
Introduction
Welcome to our blog, a beacon of guidance for the busy Indian professionals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, much like a lighthouse guiding ships through foggy seas. This blog is your compass in navigating the often-overlooked realm of cholesterol and heart health.
Picture your body as a bustling city, where cholesterol is the traffic flowing through its streets. Just like a city, your body needs a balance – too much traffic (bad cholesterol) leads to congestion (health issues), while smooth traffic (good cholesterol) keeps the city vibrant and healthy. Our blog is here to help you manage this traffic effectively.
Our friendly and motivating narrative will guide you through simple, practical steps to improve your heart health. From understanding the impact of diet and exercise to recognizing the importance of regular health checks, this blog is your step-by-step guide to a healthier heart.
So, let’s embark on this journey together. Whether you’re a busy professional juggling work and home or someone looking to make healthier life choices, this blog is your starting point towards a heart-healthy future.
The Heart’s Knowledge: Part 1
In the vibrant city of Chennai, where the days were as busy as the bustling markets, lived Ravi, a 40-year-old bank manager. His life was a ledger of numbers and deadlines, a routine that often left little room for anything else.
Ravi, a dedicated father and husband, was known for his sharp mind and tireless work ethic. However, when it came to his health, he often relied on quick meals and minimal exercise. His wife, Priya, a nurse, frequently expressed concern about his lifestyle, but Ravi’s response was always, “I feel fine, so why worry?”
LDL Cholesterol and Its Impact on Health
LDL cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol, plays a significant role in the development of cardiovascular disease. When there is an excess of LDL cholesterol in your blood, it can accumulate in the walls of your arteries, forming plaque. Over time, this can lead to a condition called atherosclerosis, which narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow.
There are several risk factors that can contribute to high LDL cholesterol levels and increase your risk of developing heart disease. These include:
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Poor diet, especially one high in saturated fat and cholesterol
- Physical inactivity
- Cigarette smoking
To lower your risk of high blood cholesterol and prevent the buildup of plaque in your arteries, it is important to make lifestyle changes. Start by avoiding foods that are high in saturated fat and cholesterol. Instead, opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Regular physical activity is also crucial for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. Engage in activities that get your heart rate up and increase your overall fitness. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and quitting smoking are key factors in reducing your risk of high blood cholesterol. Losing excess weight and avoiding tobacco smoke can have significant benefits for your overall cardiovascular health.
“It’s important to be mindful of your LDL cholesterol levels and take steps to keep them in check. By making lifestyle changes and adopting heart-healthy habits, you can reduce your risk of heart disease and maintain optimal health.”
Risk Factors for High LDL Cholesterol
Inadequate physical activity, obesity, and poor diet are common risk factors for high LDL cholesterol levels. It is crucial to address these risk factors through lifestyle changes and, if necessary, seek medical advice for further evaluation and treatment.
| Risk Factors for High LDL Cholesterol |
| High blood pressure |
| Obesity |
| Poor diet, particularly one high in saturated fat and cholesterol |
| Physical inactivity |
| Cigarette smoking |
HDL Cholesterol and Its Importance
HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, often referred to as “good” cholesterol, plays a crucial role in maintaining heart health. Unlike LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol carries cholesterol from the cells in your body back to the liver for recycling or disposal. By doing so, HDL cholesterol helps lower your overall cholesterol levels and reduces the risk of plaque buildup in your arteries.
Higher levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a lower risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. To raise your HDL cholesterol levels and improve your cardiovascular health, there are several lifestyle changes you can adopt:
- Engage in regular exercise: Physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, can help increase the levels of HDL cholesterol in your body.
- Quit smoking: Smoking lowers the levels of HDL cholesterol in your body. By quitting smoking, you can improve your HDL cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of heart disease.
- Adopt a diet low in saturated fat: Consuming foods high in saturated fat can raise your LDL cholesterol levels. Choosing a diet that is low in saturated fat and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help increase your HDL cholesterol and lower your overall cholesterol levels.
