Introduction
Can high cholesterol, often linked to heart problems, also be a whispering wind behind respiratory issues? 🤔 Imagine cholesterol as a silent player in a game of health, where its moves can unexpectedly affect different parts of your body, including your lungs.
In India, where about 25-30% of urban and 15-20% of rural populations are estimated to have high cholesterol, understanding its broader impacts is crucial.
We’ll delve into the intricate relationship between cholesterol levels and lung function, exploring how imbalances in cholesterol can potentially lead to respiratory issues. This blog will shed light on the role of cholesterol in lung surfactant production and its impact on pulmonary inflammation, offering insights into how managing cholesterol is not just about heart health but also about maintaining healthy lungs.
Join us on this enlightening journey to breathe in the knowledge about cholesterol and respiratory health. Let’s clear the air and learn how to keep both our hearts and lungs in harmony! ❤️🫁
A Hike to Remember
Part – 1
In the heart of Delhi, where the rhythm of life moves at a breakneck pace, lived Vikram, a 42-year-old marketing director for a leading e-commerce company. His days were a blur of meetings, presentations, and endless decision-making. Vikram’s family, a supportive wife and two teenage sons, often felt his absence, even when he was home, his mind preoccupied with work.
Vikram was known for his sharp mind and emotional intelligence, which allowed him to navigate the complex dynamics of his workplace with ease. However, this intelligence did not extend to his personal health. Despite knowing better, he lived in a denial bubble, convincing himself that his constant tiredness and shortness of breath were merely side effects of aging and his busy lifestyle.
Understanding Hyperlipidemia and Dyslipidemia
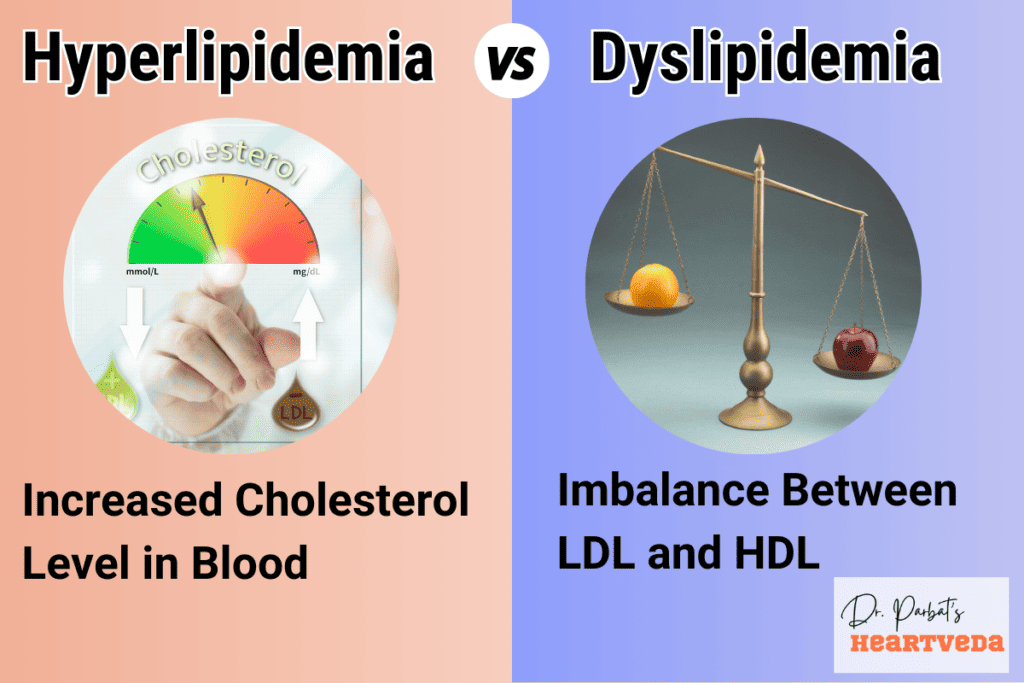
Hyperlipidemia and dyslipidemia are terms often used interchangeably to describe abnormal cholesterol levels. Hyperlipidemia refers to the presence of excessive lipids in the blood, while dyslipidemia encompasses both high cholesterol and imbalances between bad cholesterol (LDL) and good cholesterol (HDL) levels. Both conditions increase the risk of heart disease and call for interventions to lower cholesterol levels.
