
Introduction
Did you know that high cholesterol can be a silent threat, often showing no obvious signs until it’s too late? 🤔 Imagine it as a stealthy intruder in your body, quietly causing harm without any immediate alarms. This blog is tailored for busy Indian professionals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s, focusing on the crucial topic of identifying the symptoms and signs of high cholesterol levels in the blood.
In this friendly and motivating guide, we’ll explore the subtle yet significant indicators of high cholesterol, such as numbness in the legs and feet, pale nails, and signs of peripheral arterial disease. While high cholesterol often flies under the radar, being aware of these symptoms can be a game-changer in taking timely action.
We’ll delve into the causes of high cholesterol, from lifestyle choices to genetic factors, and discuss effective strategies for combating this silent health issue. Did you know that simple lifestyle changes can significantly impact your cholesterol levels and heart health?
Join us in this enlightening journey to understand and tackle high cholesterol. It’s a straightforward read, yet packed with vital insights for anyone concerned about maintaining a healthy heart. Let’s embark on this path of awareness and proactive health management together! ❤️🚶
Blueprint for a Healthy Heart
Part – 1
In the bustling lanes of Chennai, where the aroma of filter coffee blends with the ambition in the air, Vikram, a renowned architect, sculpted the skyline with his visionary designs. His life, a blueprint of success and precision, was admired by many. Yet, in his quest to leave a mark on the city, Vikram overlooked the most crucial project of all: his health.
Vikram, a single father devoted to his teenage daughter, Ananya, had always prided himself on his ability to balance the demands of his profession with the joys and responsibilities of parenthood. His emotional intelligence allowed him to navigate the most complex client demands and Ananya’s teenage years with equal finesse. However, this same intelligence failed to convince him of the silent threat brewing within his own body.
What Causes High Cholesterol?
High cholesterol can be caused by a combination of lifestyle choices and genetic factors. Lifestyle choices such as a high-fat diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to high cholesterol levels. These choices can lead to the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Genetic factors also play a role in high cholesterol, with conditions like familial hypercholesterolemia and lipoprotein (a) disorder contributing to elevated cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle Choices and High Cholesterol
A sedentary lifestyle with limited physical activity can lead to weight gain and obesity, both of which can raise cholesterol levels. Additionally, consuming a diet rich in saturated fats and trans fats can increase the production of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, which is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol. Smoking tobacco damages blood vessels and lowers the levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, or “good” cholesterol, which helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
“The connection between high cholesterol and lifestyle choices is significant. Making simple changes like adopting a heart-healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise can have a positive impact on cholesterol levels.”
The bar chart above visualizes the prevalence of cholesterol issues among college students as per the data:
- Borderline High Cholesterol Levels: 40.5% of the participants are in this category, represented by the blue bar. This indicates a significant proportion of students are at the threshold of high cholesterol.
- Hyperlipidemia (Very High Cholesterol Levels): 3.4% of the participants, shown by the red bar, have hyperlipidemia. Although a smaller percentage, it’s a notable concern given the age group (college students).
Lifestyle Factors:
- Dietary Habits: Many participants reported poor dietary habits, such as frequent consumption of sugary beverages and red meat, which can negatively impact cholesterol levels.
- Physical Activity: Only about 68.2% of participants engaged in moderate physical activity, while a significant proportion led sedentary lifestyles. Physical inactivity can adversely affect cholesterol levels.
- Alcohol Consumption: 65.5% of the participants consumed alcoholic beverages, and a subset were identified as binge drinkers. Excessive alcohol consumption can influence cholesterol levels.
Genetic Factors and High Cholesterol
While lifestyle choices can greatly influence cholesterol levels, genetic factors also contribute to the risk of high cholesterol. Familial hypercholesterolemia is an inherited condition that impairs the body’s ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood, resulting in elevated levels. Lipoprotein (a) disorder is another genetic condition that can lead to high cholesterol. People with a family history of these conditions are at a higher risk of developing high cholesterol levels.
