
Introduction
Hey there,
Take a seat; let’s have a heart-to-heart, literally. Today, we’re diving into the world of heart disease and heart health, but don’t worry, no lab coats or complicated terms here – just a friendly chat.
Imagine we’re catching up over coffee, and I’m your friendly neighborhood guide to heart disease and heart attacks. So, let’s chat about heart attacks – not in a “doom and gloom” way, but like two friends discussing life’s adventures.
Think of this as your heart’s handbook, with tips on spotting warning signs, understanding what makes your ticker tick, and how to keep it grooving happily. So, grab a virtual coffee (or tea if that’s more your style), and let’s unravel the mysteries of your heart in the most friendly and casual way possible.
Ready for a heart-to-heart chat?
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack is a medical emergency that occurs when the flow of blood to the heart is blocked or reduced. The duration of heart attack pain can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the attack. It is important to recognize the signs of a heart attack to seek immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of a heart attack may include chest pain or discomfort, pain in other areas of the upper body, shortness of breath, and other signs such as cold sweat or nausea. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent further damage to the heart muscle.
Create an abstract image that represents the duration of heart attack pain. Use bold and contrasting colors to convey the intensity of the pain. Incorporate lines and shapes that appear jagged or erratic to represent the unpredictable nature of a heart attack. Consider adding a focal point to draw the viewer’s eye, such as a bright spot or pulsing shape to represent the beating of the heart. Overall, aim to create an image that captures the urgency and severity of a heart attack

Line drawing shows rising incident of heart attack. (Source Link)
Recognizing Heart Attack Symptoms
Heart attack symptoms can vary between men and women. The most common symptom for both genders is chest pain or discomfort. However, women may also experience other symptoms such as shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, and pain in the jaw, back, or neck. It is important to pay attention to any unusual symptoms and seek medical help immediately if you suspect a heart attack. Remember, minutes matter, and fast action can save lives.
Show a person experiencing chest pain and discomfort, with their hand clenched over their heart. Their face is contorted in pain, with sweat beads on their forehead and a look of panic in their eyes. Show other subtle signs of a heart attack, such as shortness of breath or nausea, through the use of color and texture in the background. Make the image visually striking and attention-grabbing, but without being too graphic or scary.
Heartfelt Lessons from Mumbai: A ‘Dil Chahta Hai’ Tale of Health and Friendship
In the big city of Mumbai, there were two friends, Rahul and Priya, just like characters from a cool movie called “Dil Chahta Hai.” Rahul was really cool, always doing important stuff, like the heartbeat of the city. One day, he felt something weird, like a surprise in the movie.
Priya, who was smart and practical, noticed Rahul’s strange feelings weren’t just funny moments. It was like the funny parts in the movie that teach you something important. They faced lots of funny moments together, just like in the movie, but Priya knew some weren’t just for laughs.
One day, things got serious. Priya, using her smarts, understood it wasn’t just another funny scene. It was like a moment in the movie where something bad could happen. She helped Rahul, and everyone learned a big lesson. Later, they told their story to people like them, busy and grown-up. Just like ‘Dil Chahta Hai’ shows us the value of good friendships, it also teaches us to pay attention when our bodies tell us something. In life’s big story, noticing small things can be the difference between a happy twist and a bad turn. Everyone understood. “Pay attention, friends,” Priya said, “because in our life story, even funny moments can be practice for important, life-saving scenes. And so, Rahul and Priya’s story became a short, simple lesson for everyone to take care of their health and notice the little signs that can save lives.
When to Call for Help
If you experience heart attack warning signs, it is important to call emergency medical help immediately. Don’t hesitate, as time is of the essence in a heart attack situation. Calling for professional assistance is the fastest way to get lifesaving treatment and increase the chances of a positive outcome. Emergency medical services (EMS) teams are trained to respond quickly and can start treatment as soon as they arrive. They can administer necessary medications, provide resuscitation efforts if needed, and stabilize your condition on the way to the hospital.
People who arrive at the hospital with chest pain by ambulance may also receive faster treatment once they arrive. When you call for emergency medical help, the emergency responders can inform the hospital staff in advance, enabling them to be prepared for your arrival and expedite the necessary heart attack treatment. Acting swiftly and ensures a quick response time and immediate transport to the emergency room, where medical professionals can take over and provide the specialized care you need.
