
Introduction
If you think of a heart attack, you may imagine someone clutching their chest in pain. But did you know that heart attacks can also occur silently, without any noticeable symptoms? These silent heart attacks can be just as dangerous as those with obvious signs, and it’s important to understand their symptoms, causes, and risk factors.
Can a heart attack strike silently, like a thief in the night? If you think of a heart attack, you may imagine someone clutching their chest in pain. But did you know that heart attacks can also occur without any noticeable symptoms?🤔 This might sound surprising, but silent heart attacks are a real and often unrecognized danger, especially among busy professionals like you.
Hello to all the hardworking Indian professionals in your 30s, 40s, and 50s! This blog is your guide to understanding the hidden world of silent heart attacks. In India, where heart disease is a leading cause of death, with nearly 54% of adults aged 30-70 years having high cholesterol, being aware of this silent threat is crucial.
We’ll explore what silent heart attacks are, how they differ from typical heart attacks, and why they can occur without the classic symptoms of chest pain or shortness of breath. Despite their stealthy nature, silent heart attacks can cause significant damage to the heart muscle, making awareness and prevention key.
Join us as we navigate through the silent alleys of heart health, uncovering the signs and risk factors of these covert heart attacks. Let’s empower ourselves with knowledge and proactive steps to protect our hearts silently but effectively! ❤️
Silent Battles, Silent Warnings: A Health Verdict for Karan
Part – 1
In the pulsating heart of Mumbai, where the rhythm of local trains and the ceaseless chatter of the crowd define life, Karan, a seasoned lawyer, fought his battles in the courtroom with unmatched zeal. His life was a series of intense negotiations, late-night case studies, and victories that were celebrated more in solitude than with company. Karan, a bachelor living with the shadow of his achievements as his only companion, believed in the invincibility of his will and body alike.
Despite his sharp mind and keen emotional intelligence that made him a formidable force in legal circles, Karan’s understanding of health was ironically superficial. He lived in a mental frame that equated physical discomfort with temporary setbacks, ones that could be brushed off with over-the-counter remedies or ignored with a stronger focus on work.
Symptoms and Signs of Silent Heart Attacks
Silent heart attacks may present with subtle or nonspecific symptoms, which can often be overlooked or attributed to other causes. Some common symptoms of silent heart attacks include:
- Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired or lacking energy
- Discomfort or muscle spasm: Experiencing an unusual sensation in the back or chest, often described as discomfort or muscle spasm
- Indigestion: Feeling persistent discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, similar to indigestion
- Nausea: Experiencing a feeling of queasiness or an urge to vomit
- Decreased exercise tolerance: Finding it challenging to engage in physical activity without feeling excessively tired or experiencing chest discomfort
These symptoms may vary from person to person and can be nonspecific, meaning they may not always be immediately recognized as indicators of a heart attack. As a result, silent heart attacks often go unnoticed or are misattributed to other conditions, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect you may have had a silent heart attack, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital in minimizing the potential damage to your heart and reducing the risk of future complications.
| Symptom | Description |
| Fatigue | Excessive tiredness or lack of energy |
| Discomfort or muscle spasm | Unusual sensation in the back or chest, described as discomfort or muscle spasm |
| Indigestion | Persistent discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, similar to indigestion |
| Nausea | Feeling of queasiness or an urge to vomit |
| Decreased exercise tolerance | Challenges engaging in physical activity without excessive tiredness or chest discomfort |
Risk Factors for Silent Heart Attacks
Understanding the risk factors associated with silent heart attacks is crucial for detecting and preventing these potentially life-threatening events. These risk factors are similar to those for heart attacks with symptoms, placing individuals at a higher risk of experiencing a silent heart attack. By being aware of these risk factors, you can take proactive steps to reduce your chances of a silent heart attack.
Common Risk Factors for Silent Heart Attacks
1. Age: Advanced age increases the risk of silent heart attacks.
2. Diabetes: People with diabetes have a higher risk of silent heart attacks.
3. Excess Weight: Obesity and being overweight contribute to the risk of silent heart attacks.
4. Family History of Heart Disease: Having a family history of heart disease increases the risk of silent heart attacks.
5. High Blood Pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure is a significant risk factor for silent heart attacks.
6. High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood can increase the risk of silent heart attacks.
7. Lack of Exercise: Leading a sedentary lifestyle without regular physical activity raises the risk of silent heart attacks.