Combating High Cholesterol
Understanding the causes of high cholesterol is crucial for making necessary changes to prevent or manage the condition. By making positive lifestyle choices like adopting a healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and moderating alcohol consumption, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of high cholesterol. For those with genetic factors contributing to high cholesterol, it may be necessary to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that may include medication to help manage cholesterol levels.
In the next section, we will explore the different types of cholesterol and their impact on our health.
Blueprint for a Healthy Heart
Part – 2
Despite a family history of heart disease, Vikram lived in a mental frame that dismissed the need for regular health check-ups and a balanced diet. His days were fueled by caffeine and fast food, a testament to the fast-paced life he led. Exercise was a concept relegated to the occasional Sunday morning walk, more for contemplation than cardiovascular health.
The turning point came unexpectedly during a high-profile project presentation. Vikram experienced a momentary dizziness so severe it halted his words, his vision blurring as the room spun. This incident, though brief, was a glaring signal he could no longer ignore. The subsequent medical tests revealed the silent adversary he had been harboring: dangerously high cholesterol levels, with no prior symptoms to warn him of the damage being inflicted on his body.
Understanding Cholesterol Types
Cholesterol is carried in the blood by proteins called lipoproteins. There are two main types of lipoproteins: low-density lipoprotein (LDL), also known as “bad” cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), known as “good” cholesterol.
LDL cholesterol is responsible for carrying cholesterol from the liver to the cells in the body. However, when there is an excess of LDL cholesterol in the bloodstream, it can contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, transporting it back to the liver to be metabolized and eliminated from the body. High levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a reduced risk of heart disease.
Additionally, there is another type of fat called triglycerides that can also contribute to high cholesterol levels. Triglycerides are the most common type of fat found in the body and are derived from the food we eat. Elevated levels of triglycerides can increase the risk of heart disease and should be monitored along with LDL and HDL cholesterol levels.
Understanding the different types of cholesterol is essential in evaluating your risk of heart disease and determining the most appropriate treatment plan. By maintaining a healthy balance of LDL and HDL cholesterol, as well as managing triglyceride levels, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining heart health.
Common Symptoms of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol typically does not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, in some cases, there may be warning signs that indicate high cholesterol levels. It’s important to be aware of these symptoms, as they could be a sign of underlying health issues that need to be addressed.
Pain While Walking
One common symptom of high cholesterol is pain or discomfort while walking. This can occur due to reduced blood flow to the legs and feet, known as peripheral arterial disease. If you experience pain, cramping, or weakness in your legs while walking, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
Numbness in Legs and Feet
Another symptom that may indicate high cholesterol levels is numbness in the legs and feet. This can occur when there is a buildup of plaque in the arteries, restricting blood flow to the lower extremities. If you notice persistent numbness or tingling in your legs or feet, it’s important to seek medical attention for further evaluation and management.
Pale Nails
High cholesterol can also manifest as changes in the appearance of your nails. Pale or whitened nails may indicate poor blood flow, which could be related to high cholesterol levels. If you notice any changes in nail color or texture, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
In conclusion, while high cholesterol typically doesn’t present with symptoms, pain while walking, numbness in the legs and feet, and pale nails can be warning signs of underlying health issues related to high cholesterol levels. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention for further evaluation and appropriate management.
Blueprint for a Healthy Heart
Part – 3
Vikram’s darkest moment wasn’t the diagnosis itself but the realization of his negligence towards his health and the potential consequences on Ananya’s future. The thought of his daughter facing life without his guidance and support was a wake-up call louder than any alarm.
Guided by Dr. Iyer, a cardiologist and an old college friend, Vikram embarked on a journey of transformation. Dr. Iyer explained the insidious nature of high cholesterol, emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring and a lifestyle overhaul. With a newfound resolve, Vikram embraced a heart-healthy diet, integrated exercise into his daily routine, and became a vocal advocate for regular health screenings, sharing his story to inspire others.
How is High Cholesterol Diagnosed
Diagnosing high cholesterol involves a blood test called a lipid panel. This test measures the levels of different types of cholesterol, including LDL, HDL, and triglycerides, in the blood. It also provides a total cholesterol level. Regular cholesterol testing is important for early detection and monitoring of cholesterol levels, especially if you have risk factors for high cholesterol or a family history of the condition.