Causes and Risk Factors
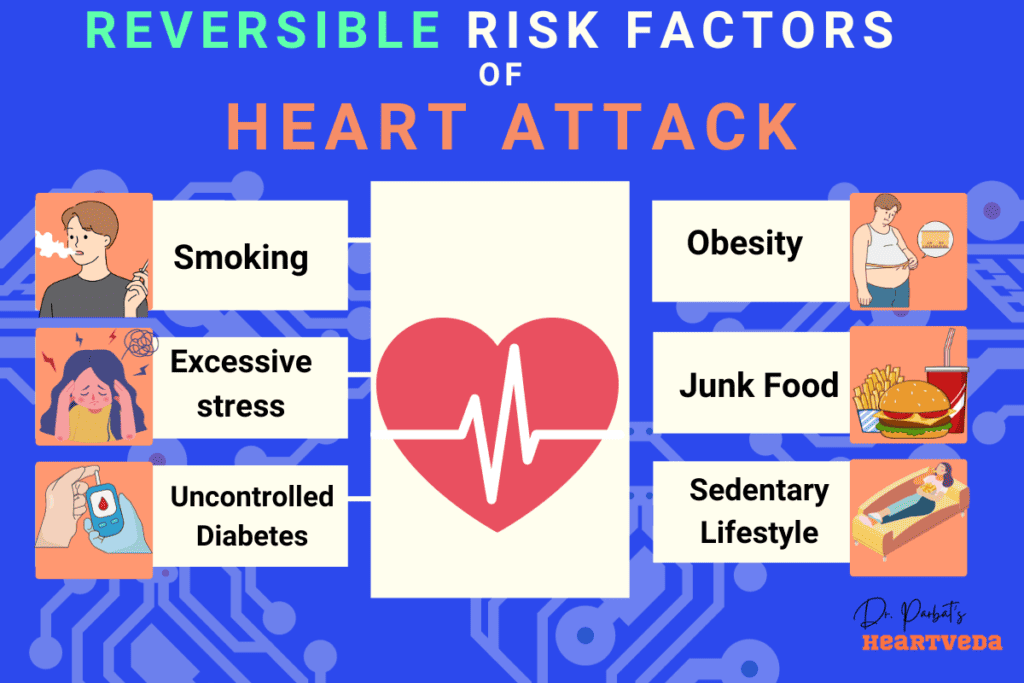
Understanding the causes and risk factors of a heart attack can help you take proactive steps to protect your heart health. The primary cause of a heart attack is coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD occurs when the arteries that supply blood to your heart become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaques made of fat and cholesterol.
In addition to CAD, other causes of heart attacks include coronary artery spasms, certain infections, and spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD).
There are several risk factors that can increase your chances of having a heart attack. These include:
Reversible factors:
- Tobacco use: Smoking and using tobacco products significantly raise your risk of heart attacks.
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure puts extra strain on your heart and arteries.
- High cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol, often known as “bad” cholesterol, can contribute to the buildup of plaques in your arteries.
- Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the waist, puts additional strain on your heart.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at higher risk for heart disease, including heart attacks.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to the development of heart disease and increase your risk of a heart attack.
- Unhealthy diet: Consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, salt, and sugar can raise your risk.
- Stress: Chronic stress can have a negative impact on your heart health.
- Drug use: Certain drugs, such as cocaine or amphetamines, can increase the risk of heart attacks.
Irreversible factors:
- Age: As you get older, your risk of heart disease, including heart attacks, increases.
- Family history: If you have close relatives who have had heart attacks, your risk may be increased.
By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with heart attacks, you can make informed choices to reduce your risk and improve your heart health.
Complications of a Heart Attack
Heart attack complications can occur as a result of heart muscle damage. These complications may include:
1. Irregular Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias)
The damage to the heart muscle caused by a heart attack can disrupt the normal electrical signals that control the heart’s rhythm. This can lead to irregular heart rhythms, which can range from mild palpitations to more serious conditions.
2. Cardiogenic Shock
Cardiogenic shock is a severe condition that occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It is a rare but life-threatening complication of a heart attack.
3. Heart Failure
Heart failure refers to the inability of the heart to effectively pump blood to the rest of the body. It can be caused by the damage caused by a heart attack.
4. Pericarditis
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the tissue surrounding the heart, called the pericardium. It can occur as a result of the heart attack or the body’s immune response to the heart muscle damage.
5. Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest is a sudden stop of the heart’s electrical activity, leading to a loss of blood flow and consciousness. It is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate medical attention.
These complications highlight the importance of prompt treatment and ongoing medical care after a heart attack. It is crucial for individuals who have experienced a heart attack to closely monitor their symptoms and follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations to minimize the risk of these complications.
Prevention and Recovery

Taking steps to prevent a heart attack is crucial, even if you have already had one. By making lifestyle changes and participating in cardiac rehabilitation, you can significantly improve your heart health and reduce the risk of future heart problems.
Adopt a healthy lifestyle:
- Quit smoking to reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall health.
- Maintain a healthy weight through a combination of regular physical activity and a balanced diet.
- Eat a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products.
- Incorporate regular physical activity into your daily routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Manage stress through practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in activities you enjoy.
Cardiac rehabilitation:
Cardiac rehabilitation programs can play a key role in your recovery after a heart attack. These programs typically include:
- Physical activity: Engage in supervised exercises that are tailored to your individual needs and abilities.
- Education and counseling: Learn about heart-healthy habits, medication management, and emotional support to help you cope with the impact of a heart attack.
Following a heart attack, it is essential to adhere to prescribed medications and incorporate positive lifestyle changes. This comprehensive approach can enhance your recovery journey, improve heart function, and reduce the risk of future heart attacks.
| Lifestyle Changes | Benefits |
| Quit smoking | Reduces the risk of heart disease and improves overall health |
| Maintain a healthy weight | Reduces strain on the heart and lowers the risk of heart disease |
| Eat a balanced diet | Provides essential nutrients and helps manage cholesterol and blood pressure |
| Engage in regular physical activity | Strengthens the heart and improves overall cardiovascular health |
| Manage stress | Reduces the risk of heart attacks and promotes emotional well-being |
Symptoms of a Heart Attack

Heart attack symptoms can manifest differently in individuals, but it is important to recognize the signs and seek immediate medical attention if they occur. The most common symptom of a heart attack is chest pain or discomfort. This pain may feel like pressure, tightness, squeezing, or aching in the chest. However, heart attack symptoms can also include:
- Pain or discomfort in the jaw, neck, back, arm, or shoulder
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling weak or light-headed
- Nausea or vomiting
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial not to ignore them. Call emergency medical services or go to the nearest emergency room immediately. Remember, minutes matter when it comes to heart attack treatment, and seeking prompt medical attention can save lives.
What to Do in Case of a Heart Attack
If you suspect a heart attack, it is crucial to call emergency medical help immediately. Time can make a significant difference in saving a life.
If you have been prescribed nitroglycerin, take it as instructed while waiting for medical help to arrive. Nitroglycerin helps relax and widen the blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart.
If recommended by a healthcare professional, take aspirin to help reduce the damage to your heart. Aspirin can prevent blood clotting and improve your chances of recovery.
If you come across someone who is unconscious and you suspect they are having a heart attack, immediately call emergency medical service. Before help arrives, check for their breathing and pulse. If there is no breathing or pulse, it is crucial to start cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) right away.
Remember, every second counts when it comes to a heart attack. Taking swift action and seeking emergency medical help should be your top priority.
| Actions to Take in Case of a Heart Attack | Explanation |
| Immediate medical attention | Immediate medical help is crucial for timely treatment. |
| Take nitroglycerin | Follow the instructions from your healthcare provider to improve blood flow to the heart. |
| Take aspirin | If recommended, aspirin can help reduce heart damage by preventing blood clotting. |
| Perform CPR | In case someone is unconscious, check for breathing and pulse. If absent, start CPR until help arrives. |

Conclusion
Understanding the signs, symptoms, and duration of a heart attack is crucial for recognizing the importance of seeking immediate medical help. A heart attack can cause varying levels of pain and discomfort, and prompt treatment is necessary to minimize damage to the heart muscle.
By recognizing the warning signs such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and pain in the jaw or upper body, individuals can take quick action and call for emergency medical assistance. It is important to remember that minutes matter when it comes to a heart attack, and seeking help promptly can save lives.
After experiencing a heart attack, recovery is a critical phase. This involves following the prescribed medications, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and participating in cardiac rehabilitation programs. By making positive lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress, individuals can improve their heart health and reduce the risk of future heart attacks.
If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of a heart attack, do not hesitate to call 911 immediately. Early intervention is crucial to ensure the best possible outcomes in terms of both pain management and overall recovery.