When it comes to managing hyperlipidemia and dyslipidemia, it’s important to consider a variety of factors beyond just cholesterol numbers. While high cholesterol is an important indicator, other factors such as inflammation and the balance between different types of cholesterol also play a crucial role.
Cholesterol particles and their distribution in the blood contribute to the overall risk of developing heart disease. There are two main types of cholesterol particles: bad cholesterol (LDL) and good cholesterol (HDL). LDL cholesterol particles are smaller and denser, making them more likely to become lodged in the arteries and contribute to plaque formation. On the other hand, HDL cholesterol particles are larger and can help remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of plaque buildup.
Cholesterol numbers are often used to assess an individual’s risk for heart disease and guide treatment decisions. These numbers include total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. While high total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of heart disease, having high levels of HDL cholesterol is considered protective.
The American Heart Association recommends the following cholesterol goals for adults:
| Cholesterol Measure | Desirable Level |
| Total Cholesterol | Less than 200 mg/dL |
| LDL Cholesterol | Less than 100 mg/dL |
| HDL Cholesterol | Greater than 60 mg/dL |
| Triglycerides | Less than 150 mg/dL |
It’s important to note that these goals may vary based on an individual’s specific health condition and risk factors. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate cholesterol targets for you.
Understanding hyperlipidemia and dyslipidemia is crucial in managing cholesterol-related risks and maintaining cardiovascular health. By examining cholesterol particles, considering cholesterol numbers, and taking appropriate measures to achieve desirable levels, individuals can reduce the risk of heart disease and achieve better overall health.
The Prevalence and Seriousness of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol is a widespread condition, affecting millions of American adults. When left untreated, high cholesterol can lead to serious complications, including the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. This can result in life-threatening conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the India. It encompasses various conditions, including coronary heart disease and peripheral artery disease. These conditions are directly linked to high cholesterol and the plaque buildup that occurs over time.
| Condition | Complications |
| Coronary Heart Disease | Increased risk of heart attacks and chest pain |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | Reduced blood flow to the limbs, leading to pain and potentially gangrene |
To prevent these life-threatening complications, it is important to manage and treat high cholesterol. Regular monitoring and appropriate medical interventions can help to control cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries.
Implementing lifestyle changes such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking can also have a significant impact on cholesterol management and overall cardiovascular health.
A Hike to Remember
Part – 2
His lifestyle, marked by long hours of sitting, fast food on the go, and minimal physical activity, was far from healthy. Vikram ignored the subtle signs his body sent him, attributing his decreasing stamina and increasing breathlessness to stress and work pressure.
The wake-up call came during a weekend family hike, a rare occasion when Vikram decided to step away from his laptop and spend some quality time outdoors. Barely halfway through, he found himself gasping for air, unable to keep up with his wife and sons. This moment of vulnerability, struggling to breathe amidst the beauty of nature, was Vikram’s darkest hour. It shattered his denial, forcing him to confront the reality of his neglected health.
Following this episode, Vikram visited Dr. Sharma, a pulmonologist recommended by a concerned friend. Dr. Sharma explained how high cholesterol could affect not just the heart but also the respiratory system, leading to reduced lung function and shortness of breath. This was a revelation to Vikram, who had never considered the broader impacts of his dietary choices and sedentary lifestyle.
How High Cholesterol Affects the Body
High cholesterol can have significant effects on the body, leading to various health conditions and complications.
Atherosclerosis: The Development of Plaque
One of the primary ways high cholesterol affects the body is through the development of atherosclerosis. This condition occurs when plaque, a sticky substance made up of cholesterol, fats, calcium, and other substances, builds up in the arteries.
The accumulation of plaque narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow. Over time, it can harden and form atherosclerotic plaques, making it harder for the blood to pass through.
| Condition | Description |
| Coronary Artery Disease | Atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries can lead to coronary artery disease. This condition can cause chest pain or angina, shortness of breath, and even heart attacks. |
| Carotid Artery Disease | The buildup of plaque in the carotid arteries can result in carotid artery disease. This condition increases the risk of transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes) and strokes. |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | Plaque buildup in the arteries that supply blood to the arms or legs can cause peripheral artery disease. This condition can lead to symptoms such as leg pain, cramping, and difficulty walking. |
Effects on Blood Flow and Organs
When plaque restricts blood flow due to atherosclerosis, it can have various effects on different parts of the body. Reduced blood flow to vital organs can lead to serious health consequences.