Why is Cholesterol Testing Important?
Cholesterol testing, also known as a cholesterol blood test or lipid panel, is a crucial step in managing your heart health. It provides valuable information about your cholesterol levels, helping you and your doctor assess your risk for cardiovascular disease. By monitoring your cholesterol levels, you can take proactive measures to prevent heart attacks, strokes, and other complications associated with high cholesterol.
If you have risk factors for high cholesterol, such as a family history or certain medical conditions, it is especially important to undergo regular cholesterol testing. Catching high cholesterol early allows for early intervention and lifestyle modifications that can help you maintain optimal cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Cholesterol testing typically involves a simple blood draw. Your doctor will order a lipid panel that measures various components of your cholesterol profile, including:
- Total cholesterol: This measures the total amount of cholesterol in your blood, including LDL, HDL, and other types.
- LDL cholesterol: Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, high levels of LDL cholesterol can contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries.
- HDL cholesterol: Known as “good” cholesterol, higher levels of HDL can actually help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Triglycerides: Elevated triglyceride levels are also associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
Based on your cholesterol test results, your doctor can provide personalized recommendations for managing your cholesterol levels. These may include lifestyle changes such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, increasing physical activity, losing weight, quitting smoking, and, in some cases, medication.
Regular cholesterol testing is essential for monitoring your cholesterol levels and making informed decisions about your health. Talk to your doctor about how often you should have cholesterol screenings based on your specific risk factors, age, and overall health.
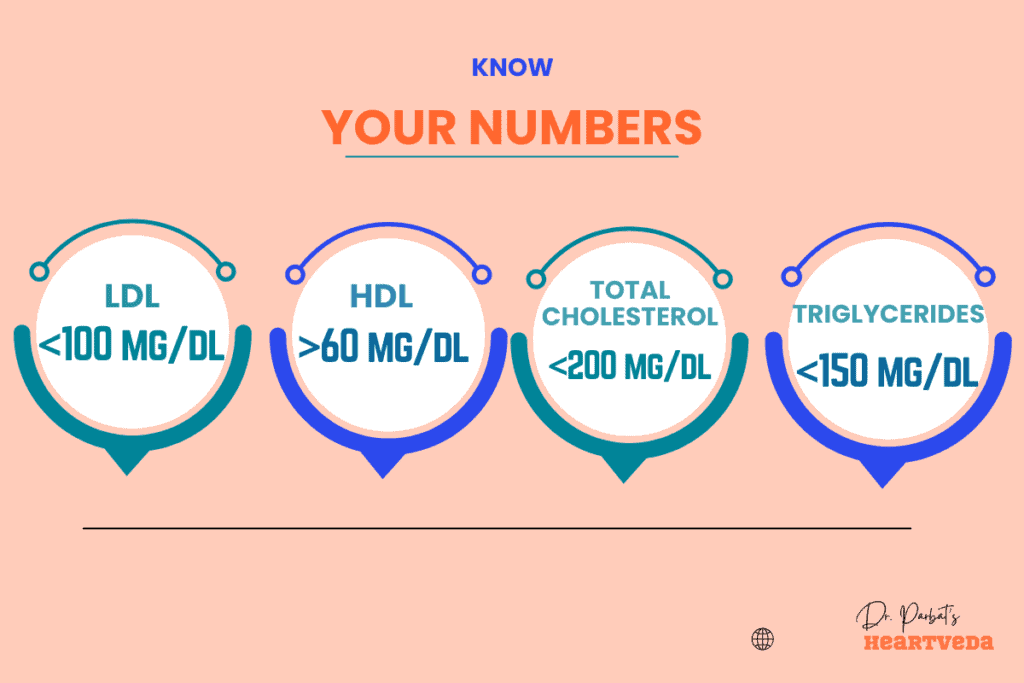
| Cholesterol Component | Desirable Level | Borderline High | High |
| Total Cholesterol | Less than 200 mg/dL | 200-239 mg/dL | 240 mg/dL and above |
| LDL Cholesterol | Less than 100 mg/dL (optimal) | 100-129 mg/dL (near or above optimal) | 130 mg/dL and above (high) |
| HDL Cholesterol | 60 mg/dL and above (high) | 40-59 mg/dL (desirable) | Less than 40 mg/dL (low) |
| Triglycerides | Less than 150 mg/dL (normal) | 150-199 mg/dL (borderline high) | 200 mg/dL and above (high) |
Treating High Cholesterol
When it comes to managing high cholesterol, a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle changes and medication can be highly effective. Making the necessary lifestyle adjustments and working closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on your individual circumstances can help you achieve optimal cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle Changes

One of the key components of high cholesterol treatment involves adopting healthy lifestyle changes. Here are some strategies that can make a significant impact:
- Follow a Healthy Diet: Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals. Aim for a low-saturated fat diet and limit your intake of processed foods and sugary drinks.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can improve heart health and contribute to lowering cholesterol levels.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can negatively affect cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. Seek professional support or join a cessation program to quit smoking.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight, especially around the waistline, can help reduce cholesterol levels. Focus on a well-balanced diet and regular exercise to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Medication
