
Introduction
Managing your body weight is like fine-tuning a musical instrument for the perfect harmony of your health. For Indian professionals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, understanding the relationship between cholesterol and body weight is crucial. This blog is your guide to unraveling this connection and discovering effective strategies to manage cholesterol by maintaining a healthy body weight.
In this blog, we delve into how being overweight can impact cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart problems and other health issues. We’ll explore the role of LDL cholesterol, known as the “bad cholesterol,” and how weight loss can significantly improve your cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health. With simple, motivating language, we aim to empower you with practical tips and knowledge to take control of your cholesterol through weight management.
Join us on this journey to better health, where we’ll navigate the path of weight loss and cholesterol management, ensuring your heart beats to the rhythm of good health. ❤️
The Weight of Success: A Software Engineer’s Path to Health
Part-1
In the bustling city of Bangalore, where the tech industry’s heart beats and the streets are alive with the promise of innovation, lived Karthik, a 38-year-old software engineer. His life was a tapestry of coding, client meetings, and the constant chase of deadlines, a rhythm so familiar yet so consuming.
Karthik’s home was a quiet contrast to the vibrant chaos of the city, shared with his wife, a high school teacher, and their young son. Despite his high emotional intelligence, which made him a beloved team leader and a compassionate family man, Karthik’s approach to his health was marked by a significant blind spot.
His daily routine was sedentary, anchored to his desk, with little physical activity beyond the walk from his car to the office. Meals were often hurried affairs, with convenience taking precedence over nutrition. This lifestyle, Karthik reasoned, was just a byproduct of his commitment to his career and family, a sacrifice he was willing to make.
The Relationship Between Cholesterol and Body Weight
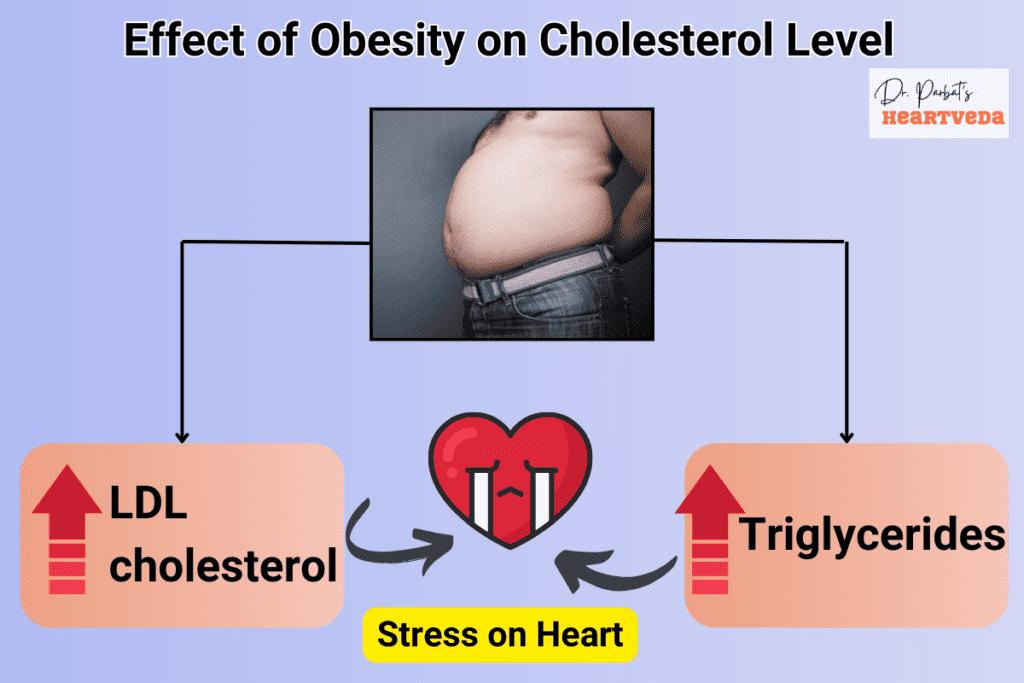
Being overweight or obese can have a significant impact on your cholesterol levels. Excess body weight can affect the production and management of important lipoproteins, including LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. When you carry excess fat tissue, it can lead to inflammation and insulin resistance in the body, which can contribute to high levels of triglycerides and cholesterol.