For example, in coronary artery disease, the narrowed arteries can deprive the heart of sufficient blood supply, resulting in chest pain or a heart attack. Similarly, carotid artery disease can increase the risk of strokes by limiting blood flow to the brain. Peripheral artery disease can cause pain and cramping in the legs due to inadequate blood flow.
Moreover, atherosclerosis can also affect other blood vessels and organs throughout the body, contributing to conditions such as kidney disease, erectile dysfunction, and poor wound healing.
Overall, high cholesterol and the resulting plaque buildup pose a significant risk to cardiovascular and overall health. Managing cholesterol levels is crucial in preventing these adverse effects.
Causes and Risk Factors of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol levels can be influenced by a combination of lifestyle factors and genetics. Understanding these causes and risk factors is essential for managing and preventing high cholesterol.
Lifestyle Factors
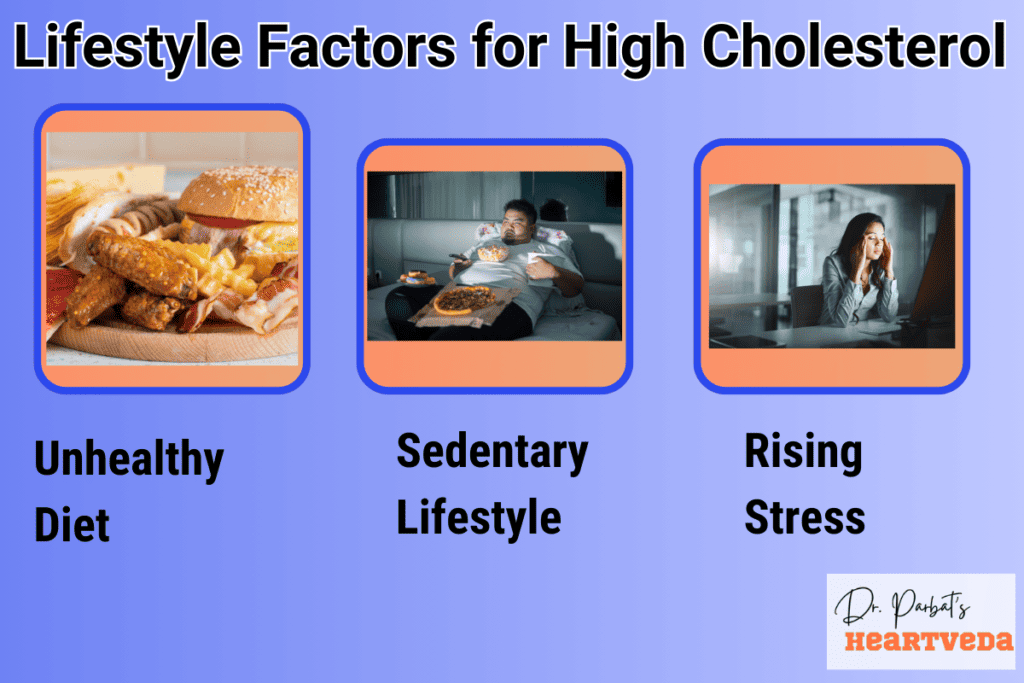
Several lifestyle factors can contribute to high cholesterol levels. These include:
- Smoking: Smoking tobacco can lower your good cholesterol (HDL) levels and increase bad cholesterol (LDL) levels, raising the risk of high cholesterol.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to unhealthy behaviors such as overeating or making poor food choices, which can impact cholesterol levels.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can raise cholesterol levels and contribute to other health issues.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lower your good cholesterol levels and increase your bad cholesterol levels.
- Diet: Consuming foods high in saturated fats and processed foods can raise cholesterol levels. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
Genetics
Your genes can also play a role in determining your cholesterol levels. Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to high cholesterol, even if they have a healthy lifestyle. If you have a family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular disease, you may be at a higher risk.
It’s important to note that while genetics contribute to high cholesterol, making positive lifestyle changes can still help manage your cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of associated health complications.
By understanding the causes and risk factors of high cholesterol, you can make informed decisions to improve your lifestyle, seek appropriate medical interventions, and ultimately maintain better cardiovascular and respiratory health.