8. Prior Heart Attack: A history of a previous heart attack increases the risk of silent heart attacks.
9. Tobacco Use: Smoking and tobacco use significantly elevate the risk of silent heart attacks.
By addressing these risk factors, you can lower your chances of experiencing a silent heart attack and improve your heart health overall.
In addition to addressing the risk factors, several lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk of silent heart attacks. These include:
- Adopting a healthy diet that is low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Managing diabetes and hypertension through medication, if necessary, and regular monitoring.
| Risk Factors | Action |
| Age | Monitor your heart health regularly as you age. |
| Diabetes | Closely manage your blood sugar levels with medication and a healthy lifestyle. |
| Excess Weight | Adopt a balanced diet and engage in regular physical exercise to maintain a healthy weight. |
| Family History of Heart Disease | Inform your healthcare provider about your family history and undergo regular cardiac screenings. |
| High Blood Pressure | Monitor your blood pressure regularly, take prescribed medications, and make lifestyle changes to manage hypertension. |
| High Cholesterol | Control your cholesterol levels through a healthy diet, exercise, and medication if necessary. |
| Lack of Exercise | Incorporate regular physical activity into your daily routine, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise every week. |
| Prior Heart Attack | Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for post-heart attack care, including medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups. |
| Tobacco Use | Seek help to quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke. |
By addressing these risk factors and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can significantly reduce your chances of a silent heart attack and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
Silent Battles, Silent Warnings: A Health Verdict for Karan
Part – 2
The consequence of his relentless pace and disregard for health came stealthily, mirroring the silent predators of the night. One ordinary evening, after a particularly grueling case, Karan felt an unusual fatigue envelop him—a weariness so profound it seemed to seep into his bones. Brushing it off as the toll of his hard work, he gave it no further thought.
Karan’s darkest moment, however, was not marked by dramatic signs but by its very lack of them. It was during a routine health check-up, prompted more by a new firm policy than personal concern, that the truth ambushed him. Tests revealed he had experienced a silent heart attack, a revelation that left him reeling. The absence of symptoms had given him a false sense of security, masking the danger that had lurked within.
Confronted with the reality of his vulnerability, Karan found himself at a crossroads. Dr. Ayesha, the cardiologist who became his guide in this uncharted territory, explained the gravity of silent heart attacks and the imperative changes needed in his lifestyle. It was a wake-up call that challenged the very foundation of his beliefs about health and strength.
Diagnosis of Silent Heart Attacks
Diagnosing a silent heart attack can be challenging, as there are no specific tests to determine the potential for having one. However, if risk factors are present, a healthcare provider may evaluate and treat these risks to reduce the chances of a silent heart attack.
Imaging tests such as electrocardiograms (ECGs or EKGs) or echocardiograms are typically used to identify signs of a silent heart attack. These tests can reveal abnormalities in the heart’s electrical activity or structure.
If you suspect you have had a silent heart attack, it is important to discuss your symptoms and medical history with your healthcare provider to determine if further tests are needed.
| Diagnostic Tests for Silent Heart Attacks | Description |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) | An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and can detect abnormal heart rhythms or patterns that may indicate a silent heart attack. |
| Echocardiogram | An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create images of the heart’s structure and can help identify any abnormalities or damage caused by a silent heart attack. |
Silent ST – T changes: electrocardiographic (ECG) ST-T changes without other manifestations of coronary heart disease.