Losing weight is crucial for improving your cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. By reducing fat tissue, you can lower inflammation and improve insulin resistance, leading to improved cholesterol levels.
“Losing weight and adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on your cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of heart disease.” – Dr. Biprajit Parbat
How Does Obesity Affect Cholesterol Levels?
Obesity is closely linked to high cholesterol levels because excess body fat can impact your body’s ability to process and regulate cholesterol. It disrupts the balance of lipoproteins, affecting both LDL cholesterol and HDL cholesterol levels. LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” can increase, while HDL cholesterol, known as “good cholesterol,” can decrease.
Additionally, obesity is associated with higher levels of triglycerides, which are a type of fat found in the blood. Elevated triglyceride levels can further contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease.
The Benefits of Weight Loss on Cholesterol Levels
Weight loss has been proven to have a positive impact on cholesterol levels. Even modest weight loss can lead to significant improvements in LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Studies have shown that losing as little as 5% of your body weight can result in noticeable reductions in cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Furthermore, shedding excess pounds can help boost HDL cholesterol, which plays a protective role in your cardiovascular health. By making healthy lifestyle changes and losing weight, you can effectively improve your cholesterol profile and reduce your risk of heart disease.
Impact of Weight Loss on Cholesterol Levels
| Weight Loss | LDL Cholesterol Reduction | HDL Cholesterol Improvement | Triglyceride Reduction |
| 5% of body weight loss | ↓ 8-10% | ↑ 5-8% | ↓ 10-20% |
| 10% of body weight loss | ↓ 15-20% | ↑ 10-15% | ↓ 20-30% |
The Weight of Success: A Software Engineer’s Path to Health
Part-2
The consequence of this sacrifice became apparent during a routine health check-up, which revealed alarmingly high cholesterol levels. The diagnosis was a stark reminder of his obesity, a condition he had long rationalized as an unavoidable aspect of his busy life.
Karthik’s darkest moment came with the realization that his health was not just a personal issue but a family one. The thought of his son growing up without him, of his wife facing the future alone, was a wake-up call that resonated with a clarity he had never experienced before.
The path to recovery was paved with challenges, but also with hope. Driven by the desire to see his son grow up, Karthik embarked on a journey of transformation. He sought the guidance of a nutritionist, who helped him understand the impact of obesity on cholesterol levels and the power of natural weight loss to reverse this trend.
The Impact of Weight Loss on Cholesterol
Weight loss has been shown to have a significant impact on cholesterol levels. Even a modest decrease in body weight can lead to improvements in LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Research has found that losing just 5% of body weight can result in these positive changes.
For men specifically, losing between 5% and 10% of body weight may yield even better results in terms of cholesterol improvement compared to women. Additionally, even a small weight loss of 1-3% can have a positive effect on levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, which is often referred to as “good cholesterol.”
“Weight loss, even in small amounts, can have a big impact on cholesterol levels. It’s not just about the number on the scale; it’s about improving your overall cardiovascular health.”
By focusing on weight loss through a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes, individuals can successfully manage their cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Impact of Weight Loss on Cholesterol
| Weight Loss Percentage | LDL Cholesterol Reduction | Total Cholesterol Reduction | Triglyceride Reduction | HDL Cholesterol Increase |
| 1-3% | No significant reduction | No significant reduction | No significant reduction | Increased levels |
| 5% | Significant reduction | Significant reduction | Significant reduction | Increased levels |
| 5-10% (men) | Potential for better results | Potential for better results | Potential for better results | Potential for better results |
The Link Between Diet and Cholesterol
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing your cholesterol levels. Consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats can raise your LDL cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease and other health issues. To lower your cholesterol, it’s important to follow a healthy eating plan, such as the Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes (TLC) diet.