“By engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and adopting a diet low in saturated fat, you can raise your HDL cholesterol levels and improve your cardiovascular health.”
| Food | HDL Cholesterol Promoting Properties |
| Fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines) | Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help increase HDL cholesterol levels |
| Olive oil | Contains monounsaturated fats that can raise HDL cholesterol levels |
| Nuts (such as almonds, walnuts, and peanuts) | High in healthy fats and other beneficial nutrients that promote HDL cholesterol production |
| Avocado | Loaded with monounsaturated fats that raise HDL cholesterol levels |
| Whole grains (such as oats and brown rice) | Contain soluble fiber that can help increase HDL cholesterol levels |
| Fruits and vegetables | Packed with antioxidants and nutrients that support HDL cholesterol production |
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into your daily routine and making healthier food choices, you can raise your HDL cholesterol levels, lower your overall cholesterol levels, and improve your cardiovascular health.

Importance of Cholesterol Testing
Regular cholesterol testing is crucial for assessing your risk of heart disease. It provides valuable information about the levels of different types of cholesterol in your blood, helping healthcare providers determine appropriate interventions and treatment strategies. One of the most common tests used to assess cholesterol levels is a lipid profile test.
The Lipid Profile Test
A lipid profile test measures various components of cholesterol in the blood, including LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and total cholesterol. It provides a comprehensive overview of your cholesterol levels, allowing healthcare professionals to evaluate your risk of heart disease effectively.
“Regular cholesterol testing is like having a window into your heart’s health. It allows you to monitor and manage your cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.”
Having a full lipid profile test is highly recommended as it evaluates the individual levels of each lipid component. This detailed analysis helps healthcare providers identify potential problems and develop a personalized approach to managing your cholesterol levels.
Understanding High Cholesterol and Saturated Fat
High cholesterol levels, especially the levels of LDL cholesterol, can increase the risk of heart disease. LDL cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol as it can contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis. A diet high in saturated fat is a significant contributor to elevated LDL cholesterol levels in the blood.
By undergoing regular cholesterol testing, you can stay informed about your cholesterol levels and make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle. It allows you to effectively monitor the impact of dietary changes, such as reducing saturated fat intake, on your cholesterol levels, and take necessary actions to maintain a healthy heart.
| Test Component | Desirable Level | Borderline High Level | High Level |
| Total Cholesterol | <200 mg/dL | 200-239 mg/dL | >=240 mg/dL |
| LDL Cholesterol | <100 mg/dL (Optimal) | 100-129 mg/dL (Near optimal/above optimal) | >=130 mg/dL (High) |
| HDL Cholesterol | >=60 mg/dL (High) | 40-59 mg/dL (Acceptable) | <40 mg/dL (Low) |
| Triglycerides | <150 mg/dL | 150-199 mg/dL | >=200 mg/dL |
These guidelines provide a general understanding of desirable cholesterol levels, but it’s important to remember that individual cases may vary. Your healthcare provider will interpret your test results and recommend appropriate interventions based on your unique health profile.
By prioritizing regular cholesterol testing, you can take an active role in managing your heart health, making informed decisions, and reducing your risk of heart disease.
The Heart’s Knowledge: Part 2
One day, during a casual conversation, Priya mentioned the importance of understanding cholesterol levels – LDL and HDL – and their impact on heart health. Ravi listened half-heartedly, not fully grasping the significance of her words.
However, a sudden health scare involving a close friend, who suffered a heart attack, jolted Ravi. He realized that feeling fine wasn’t a reliable indicator of health. Motivated by concern for his family and his own well-being, Ravi scheduled a full health check-up.
Healthy Blood Cholesterol Levels
Having healthy blood cholesterol levels is essential for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health. The levels of different cholesterol components, including total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), play a crucial role in determining your risk of heart disease and other related conditions.
For individuals with atherosclerosis or other cardiovascular risk factors, it is recommended to maintain an LDL (low-density lipoprotein) level below 70 mg/dL, which is considered ideal. LDL cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol and contributes to the formation of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
On the other hand, for people without risk factors, maintaining an LDL level below 100 mg/dL is advised. This lower threshold helps ensure that excess LDL cholesterol is not present in the blood, reducing the risk of plaque buildup and related cardiovascular complications.
“Having healthy blood cholesterol levels is crucial for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health.”
It’s important to note that individuals with diabetes may have specific cholesterol management needs. For those with diabetes and LDL levels of 70 mg/dL or higher, medication may be required to reduce cholesterol levels and mitigate the associated risks.