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to effectively manage high cholesterol levels. Your healthcare professional may prescribe medication, such as statins, to help lower your cholesterol. Statins work by blocking the enzyme responsible for producing cholesterol in the liver.
“Combining lifestyle changes with medication can provide an effective approach to treating high cholesterol, helping to mitigate the risk of heart disease and stroke.” – Dr. Biprajit Parbat
It is important to consult with your healthcare professional about the most appropriate medication based on your specific needs and medical history. They will consider factors like your overall health, cholesterol levels, and any existing health conditions to determine the best course of action.
| Treatment Approach | Benefits | Considerations |
| Lifestyle Changes | – Lowers cholesterol levels – Improves overall cardiovascular health | – Requires commitment to long-term changes – Results may take time to manifest |
| Medication | – Can effectively lower cholesterol levels – Reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke | – Potential side effects – Requires regular monitoring |
Remember, managing high cholesterol is an ongoing process. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional are crucial to assess the effectiveness of your treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments.
Complications of High Cholesterol
If left untreated, high cholesterol can lead to various complications that significantly impact your heart health and overall well-being. The excessive presence of cholesterol in your blood can result in:
- Heart Disease: High cholesterol contributes to the formation of plaque in your arteries, narrowing them and limiting blood flow to your heart. This can lead to serious conditions such as coronary artery disease, angina, and heart attacks.
- Stroke: Plaque buildup can also affect the blood vessels leading to your brain, increasing the risk of a stroke. Reduced blood flow can cause a blood clot to form, blocking vital oxygen and nutrients from reaching your brain cells.
- Peripheral Arterial Disease: Cholesterol deposits can accumulate in the arteries supplying your arms and legs, causing peripheral arterial disease. This condition can result in pain, numbness, and decreased functioning in your extremities.
Recognizing the complications of high cholesterol is essential for taking proactive steps to manage your cholesterol levels and mitigate these risks. By managing your cholesterol effectively, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of heart disease, strokes, and peripheral arterial disease.
| Complication | Description |
| Heart Disease | Abnormalities in the heart’s arteries that can lead to coronary artery disease, chest pain, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular problems. |
| Stroke | A condition caused by interrupted blood supply to the brain due to the blockage or rupture of a blood vessel, leading to brain cell damage and functional impairment. |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease | A circulatory disorder characterized by the narrowing or blockage of arteries resulting in reduced blood flow to the limbs, causing pain, numbness, and impaired function. |
Reducing Cholesterol Levels
High cholesterol levels can be effectively reduced through lifestyle changes. By adopting a healthy diet low in saturated fats and high in fiber, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress, you can significantly improve your cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
1. Diet
Making changes to your diet can have a major impact on cholesterol levels. Focus on consuming foods that are low in saturated fats, such as lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Include sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Incorporating soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, beans, and lentils, can also help reduce cholesterol levels.