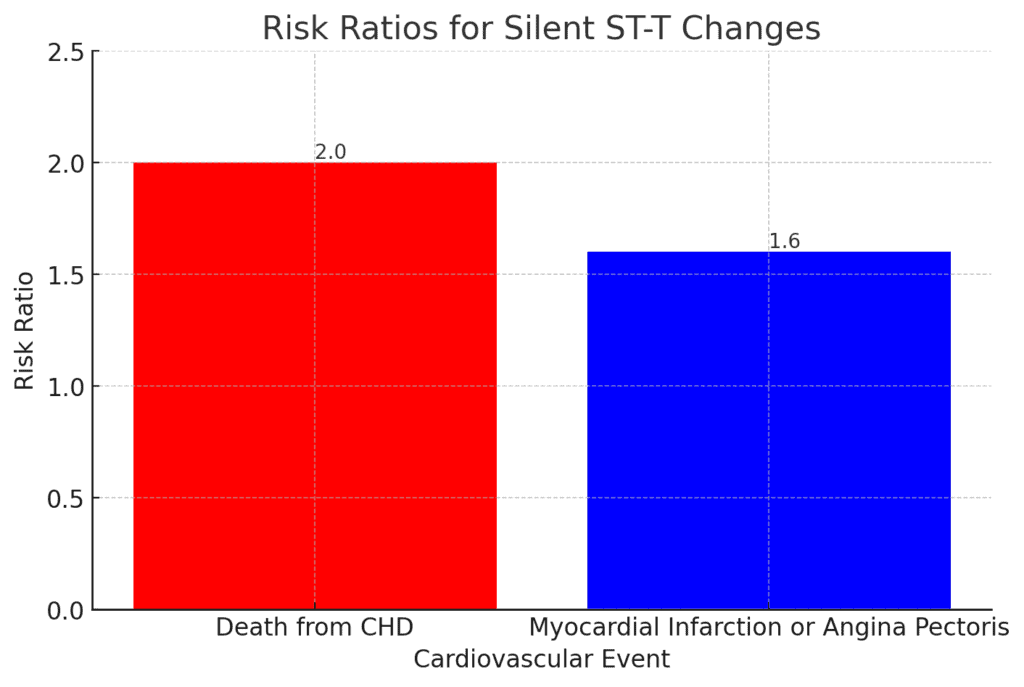
The visualization above illustrates the risk ratios associated with silent ST-T changes, indicating a significant increase in the risk of death from coronary heart disease (CHD) and the occurrence of myocardial infarction. Specifically, there is a
2.0-fold increase in the risk of death from CHD and a
1.6-fold increase in the risk of experiencing a myocardial infarction or angina pectoris for individuals with silent ST-T changes compared to those without these changes.
This emphasizes the potential danger of silent ST-T changes as indicators of underlying heart conditions.
Treatment and Management of Silent Heart Attacks
Treatment and management of silent heart attacks focus on reducing the risk of future heart attacks and complications. This involves adopting a holistic approach that combines lifestyle changes and medical interventions.
Lifestyle Changes

One of the key aspects of managing silent heart attacks is making lifestyle modifications. These changes can significantly reduce the risk of future heart attacks and promote overall heart health. Here are some lifestyle recommendations:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet: Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your daily meals. Limit the intake of processed foods, saturated fats, and sodium.
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized exercise recommendations.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease. Seek support from healthcare professionals or support groups to quit smoking effectively.
- Managing underlying conditions: If you have diabetes or hypertension, it is essential to keep these conditions under control. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations, take prescribed medications, monitor your blood sugar and blood pressure levels diligently.
Medications
In addition to lifestyle changes, medications play a crucial role in preventing future heart attacks. Your healthcare provider may prescribe certain medications to lower the risk of silent heart attacks. These may include:
- Aspirin: Aspirin helps prevent blood clots and reduces the risk of heart attack. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any aspirin regimen.
- Statins: Statins are cholesterol-lowering medications that can decrease the buildup of plaque in the arteries, reducing the risk of heart attacks.
- Beta-blockers: Beta-blockers help lower blood pressure and heart rate, reducing the workload on the heart.
- Antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications: These medications prevent the formation of blood clots and reduce the risk of future heart attacks.
It is crucial to follow the recommended treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider. Take medications as directed and undergo regular check-ups to monitor your heart health and adjust the treatment if necessary. Compliance with the treatment plan along with lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of further damage to the heart muscle and prevent future heart attacks.
| Treatment and Management Strategies | Benefits |
| Lifestyle changes (healthy diet, exercise, smoking cessation) | – Reduces the risk of future heart attacks- Promotes overall heart health- Helps manage underlying conditions |
| Medications (aspirin, statins, beta-blockers, antiplatelet/anticoagulant medications) | – Lowers the risk of silent heart attacks- Prevents blood clots and reduces plaque buildup- Controls blood pressure and heart rate- Reduces the risk of further heart damage |
Outlook and Complications of Silent Heart Attacks
The prognosis for individuals who have had a silent heart attack is similar to those who have experienced heart attacks with symptoms. However, silent heart attacks pose unique challenges in terms of early detection and timely treatment. Recognizing the complications associated with silent heart attacks is crucial in order to mitigate the risks and improve overall outcomes.
Complications of Silent Heart Attacks
Silent heart attacks can lead to various complications that can significantly impact an individual’s health and well-being. The most common complications include:
- Another Heart Attack: Individuals who have experienced a silent heart attack are at an increased risk of having another heart attack in the future.
- Heart Failure: Silent heart attacks can weaken the heart muscle over time, leading to heart failure, a condition where the heart fails to pump blood effectively.
- Stroke: Silent heart attacks are associated with a higher risk of stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted.
