Experiencing chest discomfort can be alarming and may raise concerns about your heart health. However, it’s crucial to understand that not all chest pain indicates a heart attack. In fact, chest discomfort can sometimes be attributed to muscle strain or overuse. Knowing the signs and distinguishing between a heart attack and muscle strain is essential for making informed decisions about your health.
A heart attack occurs when a blockage in an artery restricts blood flow to the heart’s muscle tissues. The pain associated with a heart attack is often described as a sensation or tightness across the chest, accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and palpitations. On the other hand, muscle strain may cause sharp, shooting, or achy pain along with tenderness in the affected area. It’s important to note that the location of the pain differs between a heart attack and muscle strain.
During a heart attack, the pain may radiate to the neck, jaw, arms, shoulders, throat, back, and upper abdominal region. In contrast, muscle strain can be felt anywhere on the body, depending on the affected muscle.
Several factors help differentiate between a heart attack and muscle strain. Cardiac chest pain can be aggravated by exercise, stress, eating, or exposure to cold air, while muscular pain typically occurs after unusual exertion or activities not performed regularly. Additionally, the duration of chest pain during a heart attack is usually a few minutes, while muscle soreness may last for a few days.
It’s important to seek immediate medical attention if you experience chest pain accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, and nausea, as these symptoms may indicate a heart attack. On the other hand, if you can pinpoint the exact location of the pain and if it intensifies with movement or specific activities, it’s more likely to be muscle strain.
Key Takeaways:
- Heart attacks are caused by a blockage in an artery, while muscle strain occurs due to overstretching or pressure on the muscles.
- Chest pain during a heart attack is accompanied by other symptoms like shortness of breath, sweating, and nausea, while muscle strain pain is mainly localized to the affected area.
- Preventing heart attacks involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and seeking prompt medical attention when necessary.
- Treating muscle strain often involves rest, ice or heat therapy, over-the-counter pain relievers, and physical therapy if necessary.
- Recognizing the signs and symptoms of both heart attacks and muscle strain can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and seek appropriate medical care.
Symptoms of Heart Attack vs. Muscle Strain
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack versus muscle strain is crucial in understanding the underlying condition and seeking appropriate medical attention. While both can cause chest discomfort, there are distinct differences between the symptoms experienced.
For a heart attack, the most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort that can feel like a sensation or tightness. This pain may also radiate to other areas of the body, such as the neck, jaw, arms, shoulders, throat, back, and upper abdominal region. Along with chest pain, other symptoms like shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, indigestion, and palpitations may also be present.
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Sensation or tightness
- Pain radiating to other areas of the body
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Indigestion
- Palpitations
On the other hand, symptoms of muscle strain mainly focus on the affected area. They may include sharp, shooting, or achy pain, along with tenderness at the site of the strain.
- Sharp, shooting, or achy pain
- Tenderness in the affected area
It is important to note that the symptoms of a heart attack can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Muscle strain pain, on the other hand, is generally less severe and can usually be managed with rest and other conservative measures.
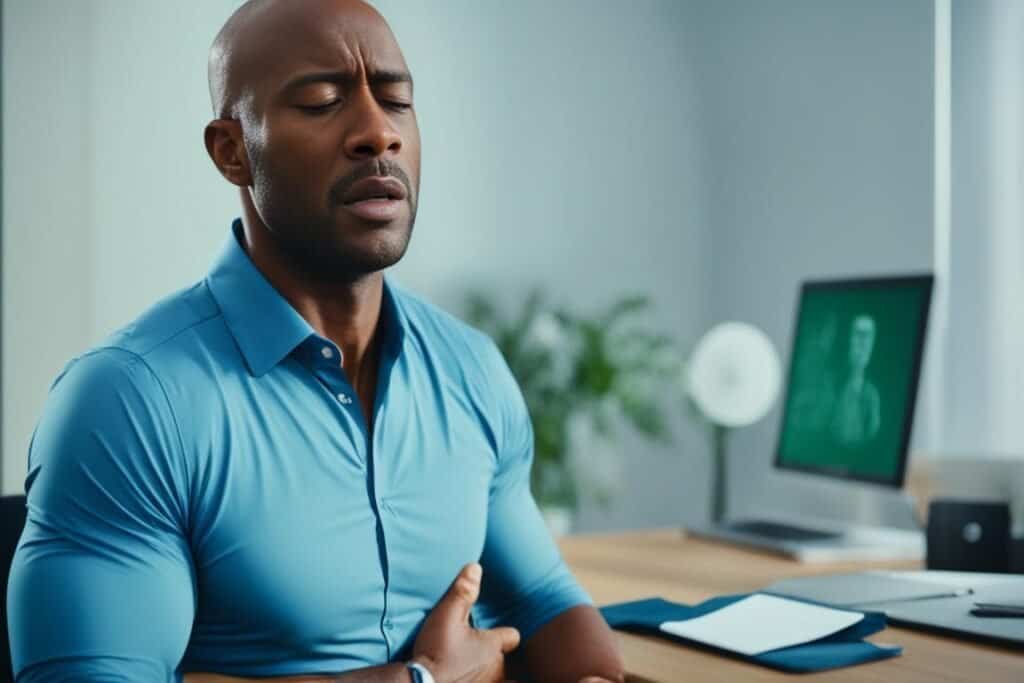

Causes of Heart Attack vs. Muscle Strain
A heart attack occurs when there is a blockage in an artery, preventing oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart’s muscle tissues. The main cause of this blockage is atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. Additionally, factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and a family history of heart disease can increase the risk of a heart attack.