The TLC diet focuses on limiting saturated fats and incorporating healthy foods into your daily meals. By making smart food choices, you can reduce your cholesterol levels and improve your heart health. Here’s a breakdown of what to include in your diet:
1. Fruits and Vegetables:
Make sure to include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your diet. These are rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, which can help lower cholesterol levels. Opt for colorful options like berries, leafy greens, citrus fruits, and cruciferous vegetables.
2. Whole Grains:
Choose whole grains over refined grains to increase the fiber content in your diet. Whole grains like oats, brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread can help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
3. Lean Proteins:
Include lean sources of protein in your meals, such as skinless poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu. These options provide essential nutrients without the unhealthy saturated fats found in fatty meats.
4. Healthy Fats:
Incorporate healthy fats into your diet, such as avocado, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats, known as unsaturated fats, can help raise your HDL cholesterol levels (the “good” cholesterol) while lowering LDL cholesterol levels.
5. Limit Saturated and Trans Fats:
Avoid foods high in saturated and trans fats, as they can increase your LDL cholesterol levels. Limit or eliminate foods like fatty meats, butter, full-fat dairy products, fried foods, and commercially baked goods.
Remember, it’s not just about what you eat but also how much you eat. Be mindful of portion sizes to maintain a balanced diet and control your calorie intake.
“By following a healthy eating plan, incorporating whole foods, and reducing saturated and trans fats in your diet, you can lower your cholesterol levels and improve your overall heart health.” – American Heart Association
Here’s a table summarizing foods to include and avoid in your cholesterol-lowering diet:
| Foods to Include | Foods to Avoid |
| Fruits and vegetables | Fatty meats |
| Whole grains | Butter |
| Lean proteins | Full-fat dairy products |
| Healthy fats (avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil) | Fried foods |
| Commercially baked goods |
The Weight of Success: A Software Engineer’s Path to Health
Part-3
With the support of his family, Karthik introduced exercise into his daily routine, starting with brisk walks in the early morning air, gradually progressing to jogging. His diet underwent a revolution, with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains replacing the processed foods that had once filled his plate.
Karthik’s journey from denial to proactive health management became a testament to the power of natural weight loss in improving cholesterol levels. He shared his story with colleagues and friends, becoming an advocate for a balanced lifestyle, even in the midst of a demanding career.
Strategies for Weight Loss
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential for weight loss. Making certain lifestyle changes, along with maintaining a healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, can have a significant impact on lowering cholesterol levels and improving overall health.
One of the key strategies for cholesterol weight loss is engaging in regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Regular physical activity can help increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, also known as “good cholesterol,” while simultaneously reducing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad cholesterol.”
Another crucial aspect of cholesterol weight loss is adopting a healthy diet. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and foods high in unsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Avoid or limit foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fried foods, processed snacks, and fatty meats, as they can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
Smoking cessation is also vital for managing cholesterol levels. Smoking damages blood vessels and lowers HDL cholesterol, which can lead to an accumulation of LDL cholesterol in the arteries. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
The Cardiovascular Benefits of Modest Weight Loss
Modest weight loss of 5-10% has been found to produce significant cardiovascular health benefits. Research shows that when you lose this amount of weight, it can lead to notable reductions in triglyceride levels, total cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol. These improvements in key risk factors for cardiovascular issues are particularly promising for patients at higher risk.
Causes of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol can be caused by various factors, including a diet high in saturated and trans fats, excess body weight, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic factors. Consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats can raise cholesterol levels, while being overweight or obese can contribute to increased production of LDL cholesterol. Leading a sedentary lifestyle can also impact cholesterol levels.
