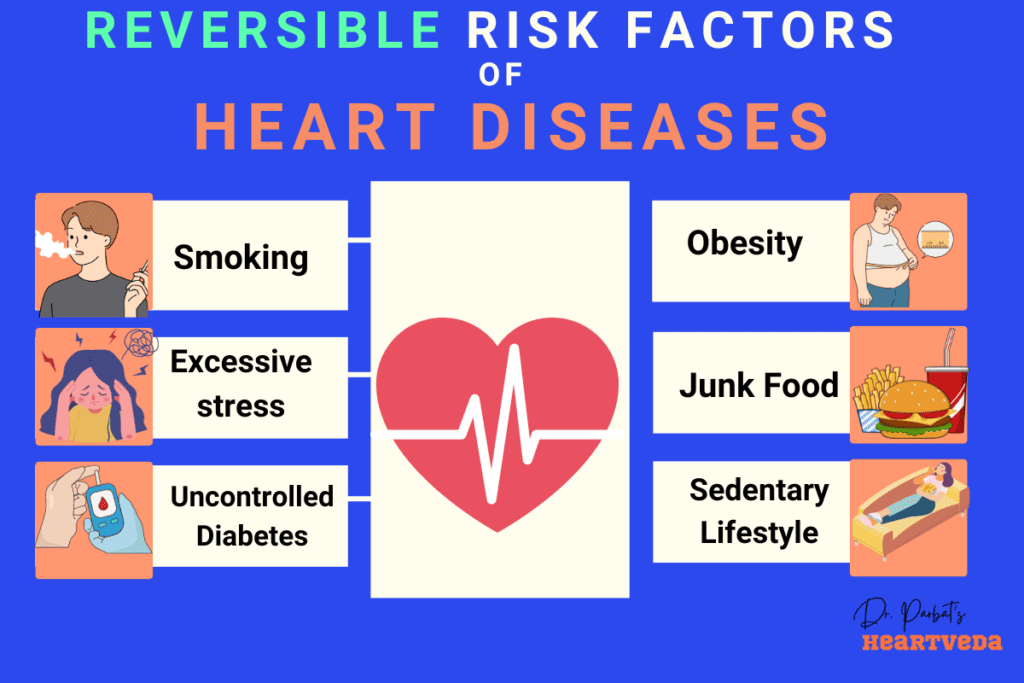
To reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, it is crucial to modify certain risk factors and adopt healthy behaviors. By making positive changes in your lifestyle, you can significantly improve your heart health and overall well-being. Here are some key strategies to consider:
Tobacco Cessation
Quitting tobacco use is one of the most impactful steps you can take to protect your heart. Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease. Seek support from healthcare professionals or join smoking cessation programs to help you quit successfully.
Healthy Diet
Adopting a healthy diet is essential for maintaining heart health. Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products into your meals. Limit your intake of saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars. Consult a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is key to improving cardiovascular health. Engage in activities that elevate your heart rate, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise every week.
Alcohol Reduction
Limiting alcohol consumption is important for heart health. Excessive drinking can raise blood pressure and contribute to the development of heart disease. Follow the recommended guidelines for moderate alcohol consumption – up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
Blood Pressure Control
High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Monitor your blood pressure regularly and take necessary steps to keep it within a healthy range. This may include lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise, as well as medication prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Diabetes Management
Diabetes increases the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. If you have diabetes, work closely with your healthcare team to manage your blood glucose levels effectively. Follow a healthy eating plan, take prescribed medications as directed, and engage in regular physical activity.
Lipid-Lowering Medication
For individuals with high blood lipids, medication may be necessary to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Your healthcare provider can prescribe lipid-lowering medications if appropriate, in combination with lifestyle changes.
Remember, these strategies work best when combined. Consult with your healthcare provider to create a personalized plan that addresses your specific risk factors and suits your individual needs.
Treatment Options for Cardiovascular Diseases
When it comes to treating cardiovascular diseases, there are several options available depending on the specific disease and its severity. These treatment options aim to improve the overall function of the heart and manage any underlying conditions contributing to the disease.
Surgical interventions are often considered for more complex cardiovascular diseases. One such procedure is coronary artery bypass surgery, where a healthy blood vessel is taken from another part of the body and used to bypass the blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. This helps restore proper blood flow to the heart muscle and alleviate symptoms.