Monitoring your cholesterol levels, including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and HDL cholesterol, through regular blood tests is essential for assessing your cardiovascular health. These tests provide valuable insights into your cholesterol profile and enable healthcare providers to formulate personalized interventions or treatment strategies to manage cholesterol effectively.
By maintaining healthy blood cholesterol levels, you can reduce the risk of heart disease and improve your overall cardiovascular well-being. It is essential for people with high cholesterol to collaborate with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized plan to lower their cholesterol levels. cholesterol management plan tailored to your individual needs and risk factors.
Managing High Cholesterol
If you have high cholesterol, don’t worry. It can often be managed effectively through simple lifestyle changes. By incorporating healthier food choices, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and quitting smoking, you can take crucial steps towards cholesterol management.
Modifying your diet is key. Focus on consuming foods that are low in saturated fat and cholesterol. Opt for lean proteins, whole grains, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Additionally, choose healthier cooking methods like grilling, baking, and steaming instead of frying.
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise each week. This could include activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
Maintaining a healthy weight is vital for managing cholesterol. Shedding excess pounds can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine your target weight and develop a personalized plan that includes a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
Quitting smoking is another essential step in cholesterol management. Smoking damages blood vessels, lowers HDL cholesterol levels, and increases the risk of heart disease. Seek support from healthcare professionals, join smoking cessation programs, or try nicotine replacement therapy to increase your chances of quitting successfully.
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to lower cholesterol levels. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to further reduce your cholesterol levels. Statins, such as atorvastatin and rosuvastatin, are commonly prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol. Other medications, like ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors, can also be used in combination with lifestyle changes to effectively manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
| Lifestyle Changes for Managing High Cholesterol | Medications for Cholesterol Management |
| Choose a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterolIncorporate lean proteins, whole grains, and fruits and vegetables into your mealsAvoid fried and processed foodsEngage in regular physical activityStrive for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise each weekMaintain a healthy weightQuit smoking | Statins (such as atorvastatin and rosuvastatin)EzetimibePCSK9 inhibitors |
The Heart’s Knowledge: Part 3
The results were eye-opening. Ravi’s LDL cholesterol was high, while his HDL was low, putting him at risk for heart disease. This revelation was Ravi’s wake-up call. He turned to Priya and Dr. Anand, a cardiologist friend, for advice.
With their guidance, Ravi embarked on a journey of transformation. He learned about heart-healthy foods, started exercising regularly, and made significant changes to his diet. He swapped fried snacks for fruits and vegetables, and incorporated whole grains and lean proteins into his meals.
Understanding Triglycerides and Their Impact
Triglycerides are a type of fat that circulates in your blood. Similar to cholesterol, having high levels of triglycerides can increase your risk of heart disease. Elevated triglyceride levels are often associated with high cholesterol, obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
To reduce your risk of heart disease, it’s important to manage both your cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Lifestyle modifications play a key role in lowering triglycerides. Incorporating a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and reducing alcohol consumption can all contribute to lowering triglyceride levels.
Here are some strategies to help lower your triglycerides:
- Choose healthy fats: Replace saturated and trans fats with healthier fats found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Eat a balanced diet: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and desserts.
- Get active: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, every week.
- Lose excess weight: Losing just a few pounds can have a significant impact on your triglyceride levels.
- Drink alcohol in moderation: Alcohol can significantly raise triglyceride levels, so limit your intake to moderate amounts.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can help to lower your triglyceride levels and reduce your risk of heart disease. It’s also important to work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor your cholesterol and triglyceride levels and determine the best course of action for managing your cardiovascular health.
Genetic and Lifestyle Factors in Cholesterol Production
The body has the remarkable ability to produce cholesterol on its own, primarily in the liver. Cholesterol is a vital substance that your body needs for various important functions, including cell membrane formation, hormone synthesis, and vitamin production.
Genetic factors can influence cholesterol production, meaning that your family history of high cholesterol may increase your risk. However, it’s important to note that lifestyle choices also play a significant role in cholesterol production.
By making healthy choices and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can effectively manage your cholesterol levels. This includes following a balanced diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking or tobacco use.
Your genetic predisposition to high cholesterol levels doesn’t determine your fate. Your lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on your cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. Embrace a heart-healthy lifestyle to take control of your cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of heart disease and other related conditions.