Contributing Factors
Several factors can contribute to high cholesterol levels in your body. These include:
- Consuming a diet high in saturated fat and trans fat
- Being overweight or obese
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle
- Having certain genetic conditions that affect cholesterol metabolism
- Having an underactive thyroid gland
- Smoking cigarettes
While some factors, like genetics and thyroid conditions, are beyond your control, others can be addressed through lifestyle modifications.
The Impact of Diet
Your diet has a significant impact on your cholesterol levels. Foods high in saturated fat, like red meat, full-fat dairy products, and fried foods, can increase your LDL cholesterol levels. Similarly, consuming trans fats found in processed and packaged foods, baked goods, and fried foods can raise your cholesterol levels.
The Role of Obesity
Being overweight or obese is closely linked to high cholesterol levels. Excess body weight, especially around the waist, can increase the production of LDL cholesterol in the body. Losing weight can help reduce the production of LDL cholesterol and improve overall cholesterol levels.
The Sedentary Lifestyle Factor
Leading a sedentary lifestyle, characterized by a lack of physical activity, can also contribute to high cholesterol levels. Regular exercise can help raise HDL cholesterol levels, also known as “good cholesterol,” and lower LDL cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to keep your cholesterol in check.
Genetic Factors
While lifestyle choices play a significant role in cholesterol levels, genetics can also be a factor. Some people have inherited conditions that affect cholesterol metabolism, such as familial hypercholesterolemia. These conditions can cause exceptionally high cholesterol levels, even in individuals who lead healthy lifestyles.
Food Sources of Saturated Fat and Trans Fat
| Food Sources | Saturated Fat | Trans Fat |
| Butter | Yes | No |
| Red Meat | Yes | No |
| Full-Fat Dairy Products | Yes | No |
| Fried Foods | Yes | Yes |
| Processed and Packaged Foods | No | Yes |
| Baked Goods | No | Yes |
By making healthier choices in your diet and lifestyle, you can reduce the risk of high cholesterol and its associated complications. Consult with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive plan that includes dietary changes, regular physical activity, and, if necessary, medication to manage your cholesterol effectively.
Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Risk Factors of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol often does not cause noticeable symptoms. However, individuals with high levels may have fatty bumps on the skin and gray-white rings around the corneas of the eyes, especially in cases of familial hypercholesterolemia.
A blood test known as a lipid profile is used to diagnose high cholesterol. This test measures various lipid components in the blood, including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. It provides a comprehensive picture of an individual’s cholesterol levels and helps healthcare professionals determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of high cholesterol. These include:
- Obesity: Excess body weight, especially around the waistline, can increase the levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while lowering HDL cholesterol.
- Family history: If your close relatives have high cholesterol or a history of heart disease, you may be more prone to developing high cholesterol yourself.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains chemicals that can damage blood vessels and increase LDL cholesterol levels.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain, which in turn can affect cholesterol levels.
Understanding Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic condition that causes high cholesterol levels from birth. It is usually inherited from one or both parents and can result in significantly elevated LDL cholesterol levels and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease at an early age.
“Familial hypercholesterolemia is caused by a genetic mutation that impairs the liver’s ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood. This leads to the accumulation of LDL cholesterol and increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes, even in young individuals.”
Risk Factors for High Cholesterol
| Risk Factors | Description |
| Obesity | Excess body weight, especially around the waistline, increases LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels while lowering HDL cholesterol. |
| Family History | If close relatives have high cholesterol or a history of heart disease, the risk of developing high cholesterol is higher. |
| Smoking | Tobacco smoke contains chemicals that damage blood vessels and increase LDL cholesterol levels. |
| Sedentary Lifestyle | Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and affect cholesterol levels. |
Maintaining Healthy Cholesterol Levels

Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial for your overall well-being. By making specific lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage your cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular issues. Here are some key strategies to help you maintain healthy cholesterol levels:
1. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity plays a vital role in managing cholesterol levels. Regular exercise can help increase your levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, also known as “good cholesterol,” while simultaneously lowering your levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad cholesterol.” Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, each week.