Symptoms and Effects of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol itself does not typically cause noticeable symptoms. In fact, you can have high cholesterol levels even if you are physically active and appear healthy. However, high cholesterol increases the risk of various conditions that can have significant impacts on your health.
Peripheral Artery Disease
One of the conditions associated with high cholesterol is peripheral artery disease (PAD). PAD occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries outside of the heart, most commonly in the legs. Reduced blood flow to the legs can cause symptoms such as leg cramps, pain during exercise, and slow-healing wounds. If left untreated, PAD can lead to more severe complications, including tissue damage and even amputation.
High Blood Pressure
Another potential consequence of high cholesterol is the development of high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. When plaque builds up in the arteries, it can narrow the blood vessels and make it harder for blood to flow. This increased resistance can raise your blood pressure, putting added strain on your cardiovascular system. Over time, high blood pressure can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
Overall, high cholesterol can have far-reaching effects on your blood vessels and organs. It increases your risk of developing heart disease, which can lead to heart attacks and other cardiovascular events. Additionally, high cholesterol can contribute to the formation of blood clots that can block blood flow, potentially causing a stroke. The impact of high cholesterol on your health should not be underestimated, and it’s crucial to manage your cholesterol levels to reduce these risks.
The Relationship Between Cholesterol and Respiratory Health
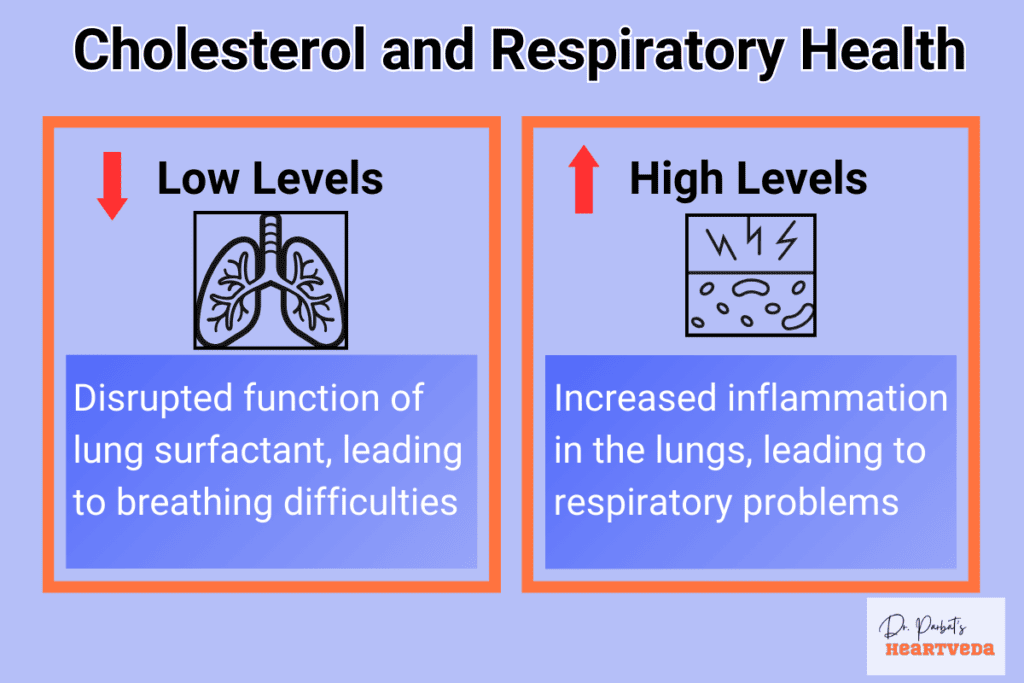
Cholesterol doesn’t just impact cardiovascular health, but it also plays a crucial role in respiratory health. One aspect of this relationship is the involvement of cholesterol in the production of lung surfactant, a substance that helps maintain normal lung function. Lung surfactant reduces surface tension in the lungs, preventing the collapse of small air sacs called alveoli during exhalation and promoting efficient gas exchange.
Imbalances in cholesterol levels can disrupt the composition and function of lung surfactant, potentially leading to respiratory issues. When the levels of cholesterol in the lungs are inadequate or faulty, it can hinder the optimal functioning of lung surfactant, compromising the ability of the lungs to expand and contract properly during breathing. This can result in symptoms such as shortness of breath and reduced lung capacity.