- Sudden Death: In some cases, silent heart attacks can result in sudden death, especially if left untreated or undiagnosed.
Improving Prognosis and Reducing Complications
While the complications of silent heart attacks can be serious, there are measures individuals can take to improve their long-term prognosis and reduce the risk of complications:
- Regular Monitoring: It is important to regularly monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels to identify any abnormalities early on. This can help healthcare providers assess the risk of future heart events and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial to reduce the risk of complications. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Prompt Reporting of Symptoms: Any unusual symptoms, such as chest discomfort, shortness of breath, or fatigue, should be promptly reported to a healthcare provider. Early detection and timely intervention are key to preventing further damage to the heart and reducing the risk of complications.
By taking proactive steps to prioritize heart health and adhering to recommended treatments and lifestyle changes, individuals can improve their outlook and reduce the impact of silent heart attacks on their overall well-being.
| Complication | Risk |
| Another Heart Attack | Increased risk |
| Heart Failure | Elevated risk |
| Stroke | Higher risk |
| Sudden Death | Potential risk |
Silent Heart Attacks and Women
Silent heart attacks may occur more frequently in women than in men. Recognizing the symptoms of silent heart attacks in women can be challenging, as they may present with atypical or subtle symptoms. It is crucial for women to be aware of the signs and symptoms of heart attacks and advocate for themselves during medical appointments to ensure appropriate testing and treatment. This is especially important due to disparities in how healthcare professionals recognize and treat heart attack symptoms in women.
Understanding Silent Heart Attacks in Women
Silent heart attacks, also known as silent ischemia, are heart attacks that occur without noticeable symptoms or with symptoms that are not recognized as a heart attack. While the classic symptoms of a heart attack, such as chest pain and shortness of breath, are often associated with men, women may experience different or more subtle symptoms.
- Fatigue: Women may experience unexplained fatigue or a constant feeling of tiredness that is not relieved by rest.
- Discomfort or pain: Some women may feel discomfort, pressure, or aching in the back, chest, jaw, or arm. This discomfort may be mistaken for muscle pain or indigestion.
- Nausea or indigestion: Women may experience feelings of nausea, indigestion, or heartburn, which can be misinterpreted as digestive issues.
- Shortness of breath: Women may have difficulty catching their breath or experience shortness of breath during physical exertion or rest.
- Sweating: Women may notice unexplained sweating, often described as a cold sweat.
- Anxiety or lightheadedness: Some women may feel anxious, dizzy, or lightheaded without an obvious cause.
It is important for women to be vigilant about their heart health and pay attention to any unusual symptoms they may experience. By being proactive and informed, women can help ensure that their silent heart attacks are diagnosed and treated promptly.
“Silent heart attacks in women can be difficult to detect, but it is important for women to trust their instincts and seek medical attention if they suspect they may be having heart problems. Women should not hesitate to speak up and advocate for themselves during medical appointments to ensure they receive the appropriate care and testing.” – Dr. Biprajit Parbat
Reducing the Risk of Silent Heart Attacks in Women
There are several steps women can take to reduce their risk of silent heart attacks:
- Manage risk factors: It is crucial for women to manage and control risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity. Regular check-ups, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications can help maintain optimal heart health.
- Adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle: Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco use can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and silent heart attacks.
- Know the warning signs: Educating oneself about the common symptoms of heart attacks and seeking medical attention immediately if any symptoms are present can potentially save lives.
- Monitor hormonal changes: Women should be aware of the impact hormonal changes, such as menopause, can have on heart health. Discussing these changes with a healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate management strategies.
By taking proactive steps to prioritize heart health, women can reduce their risk of silent heart attacks and improve their overall well-being. It is essential for women to be advocates for their own health and seek necessary medical care and support.
| Risk Factor | Prevalence in Silent Heart Attacks | Prevalence in Heart Attacks with Symptoms |
| High blood pressure | 50% | 60% |
| Diabetes | 40% | 30% |
| Obesity | 35% | 40% |
| High cholesterol | 30% | 40% |
| Cigarette smoking | 25% | 30% |
Causes of Silent Heart Attacks
Silent heart attacks, also known as silent myocardial infarctions, occur when there is a lack of blood flow to the heart. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Atherosclerotic heart disease: This is the most common cause of silent heart attacks. It occurs when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, leading to the formation of blood clots that can block blood flow to the heart.
- Coronary artery spasm: In some cases, a severe spasm or tightening of a coronary artery can occur, restricting blood flow to the heart and causing a silent heart attack.
- Exposure to extreme cold: Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can constrict blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the heart.