2. Adopt a Healthy Diet
Your diet plays a key role in managing cholesterol levels. Incorporate heart-healthy foods into your daily meals, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and sources of unsaturated fats like avocados and nuts. Avoid or limit foods high in saturated and trans fats, as they can raise your LDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, consume foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish like salmon or trout, which can help lower triglyceride levels.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking has a detrimental effect on cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. Quitting smoking not only improves your cholesterol levels but also reduces your risk of heart disease. Seek support from healthcare professionals or smoking cessation programs to help you successfully quit smoking.
4. Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed by your healthcare provider to manage your cholesterol levels effectively. Statins are commonly prescribed to individuals with high cholesterol levels. These medications work by reducing the production of cholesterol in the liver and improving cholesterol balance in your body. Remember, medication is typically used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications to achieve optimal results.
“Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels requires a combination of lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. By making these positive changes, you can take control of your cholesterol levels and improve your overall health and well-being.”
| Healthy Cholesterol Level Guidelines | Total Cholesterol | LDL Cholesterol | HDL Cholesterol | Triglycerides |
| Desirable | Less than 200 mg/dL | Less than 100 mg/dL | More than 40 mg/dL | Less than 150 mg/dL |
| Borders on High | 200-239 mg/dL | 130-159 mg/dL | N/A | N/A |
| High | 240 mg/dL and above | 160 mg/dL and above | N/A | N/A |
These guidelines provide a general overview of healthy cholesterol levels. It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine your target cholesterol levels based on your individual health profile.
Testing and Monitoring Cholesterol Levels
To assess your cholesterol levels, a blood test known as a lipid profile is performed. This test provides crucial information about your total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. The results obtained from the lipid profile allow healthcare professionals to determine whether your cholesterol levels are within the desired ranges or if further action is needed to manage your cholesterol.
Recommendations for Cholesterol Management
Managing cholesterol effectively is essential for maintaining good cardiovascular health. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and seeking medical guidance, you can keep your cholesterol levels in check and reduce the risk of related issues.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Physical activity plays a crucial role in cholesterol management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, per week. Regular physical activity can help increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, the “good cholesterol,” and lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, the “bad cholesterol.”
- Follow a Healthy Diet: Adopting a healthy diet is key to managing cholesterol levels. Focus on consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, processed snacks, and fatty meats. Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, which can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Take Prescribed Medication: In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to manage cholesterol levels. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medication, such as statins, to help lower LDL cholesterol. It’s essential to take medication as prescribed and follow up with your healthcare provider regularly to monitor its effectiveness.
- Have Regular Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring your cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. They can assess your risk factors, perform necessary tests, and recommend any changes in your treatment plan.
By combining regular physical activity, a healthy diet, medication (if prescribed), and regular check-ups, you can effectively manage your cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular issues.
The Weight of Success: A Software Engineer’s Path to Health
END
As he looked back on his journey, Karthik pondered a question that had become his mantra: “If not for our health, for whom and for what are we working so hard?” It was an invitation to his peers to prioritize their well-being, to recognize that health is the foundation upon which all other successes are built.
The message was clear: obesity and high cholesterol are not just personal health issues but signals of a lifestyle in need of change. Through natural weight loss and a commitment to wellness, it’s possible to reclaim not just your health, but the very essence of life itself.
Conclusion
The link between cholesterol levels and body weight is undeniable. Excess weight can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels, which in turn increases the risk of cardiovascular health issues, including heart disease and diabetes. However, there is good news – weight loss can have a positive impact on cholesterol levels, cardiovascular health, and overall well-being.
By making lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits, you can effectively manage your cholesterol levels and improve your cardiovascular health. Start by incorporating a nutritious diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and unsaturated fats. This dietary shift can have a significant impact on your cholesterol levels and overall health.