Research has also illuminated the connection between cholesterol and pulmonary inflammation. Dysfunctional cholesterol particles and imbalances in cholesterol levels have been linked to increased inflammation in the lungs. Inflammation in the lungs, known as pulmonary inflammation, can contribute to respiratory problems and impair lung function. It is important to maintain balanced cholesterol levels to promote healthy lung function and reduce the risk of respiratory issues.
Impact of Cholesterol on Lung Surfactant and Pulmonary Inflammation:
| Effects | Cholesterol Levels | Outcome |
| Low cholesterol levels | Below normal range | Disrupted production and function of lung surfactant, leading to breathing difficulties |
| High cholesterol levels | Above normal range | Increased inflammation in the lungs, contributing to respiratory problems |
| Imbalances in cholesterol | Uneven distribution of cholesterol particles | Poor lung surfactant function and elevated pulmonary inflammation |
Understanding the relationship between cholesterol and respiratory health allows for better management and prevention of respiratory issues. Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels through lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress, can help promote optimal lung function. Consultation with healthcare professionals is essential for monitoring cholesterol levels and addressing any respiratory concerns.
A Hike to Remember
END
Motivated by the desire to be present and active for his family, Vikram embarked on a journey of transformation. He started with small, manageable changes: swapping fast food for home-cooked meals, taking the stairs instead of the elevator, and incorporating short walks into his daily routine. Gradually, these small steps led to bigger lifestyle changes, including joining a weekend cycling group with his sons and practicing yoga to improve his breathing and reduce stress.
Vikram’s story is a powerful reminder that our health is interconnected, with choices in one area affecting our overall well-being. It highlights the importance of listening to our bodies and taking proactive steps to maintain our health. The question remains: will we wait for a crisis to take action, or will we make the necessary changes now to ensure a healthier, happier future?
The Impact of High Cholesterol on Lung Function
| Parameter | Detail |
| Population | Male Adolescents |
| HDL Cholesterol Increase | Associated with Decrease in Lung Function |
| Impact on FVC | Each 1.0 mg/dL increase in HDL cholesterol linked to 10 mL decrease in Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) |
| Impact on FEV1 | Each 1.0 mg/dL increase in HDL cholesterol linked to 10 mL decrease in Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second (FEV1) |
High cholesterol levels can have a direct impact on your lung function. Research suggests that excess cholesterol in the lungs can affect the function of alveolar macrophages, which are responsible for clearing harmful substances and fighting off infections. When these macrophages are impaired by cholesterol buildup, it can lead to increased inflammation in the lungs, potentially impairing your ability to breathe properly.
Studies have shown that cholesterol-induced inflammation in the lungs can contribute to respiratory issues and increase the vulnerability to conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other cholesterol-related respiratory disorders. This highlights the importance of maintaining healthy cholesterol levels for optimal lung function and respiratory health.
“Understanding the relationship between high cholesterol and lung function can provide insights into the development and treatment of cholesterol-related respiratory issues.”
To further illustrate the impact of high cholesterol on lung function, consider the following data:
| Lung Function with Normal Cholesterol Levels | Lung Function with High Cholesterol Levels | |
| Airflow | Unobstructed and efficient airflow | Impaired airflow due to inflammation and cholesterol buildup |
| Oxygen Exchange | Efficient oxygen exchange in alveoli | Reduced oxygen exchange due to impaired alveolar function |
| Respiratory Symptoms | No respiratory symptoms or shortness of breath | Increased risk of respiratory symptoms and shortness of breath |
| Overall Lung Health | Healthy lungs with optimal function | Increased risk of lung diseases and compromised lung health |
These findings highlight the detrimental effects of high cholesterol on lung function, emphasizing the importance of managing cholesterol levels to maintain optimal respiratory health. By addressing high cholesterol through lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and medication management, you can improve your lung function and reduce the risk of cholesterol-induced respiratory issues.
Takeaway
The impact of high cholesterol on lung function should not be overlooked. Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is not only crucial for cardiovascular health but also for optimal respiratory function. By understanding the relationship between high cholesterol and lung health, you can take proactive steps towards managing your cholesterol levels and safeguarding your overall well-being.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial for both respiratory and cardiovascular health. By making positive lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage and prevent high cholesterol.
Start by adopting a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid foods high in saturated fats and processed sugars, as they can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, can also help improve your cardiovascular health and keep your cholesterol levels in check.