On the other hand, muscle strain is caused by overstretching or excessive pressure on the muscles. This can happen during activities like sports, exercise, lifting heavy objects, or repetitive motion. Skipping warm-ups, accidents or injuries, heavy lifting with incorrect form, and sudden movements can also lead to muscle strain.
It is important to note that while a heart attack is a serious medical emergency, muscle strain is a less severe condition.
| Causes of Heart Attack | Causes of Muscle Strain |
|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis – buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries | Overstretching or excessive pressure on the muscles |
| High blood pressure | Sports, exercise, lifting heavy objects |
| High cholesterol | Repetitive motion |
| Smoking | Skipping warm-ups |
| Obesity | Accidents or injuries |
| Diabetes | Heavy lifting with incorrect form |
| Family history of heart disease | Sudden movements |
Understanding the causes of both heart attacks and muscle strains can help you take preventive measures and seek appropriate medical attention when necessary.
Treatment and Prevention of Heart Attack vs. Muscle Strain
When it comes to treating a heart attack, prompt medical intervention is crucial. The treatment typically involves a combination of medications and medical procedures. Medications such as clot-dissolving drugs are administered to restore blood flow to the heart. Pain relievers may also be prescribed to alleviate discomfort. In some cases, medical procedures like angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery may be necessary to remove blockages and restore normal blood flow.
To prevent heart attacks, adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential. Quitting smoking, following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and controlling risk factors like high blood pressure and high cholesterol are vital steps towards prevention.
On the other hand, the treatment for muscle strain focuses primarily on rest and self-care measures. Resting the affected muscles allows them to heal and recover. Applying ice or heat therapy can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers can also be used to manage discomfort. In more severe cases, physical therapy may be recommended to enhance recovery and prevent future injuries.
To prevent muscle strain, it’s important to take proactive measures. Before engaging in physical activities, warming up adequately prepares the muscles for exercise. Using proper technique and form during workouts minimizes the risk of strain. Avoiding overexertion and gradually increasing exercise intensity can also help prevent muscle strain.
Treatment and Prevention Summary:
| Treatment for Heart Attack | Treatment for Muscle Strain | |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Intervention | Medications, clot-dissolving drugs, pain relievers, angioplasty, or coronary artery bypass surgery | Rest, ice or heat therapy, over-the-counter pain relievers, physical therapy if necessary |
| Prevention | Maintain a healthy lifestyle, quit smoking, follow a balanced diet, exercise regularly, manage stress, control risk factors | Warm up before physical activities, use proper technique and form, avoid overexertion, gradually increase exercise intensity |
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a heart attack versus muscle strain is vital in understanding the proper response and seeking appropriate medical attention. Chest discomfort can be caused by both cardiac and muscular reasons, but there are distinct differences between the two.
The pain associated with a heart attack is often described as a sensation or tightness across the chest, accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, and nausea. It may also radiate to other areas of the body, such as the neck, jaw, arms, shoulders, throat, back, and upper abdominal region. On the other hand, muscle strain typically causes sharp, shooting, or achy pain in the affected area, along with tenderness.
By understanding the causes, treatment, and prevention methods for both heart attacks and muscle strains, you can make informed decisions about your health. It is important to seek prompt medical care when necessary to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. Follow a healthy lifestyle, manage risk factors, and listen to your body to reduce the likelihood of heart attacks and muscle strains.