The Role of Cholesterol in Atherosclerosis
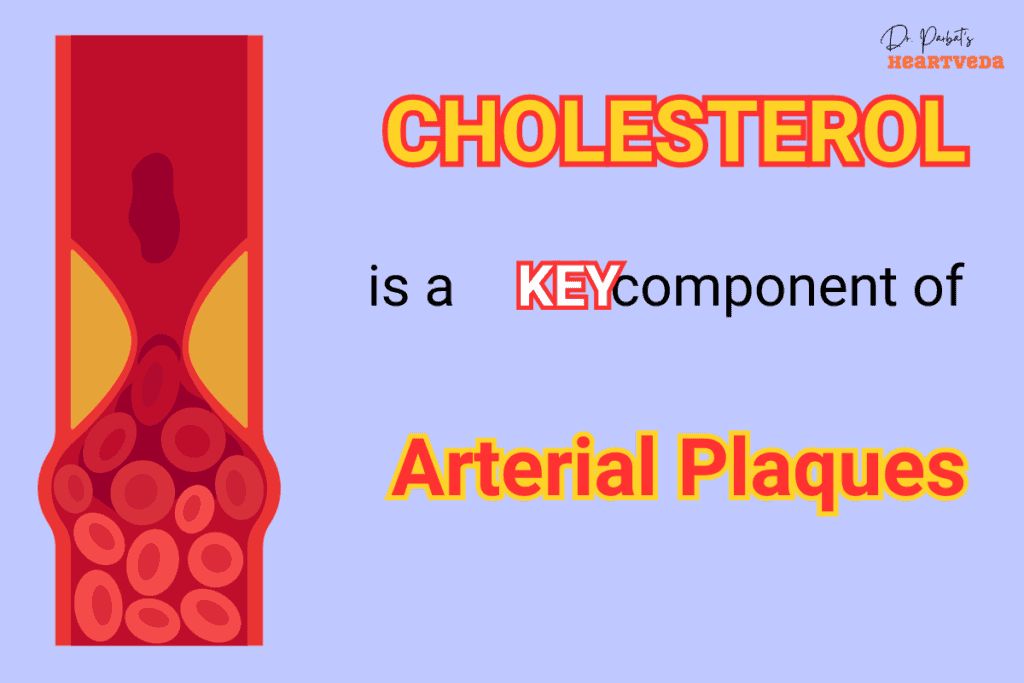
Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the walls of your arteries. Cholesterol, especially LDL cholesterol, plays a significant role in the formation of this plaque.
Over time, the plaque can narrow your arteries, leading to reduced blood flow and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke. This is why it’s crucial to understand how cholesterol affects your cardiovascular health.
When you have high cholesterol levels, there is an excess of cholesterol circulating in your body. This extra cholesterol can penetrate the walls of your arteries and trigger an inflammatory response, attracting cells to the site and causing the accumulation of plaque.
If you have a family history of high cholesterol, your risk of developing atherosclerosis may be higher. Genetic factors can influence how your body handles cholesterol, making it important to monitor your cholesterol levels regularly.
Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a diet high in saturated fat and lack of physical activity, can also contribute to high cholesterol levels and increase your risk of atherosclerosis.
“Cholesterol, particularly LDL cholesterol, can contribute to the formation of plaque in the walls of the arteries.”
By managing your cholesterol levels and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can reduce your risk of atherosclerosis and its associated complications.
| Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis: | Ways to Reduce Risk: |
| High cholesterol levels | Get regular cholesterol screenings |
| Family history of high cholesterol | Follow a heart-healthy diet |
| Unhealthy lifestyle choices | Incorporate regular physical activity |
By taking proactive steps to manage your cholesterol levels, you can prioritize your cardiovascular health and reduce your risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Disease
High cholesterol levels pose a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke. It is crucial to prioritize the management of cholesterol levels to reduce the incidence of these conditions. Regularly getting your cholesterol checked is essential for identifying your risk level and taking appropriate measures. Understanding the different types of cholesterol and their respective roles is key to effective prevention and management of cardiovascular disease.