2. Exercise
Regular physical activity is an effective way to lower cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, most days of the week. Engaging in activities that get your heart rate up can help improve cardiovascular health and lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels while increasing HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese can contribute to high cholesterol levels. Focus on achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise. Losing just a few pounds can have a significant impact on cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
4. Stress Management
Chronic stress has been linked to higher cholesterol levels. Implement stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that help you relax. By managing stress effectively, you can positively impact your cholesterol levels and overall well-being.
Remember, making sustainable lifestyle changes is key to achieving and maintaining optimal cholesterol levels. Consult a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan that suits your specific needs and medical history.
5. The Power of Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes not only helps reduce cholesterol levels, but it also promotes overall heart health. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle that includes a nutritious diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress, you can significantly improve your cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
| Ways to Reduce Cholesterol Levels |
| Avoid foods high in saturated fats |
| Incorporate fruits and vegetables in your diet |
| Engage in regular physical activity |
| Include sources of healthy fats in your diet |
| Eat foods rich in soluble fiber |
| Maintain a healthy weight |
| Manage stress effectively |
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have risk factors for high cholesterol or a family history of the condition, it is important to have regular cholesterol screenings. These screenings can help detect high cholesterol levels early on, allowing for timely intervention and management.
The first cholesterol screening should occur between the ages of 9 and 11. For individuals without risk factors, subsequent screenings should be done every five years. However, if you experience symptoms of high cholesterol, it is crucial to seek medical attention regardless of your screening schedule.
Some common symptoms of high cholesterol include pain while walking, numbness in the legs and feet, and pale nails. These symptoms may indicate a buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can be serious and require immediate medical evaluation.
By staying proactive and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can ensure that high cholesterol is detected and managed effectively, reducing the risk of complications such as heart disease and stroke. Regular check-ups and cholesterol screenings are essential components of maintaining optimal heart health.
Cholesterol Screening Recommendations:
| Age | Screening Frequency |
| 9-11 years | First screening |
| 12-25 years | Every 5 years for individuals without risk factors |
| 26 years and older | Every 5 years for individuals without risk factors |
| Individuals with risk factors | As recommended by healthcare provider |
Importance of Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection of high cholesterol is crucial for preventing the development of heart disease and other related complications. By recognizing and managing high cholesterol levels through lifestyle changes and medication, you can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Regular check-ups and cholesterol screenings play a vital role in early detection. These screenings help identify high cholesterol levels, allowing you to take proactive steps in managing your cholesterol and preventing further health issues.
“Early detection is key in tackling high cholesterol and its associated risks. By identifying elevated cholesterol levels early on, individuals can implement necessary lifestyle changes and receive appropriate medical interventions to manage their cholesterol effectively.”
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to heart disease. It is important to prioritize your health and take steps to manage your cholesterol levels. This may include adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, such as maintaining a balanced diet low in saturated fats, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Remember, managing your cholesterol levels is a lifelong commitment. Regular monitoring, in combination with healthy habits, can help you lead a heart-healthy life.
| Benefits of Early Detection and Prevention |
| 1. Reduced Risk of Heart Disease |
| 2. Lower Chance of Developing Complications |
| 3. Better Control over Cholesterol Levels |
| 4. Improved Overall Cardiovascular Health |
Lifestyle Tips for Maintaining Healthy Cholesterol Levels
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial in maintaining optimal cholesterol levels and promoting overall well-being. By incorporating the following tips into your daily routine, you can effectively manage your cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of high cholesterol-related complications.
1. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity is important for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, per week. Exercise helps increase HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol) while reducing LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) and triglyceride levels. It also promotes overall cardiovascular health and strengthens the heart muscle.
2. Balanced Diet
Follow a balanced diet that focuses on whole, natural foods. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals. Avoid or minimize saturated and trans fats, as they can increase LDL cholesterol levels. Opt for healthier sources of fats, such as nuts, seeds, and avocados. Consider incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna) and walnuts, as they can contribute to healthier cholesterol levels.
3. Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Smoking damages blood vessels and lowers HDL cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Quitting smoking can have a significant positive impact on your cholesterol levels and overall health. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can raise triglyceride levels and contribute to high cholesterol. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation as recommended by health guidelines.