- Stress or pain: Emotional or physical stress and severe pain can trigger a silent heart attack by increasing the workload on the heart and reducing blood flow.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and contributes to the formation of plaque, increasing the risk of silent heart attacks.
- Drug use: Certain drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines, can constrict blood vessels and disrupt normal heart function, leading to silent heart attacks.
Although these factors are known to contribute to silent heart attacks, further research is needed to fully understand all the underlying causes and mechanisms involved.
Silent Battles, Silent Warnings: A Health Verdict for Karan
END
Emboldened by Dr. Ayesha’s counsel and his own resolve to change, Karan embarked on a journey of transformation. He adopted a balanced diet, integrated regular exercise into his daily routine, and learned stress management techniques. More importantly, he began to listen to his body, recognizing the importance of rest and medical check-ups.
Karan’s path to recovery was not just about physical health but about a profound shift in perspective. He became an advocate for health awareness in his professional circle, sharing his story to dispel myths about silent heart attacks and the illusion of invulnerability. His experience became a testament to the silent dangers that busy professionals often ignore, emphasizing the need for regular health screenings and a balanced lifestyle.
Karan’s story is a reminder that silent heart attacks are the unseen threats in our midst, striking without warning. It prompts us to ask: Are we listening to the silent alarms of our body, or are we waiting for a wake-up call that might come too late?
Prevention of Silent Heart Attacks
To prevent silent heart attacks and reduce the risk of future cardiac events, it is essential to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle and manage potential risk factors. By making positive changes in your daily habits, you can prioritize your heart health and lower the chances of experiencing a silent heart attack.
1. Maintain a Balanced Diet
Start by consuming a nutritious diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. Incorporate foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals to support heart health.
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Be physically active on a regular basis. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous intensity aerobic exercise per week. Additionally, include strength training exercises to improve your overall fitness level and support cardiovascular health.
3. Manage Stress Levels
Stress can contribute to heart problems. Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in activities you enjoy. Taking time for self-care and relaxation can help reduce stress and promote a healthier heart.
4. Avoid Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of heart disease and silent heart attacks. If you are a smoker, take steps to quit. Seek support from healthcare professionals, join smoking cessation programs, and utilize nicotine replacement therapies to help you successfully quit smoking.
5. Control Underlying Conditions
If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, it is crucial to manage these conditions effectively. Strictly follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations, take prescribed medications regularly, monitor your blood glucose levels, and maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of silent heart attacks.
6. Regularly Monitor Risk Factors
Regularly check your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other risk factors associated with heart disease. Maintaining optimal levels and addressing any abnormalities promptly can significantly reduce the risk of silent heart attacks. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your heart health.
Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any unusual symptoms or suspect you may have had a silent heart attack, do not hesitate to seek immediate medical attention. Fast diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for preventing further damage to the heart and reducing the risk of complications.
| Preventive Measures | Benefits |
| Maintaining a balanced diet | Supports heart health, provides essential nutrients |
| Engaging in regular physical activity | Improves cardiovascular fitness, reduces the risk of heart disease |
| Managing stress levels | Reduces the impact of stress on the heart |
| Avoiding smoking | Reduces the risk of heart disease and silent heart attacks |
| Controlling underlying conditions | Manages diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol |
| Regularly monitoring risk factors | Allows for timely intervention and risk reduction |
Conclusion
Overall, silent heart attacks can occur without noticeable symptoms or with symptoms that are not immediately recognized as a heart attack. These silent heart attacks are associated with a blockage of blood flow to the heart, which can lead to damage in the heart muscle. The risk factors for silent heart attacks are similar to those for heart attacks with symptoms, including age, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and tobacco use. It is crucial to detect and treat silent heart attacks early to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
The key to reducing the risk of silent heart attacks lies in adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions. By prioritizing regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, you can lower the risk of silent heart attacks. Additionally, it is important to stay vigilant and be aware of the signs and symptoms of heart attacks. If you suspect you may have had a silent heart attack, seeking medical attention promptly is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In summary, silent heart attacks without artery blockage are a serious health concern, as they can go unnoticed and lead to long-term complications. By taking proactive steps to prioritize heart health, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors, you can significantly reduce the risk of silent heart attacks and improve your overall well-being. Remember, early detection and treatment are crucial in mitigating the impact of silent heart attacks and preventing future heart events.
Key Takeaways:
- Silent heart attacks occur without noticeable symptoms or with symptoms that are not recognized as a heart attack.