The Types of Cholesterol
Cholesterol exists in the body in different forms, each with distinct functions and effects on cardiovascular health. The two main types of cholesterol are:
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Cholesterol: Known as the “bad” cholesterol, this carries cholesterol to the cells in your body which need some cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol can contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Cholesterol: Referred to as the “good” cholesterol, HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
A healthy balance between LDL and HDL cholesterol is crucial for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health.
Cholesterol Levels and Heart Disease Risk
| Test Component | Desirable Level | Borderline High Level | High Level |
| Total Cholesterol | <200 mg/dL | 200-239 mg/dL | >=240 mg/dL |
| LDL Cholesterol | <100 mg/dL (Optimal) | 100-129 mg/dL (Near optimal/above optimal) | >=130 mg/dL (High) |
| HDL Cholesterol | >=60 mg/dL (High) | 40-59 mg/dL (Acceptable) | <40 mg/dL (Low) |
| Triglycerides | <150 mg/dL | 150-199 mg/dL | >=200 mg/dL |
| Cholesterol Levels | Heart Disease Risk | Mortality Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Low/Optimal | Lower | Lower |
| Borderline | Higher | Higher |
| Increasingly High | Higher | Higher |
| High and Decreasing | Higher | Higher |
| Highest LDL | Highest | Highest |
Importance of Cholesterol Checks
Regular cholesterol checks are essential for identifying individuals at risk of developing heart disease and stroke. By monitoring your cholesterol levels, you can take preventive measures and adopt lifestyle changes to manage and reduce your risk. These checks allow healthcare professionals to tailor interventions based on individual cholesterol profiles, helping protect your heart and overall well-being.
Preventing and Managing Cardiovascular Disease
Preventing and managing cardiovascular disease go hand in hand with effective cholesterol management. By working with your healthcare provider and implementing lifestyle changes, you can lower your risk of heart disease and stroke. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial steps in cholesterol management.
“Regular cholesterol checks are essential for identifying individuals at risk of developing heart disease and stroke.”
Here is an example of how having too much cholesterol in your blood can impact your risk of heart disease and stroke:
| Cholesterol Levels | Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke |
| Optimal Levels | Low |
| High LDL Cholesterol | High |
| Low HDL Cholesterol | High |
| High Total Cholesterol | High |
As shown in the table above, high LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, and high total cholesterol levels increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Regular cholesterol checks provide valuable insights into your cholesterol profile and enable the development of personalized strategies to reduce these risks.
By understanding the impact of cholesterol on cardiovascular disease and proactively managing your cholesterol levels, you can safeguard your heart health and reduce the likelihood of developing heart disease and stroke.
Treatment Options for High Cholesterol
The treatment of high cholesterol involves addressing risk factors through lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, using medication to lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels. There are several treatment options available that can help you manage your cholesterol levels effectively and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing healthy lifestyle changes to lower cholesterol and reduce your risk is an important step in managing high cholesterol. Here are some recommended modifications:
- Follow a heart-healthy diet: Reduce your intake of saturated fat, trans fat, and dietary cholesterol.
- Incorporate regular exercise into your routine to lower cholesterol and reduce your risk: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Losing excess weight can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces HDL cholesterol levels.
Medication Options
In some cases, lifestyle changes may not be sufficient to bring your cholesterol levels within a healthy range. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medication to help lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. Some commonly prescribed medications include:
| Medication | Function |
| Statins (e.g., atorvastatin, rosuvastatin) | Lower LDL cholesterol levels by inhibiting its production in the liver. |
| Ezetimibe | Decreases the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine. |
| PCSK9 inhibitors (e.g., evolocumab, alirocumab) | Helps lower LDL cholesterol levels by blocking the action of PCSK9, a protein that reduces the liver’s ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood. |
It’s important to discuss the medication options with your healthcare provider to determine which one is most suitable for your specific needs and medical history.
By making necessary lifestyle changes and following your prescribed treatment plan, you can effectively manage your cholesterol and triglyceride levels, reducing the risk of complications associated with high cholesterol levels. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.
The Heart’s Knowledge: END
As weeks turned into months, Ravi’s efforts paid off. His cholesterol levels improved, and he felt more energetic and alive than ever. His transformation inspired his colleagues and friends, leading to a ripple effect of health consciousness in his community.
Reflecting on his journey, Ravi realized the power of knowledge. “It’s not just about living longer; it’s about living healthier,” he thought, grateful for the second chance.