4. Stress Management
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on cholesterol levels. Implement stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that help you relax and unwind. Prioritizing self-care and finding healthy outlets for stress can help in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
“By incorporating regular exercise, a balanced diet, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress, you can maintain healthy cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of high cholesterol-related complications.”
By incorporating these lifestyle tips into your daily routine, you can maintain healthy cholesterol levels and promote optimal heart health. Remember, small changes can lead to significant improvements in your overall well-being.
| Eating Habits | Exercise | Smoking and Alcohol | Stress Management |
| Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your diet. | Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. | Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels. | Practice stress management techniques such as meditation and deep breathing exercises. |
| Avoid or minimize saturated and trans fats. | Include strength training exercises to build muscle. | Quit smoking to improve cholesterol levels. | Prioritize self-care and engage in activities that help you relax. |
| Choose healthier sources of fats, such as nuts and avocados. | Stay physically active throughout the day, such as taking regular breaks from sitting. | Limit alcohol consumption to recommended guidelines. | Find healthy outlets for stress, such as hobbies or spending time with loved ones. |
Blueprint for a Healthy Heart
END
This path to recovery was not just about lowering his cholesterol but about redefining his priorities. Vikram’s journey from neglect to awareness transformed him into a role model for his daughter, showing her the value of health and resilience. Together, they explored new cuisines that were both nutritious and delicious, and weekend walks became adventures in nature they both cherished.
Vikram’s story is a poignant reminder that success is not just measured by the monuments we build or the accolades we receive but by the care we take of our health and well-being. It challenges us to ask: Are we building a foundation for a healthy future, or are we ignoring the blueprint of our body’s needs?
Conclusion
Managing high cholesterol is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart and overall well-being. By recognizing the symptoms early on and taking proactive steps, you can effectively manage high cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. It is important to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management. Moreover, regular check-ups and adherence to prescribed treatments are key to successful cholesterol management.
By making sustainable lifestyle changes, such as consuming a diet low in saturated fats and high in fiber, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, you can improve your cholesterol levels and enhance your overall cardiovascular health. These lifestyle modifications play a vital role in reducing the risk of high cholesterol-related complications.
In conclusion, taking charge of your cholesterol health through a healthy lifestyle and regular monitoring is essential. With awareness, determination, and support from healthcare professionals, you can successfully manage high cholesterol and protect your heart for a lifetime. Remember, your commitment to a heart-healthy lifestyle is the key to maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and leading a long and fulfilling life.
Key Takeaways:
- High cholesterol can increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Symptoms of high cholesterol include numbness in the legs and feet, pale nails, and signs of peripheral arterial disease.
- Early recognition of high cholesterol symptoms is vital for taking steps to lower cholesterol levels.
- Regular cholesterol screenings and maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle are essential preventive measures.
- Consult a healthcare professional if you experience symptoms or have risk factors for high cholesterol.
Q: What are the risk factors for high cholesterol?
A: Risk factors for high cholesterol include high blood pressure, family history of high cholesterol, high LDL levels, and diet high in saturated and trans fats.
Q: What are the symptoms of high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol typically doesn’t cause any symptoms. Symptoms of cholesterol-related conditions such as atherosclerosis and heart disease may include chest pain, shortness of breath, and leg pain while walking.
Q: How does high cholesterol affect heart disease?
A: High cholesterol can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, increasing the risk for heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
Q: What is LDL and HDL cholesterol?
A: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol is often referred to as “bad cholesterol” as it contributes to plaque buildup in the arteries. HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol is known as “good cholesterol” as it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Q: How is high cholesterol diagnosed?
A: High cholesterol is diagnosed through a blood test to measure the levels of cholesterol, including LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol.
Q: What are the signs of artery disease related to high cholesterol?
A: Signs of artery disease linked to high cholesterol may include chest pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, and poor circulation in the legs. These symptoms can indicate reduced blood flow due to narrowed or blocked arteries.
Q: Can you have high cholesterol without any symptoms?
A: Yes, high cholesterol typically doesn’t cause any symptoms. It is important to get regular check-ups and blood tests to monitor cholesterol levels and assess the risk for heart disease.
Q: How can I tell if my cholesterol levels are high?