- They involve a blockage of blood flow to the heart and can cause damage to the heart muscle.
- Risk factors for silent heart attacks are similar to those for heart attacks with symptoms.
- Imaging tests like electrocardiograms or echocardiograms are used to diagnose silent heart attacks.
- Seek medical attention if you suspect you may have had a silent heart attack.
Q: What is a silent heart attack?
A: A silent heart attack is a type of heart attack that occurs with minimal or no symptoms. It is often unnoticed and can go undetected, which makes it particularly dangerous.
Q: What are the risks associated with a silent heart attack?
A: The risks of a silent heart attack are similar to those of a typical heart attack, including the possibility of developing coronary artery disease and an increased risk of subsequent heart attacks.
Q: What are the risk factors for a silent heart attack?
A: The risk factors for a silent heart attack are the same as those for a traditional heart attack, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and a family history of heart disease.
Q: What are the signs and symptoms of a silent heart attack?
A: Unlike a typical heart attack, a silent heart attack may not present obvious symptoms. However, some people may experience mild symptoms such as fatigue, discomfort in the chest, or shortness of breath.
Q: How can one identify a silent heart attack?
A: Identifying a silent heart attack can be challenging, as it may not present noticeable symptoms. It often goes undetected until further medical tests reveal evidence of prior heart muscle damage.
Q: What should I do if I suspect I may have had a silent heart attack?
A: If you suspect you may have had a silent heart attack, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Even if you did not experience obvious symptoms, it is crucial to have a healthcare professional evaluate your condition.
Q: Are there any specific preventive measures for silent heart attacks?
A: Preventive measures for silent heart attacks are similar to those for traditional heart attacks and involve lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, and managing risk factors like high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Q: Who is at a higher risk of experiencing a silent heart attack?
A: People with a history of coronary artery disease, those with diabetes, and individuals with a higher risk of heart disease are more likely to experience a silent heart attack. It’s essential for these individuals to be vigilant about their heart health.
Q: What is “Go Red for Women” campaign related to silent heart attacks?
A: The “Go Red for Women” campaign aims to raise awareness about heart disease in women, including the risk of silent heart attacks. It encourages women to take charge of their heart health and become proactive in recognizing and preventing heart issues.
Q: Can a silent heart attack lead to a traditional heart attack later on?
A: Yes, a silent heart attack can increase the risk of experiencing a traditional heart attack weeks, months, or even years later. It is crucial to address any potential heart health concerns promptly to prevent further complications.
Q: What is a silent heart attack?
A: A silent heart attack is a heart attack that has mild or no symptoms, making it hard for individuals to know they have had one. It is also known as a silent myocardial infarction.
Q: What are the risks associated with silent heart attacks?
A: Silent heart attacks can increase the risk of having a more severe heart attack later on. They can also lead to complications such as heart failure or sudden cardiac arrest.
Q: How does a silent heart attack differ from a regular heart attack?
A: Unlike a regular heart attack, a silent heart attack may go unnoticed as there are little to no symptoms. However, it still impacts the heart muscle and increases the risk of future cardiovascular issues.
Q: What are the signs of a silent heart attack?
A: The signs of a silent heart attack may be subtle and include fatigue, mild chest discomfort, or shortness of breath. Some individuals may not notice any symptoms at all.
Q: How can one prevent a silent heart attack?
A: It’s essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, attend regular check-ups, and manage risk factors such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes. Making smart dietary choices and staying physically active can also contribute to prevention.
Q: Are there people who have a silent heart attack and not know it?
A: Yes, many individuals who experience a silent heart attack do not realize it at the time and may only become aware of it weeks or even months later during medical tests or evaluations.
Q: What is the connection between silent heart attacks and coronary artery disease?
A: Silent heart attacks are often related to coronary artery disease, where the arteries supplying the heart with blood become narrowed or blocked, increasing the risk of a heart attack.
Q: Can a silent heart attack lead to a heart attack later on?
A: Yes, a silent heart attack can contribute to a higher risk of experiencing a more severe heart attack in the future, which is why it’s crucial to address and manage potential risk factors promptly.
Q: How are silent heart attacks associated with ischemic heart disease?
A: Ischemic heart disease is a common underlying cause of silent heart attacks. It occurs when there is a reduction in blood flow and oxygen to the heart, leading to potential damage or infarction of the heart muscle.
Q: What should one do if they suspect they may have had a silent heart attack?
A: It’s important to seek medical attention and discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional. Diagnostic tests and evaluations can help determine if a silent heart attack has occurred and what steps should be taken for management and prevention.