Another common procedure is balloon angioplasty, which involves threading a thin tube (catheter) with a deflated balloon on the end into the blocked or narrowed blood vessel. The balloon is then inflated to widen the vessel and improve blood flow. In some cases, a stent may be inserted to keep the blood vessel open.
Valve repair or replacement is often necessary when there is damage or dysfunction in the heart valves. This can be done through surgical intervention, where the affected valve is repaired or replaced with a prosthetic valve, restoring proper blood flow through the heart.
In more severe cases, heart transplantation may be considered. This involves replacing the diseased heart with a healthy heart from a donor. Heart transplantation is typically reserved for patients with end-stage heart failure who have exhausted other treatment options.
Medical devices also play a crucial role in the management of cardiovascular diseases. Pacemakers, for example, are implanted to regulate abnormal heart rhythms and ensure the heart beats at a steady and regular pace. Prosthetic valves are used to replace damaged or malfunctioning heart valves, restoring proper blood flow. Additionally, patches can be used to close certain heart defects, improving overall heart function.
It is important to note that the choice of treatment depends on the specific cardiovascular disease, its severity, and the individual patient’s overall health condition. A thorough evaluation and consultation with a healthcare professional are essential in determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Heartbreak in the Fast Lane
END
Through Sweta’s efforts, Sameer’s legacy lived on, not as a cautionary tale of what happens when health is neglected, but as a beacon of hope and a call to action for the living. It underscored the message that complications following a heart attack are immediate and often fatal, but with awareness and prompt action, they can be prevented.
Sameer’s story prompts us to ask: Are we listening to our hearts, or are we too caught up in the race to notice the signs until it’s too late?
Global Efforts to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease Burden
The World Health Organization (WHO) has implemented a comprehensive global action plan to combat the burden of noncommunicable diseases, including cardiovascular diseases. This action plan aims to reduce risk factors, improve access to medication and healthcare services, and provide normative guidance for effective management.
Reducing Risk Factors and Enhancing Access to Medication
One of the key focuses of the global action plan is to address risk factors that contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases. Through targeted interventions, such as promoting healthy lifestyles and raising awareness about the harmful effects of tobacco use, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and excessive alcohol consumption, the plan aims to reduce the prevalence of these risk factors on a global scale.
Additionally, the action plan emphasizes the importance of improving access to medication for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Ensuring that individuals have affordable and timely access to essential medications is crucial in reducing the burden of these conditions and preventing complications.
Hypertension Programs for Effective Prevention
One of the key areas of focus in combating cardiovascular diseases is the implementation of hypertension programs. These programs aim to identify individuals with high blood pressure, provide appropriate treatment and ongoing management, and raise awareness about the importance of blood pressure control. By effectively managing hypertension, these programs have shown significant success in reducing the incidence of coronary heart disease and stroke.
Investment in Health Systems and Normative Guidance
In order to effectively address the burden of cardiovascular diseases, there is a need for increased investment in health systems. This includes strengthening healthcare infrastructure, training healthcare professionals, and ensuring the availability of essential diagnostic tools and treatment modalities.
Furthermore, the development and implementation of normative guidance play a crucial role in standardizing the management of acute coronary syndrome and stroke. By providing healthcare providers with evidence-based guidelines, the action plan aims to improve the quality and effectiveness of care for individuals with these conditions.
By implementing the global action plan, countries can work together towards reducing the burden of cardiovascular diseases worldwide. Through a combination of risk assessment, hypertension programs, improved access to medication, and normative guidance, we can make significant progress in preventing and managing these conditions and improving overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and risk factors of heart attacks is crucial for preventing these life-threatening events and maintaining cardiovascular health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and promote a stronger heart.
To prevent heart attacks, it is important to prioritize a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, quit tobacco use, and consume alcohol in moderation. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products can provide essential nutrients while minimizing the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
In addition to lifestyle choices, access to quality healthcare services plays a vital role in heart attack prevention. Timely detection and effective management of heart conditions can be achieved through regular check-ups, screenings, and prompt treatment. It is crucial to prioritize healthcare access, especially in low- and middle-income countries where barriers to healthcare exist.
By prioritizing heart attack prevention, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and ensuring healthcare access, individuals and communities can work together to reduce the lethality of heart attacks, promote cardiovascular health, and enhance overall well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- Heart attacks are a leading cause of mortality, often linked to cardiovascular diseases and heart failure.
- Unhealthy behaviors such as an unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use, and excessive alcohol consumption increase the risk of heart attacks.