A: You can tell if your cholesterol levels are high through a blood test that measures the levels of LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol in your bloodstream. Your healthcare provider can help interpret the results and assess your risk for heart disease.
Q: What health problems can high cholesterol lead to?
A: High cholesterol can lead to atherosclerosis, which increases the risk for heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. It can also cause nerve damage, kidney problems, and peripheral artery disease.
Q: Are there any symptoms of heart disease related to high cholesterol?
A: Symptoms of heart disease related to high cholesterol may include chest pain, shortness of breath, and discomfort in the arms, shoulders, and jaw. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms.
Q: What are the symptoms of high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol rarely has noticeable symptoms. The only way to detect it is through a blood test.
Q: What are the signs of high cholesterol?
A: Signs of high cholesterol can include chest pain, heart attacks, and strokes. However, these are more related to the complications of high cholesterol.
Q: How do I know if I have high cholesterol?
A: You can only know if you have high cholesterol through a blood test. Consulting your healthcare provider for a lipid profile test can provide accurate information about your cholesterol levels.
Q: What is the significance of “good cholesterol” and “bad cholesterol”?
A: “Good cholesterol” (HDL) helps remove “bad cholesterol” (LDL) from the bloodstream. Maintaining a healthy balance between the two is critical for reducing the risk of heart diseases.
Q: Can high cholesterol cause noticeable symptoms?
A: High cholesterol doesn’t typically cause symptoms that can be felt. Instead, it silently affects the arteries, leading to a condition called atherosclerosis, which can eventually result in heart-related issues.
Q: What are the potential complications of high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaque in the arteries, which increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. It is also linked to high blood pressure.
Q: How can I address high cholesterol?
A: A healthier lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and potentially medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider, can help manage high cholesterol levels.
Q: What are the factors that can contribute to high cholesterol levels?
A: Factors such as diet, weight, physical activity, and family history can impact cholesterol levels. Understanding these and making necessary lifestyle changes can help manage high cholesterol.
Q: What is the connection between high cholesterol and heart disease?
A: High cholesterol is a significant risk factor for heart disease. It can contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries, leading to various heart-related complications.
Q: Can high cholesterol be managed without medication?
A: For some individuals, lifestyle changes alone can help manage high cholesterol levels. However, in some cases, medications may be necessary to adequately control cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart diseases.
Q: What are the symptoms of high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol usually doesn’t cause any symptoms, which is why it’s important to get regular blood tests to check your cholesterol levels.
Q: How is high cholesterol diagnosed?
A: High cholesterol is diagnosed through a blood test called a lipid panel. This test measures your cholesterol levels and helps in identifying if they are within the healthy range.
Q: What are the signs and symptoms of high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol doesn’t usually have any obvious signs or symptoms. However, it can lead to serious health issues if left untreated, so it’s essential to monitor your cholesterol levels regularly.
Q: What is the difference between “bad cholesterol” and “good cholesterol”?
A: Cholesterol is a waxy substance that is carried through the bloodstream by lipoproteins. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” as it can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is known as “good cholesterol” since it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the arteries.
Q: Can high cholesterol cause plaque buildup in the arteries?
A: Yes, high cholesterol can contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow and lead to serious health complications such as heart disease and stroke.
Q: How can you tell if you have high cholesterol without symptoms?
A: The only way to know for sure if you have high cholesterol is by getting a blood test. Talk to your healthcare provider about getting regular cholesterol screenings to monitor your levels.
Q: Can high cholesterol put you at risk for heart disease?
A: Yes, high cholesterol is a significant risk factor for heart disease. It can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and other cardiovascular issues.
Q: What role does diet play in managing cholesterol levels?
A: A diet high in saturated fats can contribute to high cholesterol levels. To manage your cholesterol, focus on a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Q: Can you have high cholesterol even if you’re not overweight?
A: Yes, high cholesterol can affect individuals of any weight. It is essential to monitor cholesterol levels through blood tests, regardless of weight, to ensure overall heart health.
Q: What are the implications of having high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. It’s crucial to work with a healthcare provider to manage and lower high cholesterol levels for long-term health.