It’s important to quit smoking and manage your stress levels, as both can have detrimental effects on your cholesterol levels and overall health. Smoking not only raises your bad cholesterol (LDL) but also lowers your good cholesterol (HDL), increasing your risk of cardiovascular disease. Stress can lead to unhealthy lifestyle habits and trigger inflammation in your body, further compromising your respiratory and cardiovascular health.
Remember to prioritize regular cholesterol checks with your healthcare provider. They can provide valuable insights into your cholesterol levels and help you determine the most appropriate medical interventions, if needed. By understanding the link between cholesterol and respiratory issues, you can take proactive steps to protect your health and well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- High cholesterol is a widespread condition that affects millions of adults.
- Research has highlighted the link between cholesterol levels and respiratory health.
- Imbalances in cholesterol levels can lead to changes in lung function and increased inflammation.
- Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial for both respiratory and cardiovascular health.
- Lifestyle changes and appropriate medical interventions play a key role in managing high cholesterol.
Q: What are the causes of high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol can be caused by a variety of factors including genetics, diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and certain health conditions such as diabetes or liver disease.
Q: What are the signs of high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol may not show any symptoms, but a blood test is the only way to detect it. In some cases, symptoms of high cholesterol can be seen as cholesterol deposits in the skin, yellowish spots on the eyelids, or fatty deposits on the hands, elbows, knees, or tendons.
Q: How does high cholesterol relate to heart disease?
A: High cholesterol can cause plaque to build up in the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis, which increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. It can limit or block blood flow to the heart, brain, and other organs.
Q: What is the significance of lipoprotein in relation to cholesterol?
A: Lipoproteins are particles made of fat and protein that carry cholesterol through the blood. There are two main types: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, while HDL is considered “good” cholesterol.
Q: How can I lower my cholesterol naturally?
A: Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight are key strategies to naturally lower cholesterol levels. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can also help in lowering cholesterol.
Q: What are the symptoms of high cholesterol?
A: As mentioned, high cholesterol may not show any symptoms. However, if there is a high level of cholesterol in your blood, it may cause your heart to work harder to pump blood, leading to serious health problems such as heart disease and stroke.
Q: How is high cholesterol diagnosed?
A: High cholesterol is typically diagnosed through a simple blood test called a lipid panel. This test measures the levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides in the blood.
Q: What are the health problems associated with high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol can lead to serious health problems such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. It can also increase the risk of developing other health issues related to inadequate blood flow throughout the body.
Q: How does high cholesterol affect blood flow?
A: When cholesterol is high, it can cause plaque to build up in the arteries, restricting blood flow to vital organs. This can lead to problems such as chest pain, heart attack, or stroke, as the blood can’t flow freely to where it is needed.
Q: Can high cholesterol be a risk factor for heart disease and stroke?
A: Yes, high cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. It contributes to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries become narrowed and hardened due to a buildup of plaque, which can lead to cardiovascular events.
Q: What are the common causes of high cholesterol?
A: High cholesterol can be caused by factors such as an unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, smoking, obesity, and genetics.
Q: How does high cholesterol affect the body?
A: High cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular issues.
Q: What are some common symptoms of high cholesterol?
A: Common symptoms of high cholesterol may include chest pain, yellowish patches on the skin, and a yellow tint to the eyes.
Q: How can I lower my cholesterol levels?
A: You can lower your cholesterol levels by making lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and quitting smoking.
Q: When should I get my cholesterol checked?
A: It’s important to know your cholesterol levels, so get your cholesterol checked regularly, especially if you have risk factors such as a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease.
Q: What is the significance of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol?
A: HDL cholesterol is known as “good” cholesterol as it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Q: Can high cholesterol cause respiratory issues?
A: While high cholesterol typically affects the cardiovascular system, it may indirectly contribute to respiratory issues by increasing the risk of conditions such as coronary artery disease which can impact lung function.
Q: Are there noticeable signs that I have high cholesterol?
A: Some signs of high cholesterol include chest pain, shortness of breath, and yellowish deposits around the eyes, but often high cholesterol doesn’t cause symptoms until it leads to complications.
Q: How does cholesterol affect the circulation of blood in the body?
A: Too much cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of cardiovascular issues like heart attack and stroke.
Q: What are the implications of developing high cholesterol?
A: Developing high cholesterol may increase the risk of serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease, so it’s important to make lifestyle changes and get your cholesterol levels under control.