Key Takeaways:
- Heart attack pain duration varies depending on the individual and severity of the attack.
- Recognizing the signs of a heart attack is crucial for seeking immediate medical attention.
- Common symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain, shortness of breath, and pain in the upper body.
- Prompt treatment is necessary to prevent further heart muscle damage.
- Call emergency medical help if you experience symptoms of a heart attack.
Learn More with Our FAQs
A: Heart attack symptoms, such as chest pain or discomfort, often come on suddenly and can be severe. Other heart-related conditions may have more gradual or chronic symptoms, and it’s important to seek medical attention for any concerning symptoms.
A: Emergency treatment for a heart attack may involve medications to help dissolve a blood clot, procedures to open blocked arteries, and ongoing monitoring and support to stabilize the individual’s condition.
A: During a heart attack, the blood flow to part of the heart is blocked, leading to damage to the affected area of the heart muscle. This can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and other discomfort.
A: Yes, heart attack symptoms can vary between men and women. While men commonly experience chest pain, women may have subtle symptoms or no chest pain at all, making it important to be aware of other possible signs of a heart attack.
A: The leading cause of death in individuals with heart disease is often complications related to a heart attack, such as heart failure or cardiac arrest.
A: Sudden cardiac arrest is a condition in which the heart unexpectedly stops beating, leading to a loss of blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. While sudden cardiac arrest can be related to heart attacks, it’s important to recognize that they are separate medical emergencies with different causes and treatments.
A: If you experience symptoms of a heart attack, such as chest pain or discomfort, it’s important to seek emergency medical treatment immediately. Call for an ambulance or have someone take you to the nearest hospital.
A: A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot. This can lead to damage or death of the affected heart muscle.
A: The recovery time from a heart attack can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the heart attack. It may take weeks to months for a full recovery, and ongoing medical treatment and lifestyle changes are often necessary.
A: The duration of a heart attack can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the attack. In general, the pain or discomfort of a heart attack can last for a few minutes to several hours. It’s important to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect you’re having a heart attack.
A: Common signs of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness, and discomfort in other areas of the upper body, such as the arms, back, neck, or jaw.
A: Some heart attacks can occur suddenly without any prior warning signs(silent heart attack), but most heart attacks involve some level of discomfort or symptoms. It’s essential to be aware of the potential signs and symptoms of a heart attack and seek medical attention if you have concerns about your heart health.
A: The healing process for heart tissue after a heart attack can take several weeks. During this time, it’s important to follow medical advice, take prescribed medications, and make necessary lifestyle changes to support the healing and recovery of the heart.
A: While some heart attack symptoms may last for several hours, it’s less common for them to persist for days. However, it’s important not to dismiss any signs of a heart attack and seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of concern.
A: It’s crucial to call emergency medical service immediately if you suspect you or someone else is having a heart attack. Time is of the essence in getting emergency medical treatment, and calling for help can increase the chances of surviving a heart attack.
A: A heart attack is a medical emergency, and prompt treatment is crucial for a positive outcome. Without immediate medical attention, a heart attack can lead to severe complications and can be life-threatening. Always seek help as soon as possible.
A: Yes, the signs and symptoms of a heart attack can come and go, or they may fluctuate in intensity. Don’t dismiss the symptoms if they subside—seek immediate medical attention as this can be a sign of a heart attack.
A: Factors that can increase your risk for a heart attack include a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. It’s important to manage these risk factors to prevent a heart attack.
A: In addition to chest discomfort, men experiencing a heart attack may also have symptoms such as pain in the arms, back, neck, or jaw, as well as shortness of breath, nausea, and lightheadedness. It’s important for men to be aware of these warning signs and seek prompt medical attention if they occur.
A: Women may experience unique symptoms during a heart attack, including chest discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness, and pain in the arms, back, neck, or jaw. It’s important for women to recognize these warning signs and not dismiss them as something less serious than a heart attack.
A: Risk factors for heart disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and family history of heart disease. Managing these risk factors can help prevent heart attacks and heart disease.
A: Preventive measures for heart attacks and heart disease include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet, staying physically active, managing stress, avoiding tobacco, and getting regular check-ups to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and overall heart health..
A: A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a section of the heart muscle is blocked. This blockage is often due to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to a lack of blood flow and damage to the heart muscle.