“Are you aware of what your heart needs? Remember, knowledge is the key to a healthy heart.”
Conclusion
Understanding the role of cholesterol in the body is essential for maintaining optimal health. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and proactively managing cholesterol levels, you can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health.
To effectively manage your cholesterol, it is crucial to get regular screenings to monitor your cholesterol numbers and identify any potential issues. Working closely with your healthcare provider will help you develop a personalized cholesterol management plan based on your individual risk factors and needs.
Remember, cholesterol numbers indicate the levels of different types of cholesterol in your body. By incorporating lifestyle changes such as following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and quitting smoking, you can maintain healthy cholesterol levels and promote a healthy heart.
Take the necessary steps to take control of your cholesterol numbers and prioritize your cardiovascular health. By proactively managing your body’s cholesterol, you can lead a healthier and more fulfilling life.
Key Takeaways:
- Cholesterol is vital for your body, but high levels of LDL cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease.
- HDL cholesterol plays a protective role in removing LDL cholesterol from your bloodstream.
- Regular cholesterol testing is essential to assess your risk and determine appropriate interventions.
- Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, are key to managing high cholesterol levels.
- Genetic and lifestyle factors both contribute to cholesterol production, but healthy choices can help control it.
FAQ Section on High Blood Cholesterol and Its Impact
A: Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in the cells of your body. It’s important for building cell membranes, producing hormones, and making vitamin D. However, too much cholesterol can be harmful to your health.
A: No, cholesterol is not water-soluble, which means it cannot dissolve in the blood and needs transport molecules called lipoproteins.
A: The body makes all the cholesterol it needs, primarily in the liver. Cholesterol is also obtained from the food we eat, particularly animal products such as meat, dairy, and eggs.
A: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein) are two types of cholesterol in your bloodstream. LDL cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, as high levels can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, while HDL cholesterol is known as “good” cholesterol, as it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the arteries.
A: Having unhealthy levels of cholesterol, particularly high LDL cholesterol, can increase the risk for heart disease and stroke. It can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque buildup can block blood flow in the arteries.
A: Several factors can contribute to high cholesterol, including unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, obesity, and genetics. Certain medical conditions and medications can also impact cholesterol levels.
A: To lower your cholesterol, you can make lifestyle changes such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco smoke. In some cases, medications may also be prescribed.
A: Yes, foods of animal origin contain cholesterol. This includes meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, and dairy products. Plant-based foods do not contain cholesterol.
A: Cholesterol levels are typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) of blood. The desirable range for total cholesterol is below 200 mg/dL. LDL cholesterol levels should ideally be below 100 mg/dL, while HDL cholesterol levels should be 60 mg/dL or higher.
A: You can take steps to prevent high cholesterol by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can also help monitor and manage cholesterol levels.
A: The American Heart Association recommends a diet low in saturated and trans fats, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to help lower cholesterol. They also recommend regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight.
A: Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that is found in all cells of the body. It is essential for the production of hormones, Vitamin D, and substances that help digest food.
A: The body makes all the cholesterol it needs. However, cholesterol can also be obtained from food sources such as meat, poultry, and full-fat dairy products.
A: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol as it can build up on the walls of your arteries, while HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol is known as “good” cholesterol as it helps remove LDL from the bloodstream.
A: Factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, obesity, and genetics can contribute to high cholesterol levels.
A: The liver makes all the cholesterol the body needs. However, additional cholesterol can also be obtained from dietary sources.
A: High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions as it can lead to the accumulation of plaque in the arteries, which can block blood flow.
A: Lowering cholesterol can be achieved through lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and, if necessary, taking medication prescribed by a healthcare professional.
A: Cholesterol numbers in a blood test indicate the levels of LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol in the bloodstream, providing insight into the individual’s risk for heart disease and other related conditions.
A: Cholesterol is important for the body as it is essential for the formation of cell membranes, and plays a vital role in the production of hormones and Vitamin D, aiding in various bodily functions
A: Maintaining LDL levels within the optimal range is important for reducing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular complications, as well as promoting overall health.
A: No, cholesterol is not a phospholipid. While both cholesterol and phospholipids are essential components of cell membranes, they have different chemical structures and functions in the body.