In addition to a healthy diet, regular physical activity is crucial. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week can help lower cholesterol levels and improve your cardiovascular fitness. It’s important to find activities you enjoy, whether it’s brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or any other form of exercise that gets your heart pumping.
Remember, seeking medical guidance is essential for cholesterol management. Your healthcare provider can monitor your cholesterol levels, provide tailored advice, and prescribe medication if necessary. Regular check-ups will enable you to stay on track, make any necessary adjustments, and ensure that your cholesterol management plan is effective in the long term.
Key Takeaways:
- Losing weight can lead to improved cholesterol levels and better cardiovascular health.
- Being overweight or obese can affect the production and management of lipoproteins, including LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
- Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can result in significant reductions in LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglyceride levels.
- Diet plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels, and a healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats is recommended.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity, is essential for cholesterol weight loss and overall well-being.
Q: What is the relationship between body weight and high cholesterol?
A: The relationship between body weight and high cholesterol is significant. Being overweight or obese can lead to higher levels of cholesterol in the blood, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Q: How does being overweight or obese affect cholesterol levels?
A: Being overweight or obese can raise the level of triglycerides and decrease the level of “good” HDL cholesterol. This imbalance can increase the risk of developing high cholesterol.
Q: Can losing weight lower your cholesterol?
A: Yes, losing weight can help lower cholesterol levels, particularly if the weight loss is achieved through a healthy diet and regular exercise. Even a modest amount of weight loss can have a positive impact on cholesterol levels.
Q: How does body weight impact the response to cholesterol-lowering diets?
A: Body weight can influence the body’s response to cholesterol-lowering diets. Individuals who are overweight or obese may be less responsive to reducing their cholesterol levels through diet alone compared to those at a healthy weight.
Q: Is there a genetic component to the relationship between body weight and high cholesterol?
A: Yes, family history of high cholesterol can play a role in the relationship between body weight and high cholesterol. Some individuals, particularly women, may be less responsive to reducing their cholesterol levels through weight loss due to genetic factors.
Q: How can maintaining a healthy weight help lower the risk of high cholesterol?
A: Maintaining a healthy weight can help lower the risk of high cholesterol by reducing the odds of developing elevated plasma cholesterol. This, in turn, can lower the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Q: What lifestyle changes can contribute to lowering cholesterol levels with diet and weight management?
A: Lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, engaging in regular physical activity, and achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can contribute to lowering cholesterol levels without medication.
Q: Can being overweight or obese make cholesterol levels less responsive to dietary changes?
A: Yes, being overweight or obese may make cholesterol levels less responsive to dietary changes alone. However, combining dietary changes with weight management and exercise can still have a positive impact on cholesterol levels.
Q: What are the potential health implications of the relationship between body weight and high cholesterol?
A: The relationship between body weight and high cholesterol can have significant health implications, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. It underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy weight and managing cholesterol levels through lifestyle modifications.
Q: How can individuals with elevated plasma cholesterol benefit from weight management?
A: Individuals with elevated plasma cholesterol can benefit from weight management as it may improve their response to cholesterol-lowering interventions, potentially reducing the need for medication and lowering their risk of cardiovascular disease.
Q: How does body weight affect high cholesterol levels?
A: Excess body weight can lead to increased levels of triglycerides and LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, while decreasing HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, which can raise the risk of developing high cholesterol.
Q: What is the role of genetics in cholesterol level?
A: Genetics can influence how your body processes cholesterol, affecting your LDL and HDL levels. Individuals with a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease may have a higher predisposition to elevated cholesterol levels.
Q: Can losing weight help lower high cholesterol?
A: Yes, weight loss can positively impact cholesterol levels. It may lead to a decrease in triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and total cholesterol, while increasing HDL cholesterol, thus reducing the risk of high cholesterol.
Q: What are the odds of having high cholesterol if you are overweight?
A: Being overweight raises your risk of having high cholesterol. Studies have shown that overweight individuals are more likely to have elevated levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, and lower levels of HDL cholesterol.