- Risk factors like high blood pressure, high blood glucose levels, high blood lipids, overweight, and obesity also contribute to heart attack risk.
- Lack of access to healthcare and poverty in low- and middle-income countries contribute to higher mortality rates from cardiovascular diseases.
- Promoting healthy choices and improving healthcare access are essential for preventing and managing heart attacks.
Q: What is the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the India?
A: Cardiovascular disease is prevalent in the United States, affecting millions of individuals and contributing to a significant burden of disease and mortality.
Q: What are the leading causes of death related to cardiovascular disease?
A: The leading causes of death related to cardiovascular disease include myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac arrest, and congestive heart failure.
Q: What are the mortality rates of heart disease?
A: The mortality rates of heart disease are alarming, with a substantial number of deaths occurring each year due to heart-related disorders.
Q: What are the risk factors for heart disease?
A: Risk factors for heart disease include increased cardiovascular risk, ischemic heart disease, and an elevated risk of death due to heart-related conditions.
Q: How can heart disease be prevented?
A: Heart disease prevention involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine medical check-ups to monitor cardiovascular health.
Q: What are the recommended strategies for reducing the risk of heart disease?
A: Recommended strategies for reducing the risk of heart disease include maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Q: Is a heart attack in the morning more dangerous?
A: While heart attacks can occur at any time, research suggests that heart attacks in the morning may be more dangerous due to factors such as increased blood clotting and rising stress hormone levels.
Q: Is there a link between mental health and heart health?
A: Yes, there is a strong link between mental health and heart health. Stress, anxiety, and depression can contribute to the development of heart disease and increase the risk of heart attacks.
Q: What are the key findings in the report from the American Heart Association?
A: The report from the American Heart Association highlights the significant impact of cardiovascular disease on the population and emphasizes the need for proactive measures to address this health concern.
Q: What are the statistics related to heart disease mortality?
A: The statistics related to heart disease mortality reveal a concerning number of deaths attributed to cardiac disorders, necessitating a focused approach to improve cardiovascular health.
Q: What is the significance of early detection and treatment for heart disease?
A: Early detection and treatment are crucial in managing heart disease, as they can help prevent fatal outcomes and improve the overall prognosis for patients with heart-related conditions.
Q: What are the implications of heart disease on public health and healthcare systems?
A: Heart disease has significant implications for public health and healthcare systems, requiring comprehensive strategies to address the burden of cardiovascular disease and improve patient outcomes.
Q: What are the long-term effects of a heart attack?
A: The long-term effects of a heart attack can vary from person to person, and may include reduced heart function, increased risk of future heart issues, and potential lifestyle changes to manage heart health.
Q: What is the difference between angina and a heart attack?
A: Angina is chest discomfort caused by reduced blood flow to the heart, usually temporary and reversible. A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, leading to damage or death of the heart muscle.
Q: What is the current death rate from cardiovascular disease?
A: The current death rate from cardiovascular disease is approximately 17.3 million people each year globally, according to the World Health Organization.
Q: What are some common causes of fatal heart conditions?
A: Fatal heart conditions can be caused by acute myocardial infarction, ischaemic heart disease, and acute coronary heart disease, among others.
Q: What are the statistics on mortality rates of heart disease in Europe?
A: In Europe, cardiovascular disease is responsible for over 4 million deaths each year, making it the leading cause of mortality in the region.
Q: What are some factors that can increase the risk for heart disease?
A: Factors that can increase the risk for heart disease include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity.
Q: How many patients die from heart disease annually?
A: Annually, millions of people die from heart disease globally, making it one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
Q: What are the key findings regarding heart disease risk from the National Institute of Health?
A: The National Institute of Health has identified various risk factors such as family history, age, and gender that contribute to the increased risk of heart disease.
Q: How does cardiovascular mortality affect the population?
A: Cardiovascular mortality has a significant impact on the population, leading to a substantial number of deaths and contributing to the burden of heart disease globally.
Q: What is the leading cause of death after myocardial infarction?
A: The leading cause of death after myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack, is often related to complications arising from cardiovascular disease.
Q: How does the European Heart Foundation contribute to reducing heart disease risk?
A: The European Heart Foundation works towards reducing heart disease risk by promoting awareness, education, and advocating for healthier lifestyle choices and preventive measures.
Q: What are some major initiatives by the National Heart Foundation to address heart disease?
A: The National Heart Foundation focuses on initiatives related to research, education, and community outreach to address heart disease and its associated risks.