Q: How does cholesterol and weight relate to each other?
A: The relationship between weight and response to cholesterol-lowering treatment varies. Overweight individuals, especially women, with elevated plasma cholesterol may be less responsive to certain treatments, indicating a potential link between weight and cholesterol response.
Q: Will participating in weight loss programs help improve cholesterol levels?
A: Participating in weight loss programs that focus on reducing body weight, incorporating physical activity, and adopting a heart-healthy diet can lead to improvements in cholesterol levels, particularly in overweight individuals with high cholesterol.
Q: What role do free fatty acids play in the relationship between body weight and high cholesterol?
A: Free fatty acids, which are elevated in individuals with excess body weight, are associated with increased triglyceride levels and decreased HDL cholesterol, contributing to the development of high cholesterol.
Q: How do high weight and high cholesterol affect women?
A: Research suggests that overweight women with elevated plasma cholesterol have higher odds of developing high cholesterol. Their response to cholesterol-lowering interventions may be less effective compared to non-overweight counterparts.
Q: What do the results of the analysis of variance on cholesterol and weight indicate?
A: The analysis of variance on cholesterol and weight indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between body weight and blood cholesterol levels, particularly when assessing the impact of weight on lipid profile.
Q: Is it important to know your risk if you are overweight?
A: Yes, knowing your risk of developing high cholesterol due to excess weight is crucial. It can facilitate proactive measures such as adopting a healthy lifestyle, undergoing cholesterol screenings, and seeking medical guidance to prevent and manage high cholesterol.
Q: Are low-fat diets effective for overweight individuals with high cholesterol?
A: Low-fat diets have been shown to have a positive impact on cholesterol levels in overweight individuals. Incorporating a low-fat diet along with weight management strategies can help in improving blood cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of high cholesterol.
Q: How does body weight influence high cholesterol?
A: Research suggests that factors related to body weight might influence the cholesterol lowering response to diet. In particular, percent weight might influence the cholesterol lowering response. It was observed that overweight women had odds of high cholesterol that were significantly affected by their body weight.
Q: How do high triglyceride levels relate to body weight?
A: High triglyceride levels are linked to body weight, as weight might influence the cholesterol lowering response to diet. So, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in managing triglyceride levels and reducing the risk of high cholesterol and heart disease.
Q: Can body weight affect lipoprotein levels?
A: Yes, body weight might influence the cholesterol lowering response to diet, including the levels of lipoproteins. Therefore, managing body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help in maintaining healthy lipoprotein levels.
Q: What are the implications of body weight on managing high cholesterol?
A: The results suggest that overweight individuals may have a different response to cholesterol-lowering diets. Therefore, managing body weight is vital in the overall management of high cholesterol and reducing the risk of heart disease.
Q: Can overweight individuals influence their cholesterol levels through weight management?
A: Yes, it is indicated that overweight women had significantly affected odds of high cholesterol based on their body weight. Therefore, managing weight through healthy lifestyle choices may play a crucial role in influencing cholesterol levels.
Q: How much does body weight impact the risk of high cholesterol?
A: Body weight does impact the risk of high cholesterol, as the odds of high cholesterol were found to be significantly affected by weight. Therefore, maintaining a healthy weight is important in reducing the risk of developing high cholesterol.
Q: What is the significance of body weight in the context of high cholesterol?
A: The relationship between body weight and high cholesterol is important to understand, as it can affect the odds of developing high cholesterol. This underscores the importance of healthy weight management in preventing high cholesterol and its associated health risks.
Q: Can diet influence the relationship between body weight and high cholesterol?
A: Yes, the cholesterol lowering response to diet was significantly affected by body weight. This suggests that dietary choices and weight management are interconnected in influencing cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
Q: How can managing body weight impact the odds of high cholesterol?
A: Managing body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can influence the odds of high cholesterol. It’s important to recognize that weight management plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart disease.
