Heart attack symptoms are not to be taken lightly. The signs can vary from person to person, and it’s important to recognize them early. Some heart attacks start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort, while others can be sudden and intense.
The most common symptom of a heart attack is chest pain or discomfort. It may feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest. However, it’s crucial to note that heart attack symptoms can extend beyond the chest. You may also experience pain or discomfort in other areas of the body, such as the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Other signs can include shortness of breath, arm pain, jaw pain, dizziness, nausea, sweating, fatigue, and anxiety. These symptoms should not be ignored, as they could be indicative of a heart attack.
Key Takeaways:
- Heart attack symptoms can vary from person to person.
- Common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and arm/jaw pain.
- Other signs can include dizziness, nausea, sweating, fatigue, and anxiety.
- Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for seeking medical help.
- Do not hesitate to call for emergency assistance if experiencing heart attack warning signs.
Heart Attack Symptoms in Women
When it comes to heart attacks, women may experience different symptoms compared to men. While chest pain is still a common symptom, it’s important to be aware of other signs that may indicate a heart attack in women.
Along with chest pain, women may also experience:
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Back pain
- Jaw pain
It’s crucial for women to recognize these atypical symptoms and seek immediate medical attention if they occur. Paying attention to your body can save lives and lead to timely intervention. No symptom should be ignored, as early detection and treatment greatly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
Remember, heart attacks can present differently in women, so it’s important to trust your instincts and seek medical help if you suspect a heart attack, even if the symptoms seem unusual or mild.
| Common Heart Attack Symptoms in Women | Atypical Heart Attack Symptoms in Women |
|---|---|
| Chest pain | Shortness of breath |
| Shortness of breath | Nausea or vomiting |
| Nausea or vomiting | Back pain |
| Back pain | Jaw pain |
| Jaw pain |
Recognizing Heart Attack Symptoms: Don’t Hesitate to Call 911
If you or someone you know experiences heart attack warning signs, it’s crucial to call for emergency help immediately. The sooner medical assistance is received, the higher the chances of a positive outcome. Ignoring the symptoms or hesitating to seek help can have serious consequences.
Chest discomfort is a common symptom of a heart attack. It may feel like pressure, tightness, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest. This discomfort may last for more than a few minutes or come and go. It is important not to ignore this chest pain and seek medical attention right away.
In addition to chest discomfort, a heart attack can cause pain or discomfort in other areas of the upper body. This includes the arms, back, neck, jaw, and stomach. These areas should also be taken seriously if pain or discomfort is experienced.
Another warning sign of a heart attack is shortness of breath. This can occur with or without chest discomfort. If you find it difficult to breathe, or if you experience sudden and unexplained shortness of breath, it is essential to seek medical help immediately.
Other symptoms to watch out for include cold sweats, nausea, and lightheadedness. These can be indicators of an impending heart attack and should not be ignored.
Remember, every minute counts during a heart attack. Delaying medical attention can lead to further damage to the heart muscle and increase the risk of complications. Calling 911 ensures that help arrives promptly and appropriate treatment can be administered without delay.

By recognizing the warning signs of a heart attack, you can take immediate action and potentially save a life. If you or someone around you experiences chest discomfort, pain in other areas of the upper body, shortness of breath, cold sweats, nausea, or lightheadedness, don’t hesitate to call 911. It’s always better to be safe than sorry when it comes to heart health.
First Aid for Heart Attacks: CPR and AED
If someone is experiencing a heart attack and stops breathing, performing CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) can help. Manual chest compressions should be carried out by placing the base of the hands in the center of the chest and pressing hard and fast. An automatic external defibrillator (AED) may also be used to deliver a shock that can restart the heart. It’s important to follow the instructions provided by emergency services and continue these actions until professional medical help arrives.
During a heart attack, time is of the essence. Taking immediate action by performing CPR and using an AED can greatly increase the person’s chances of survival. CPR helps maintain blood circulation and provides oxygen to the brain until medical professionals take over. The AED, when used correctly, can deliver a potentially life-saving shock to restore the heart’s normal rhythm.
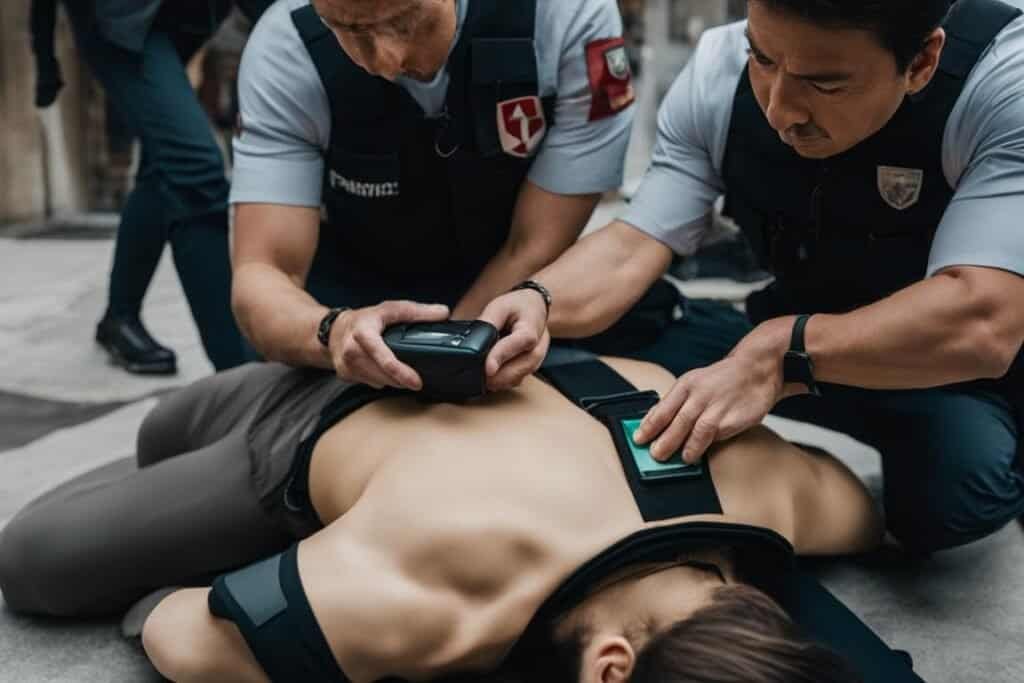
Performing CPR involves a combination of chest compressions and rescue breaths. If you’re not trained in CPR, it’s best to focus on continuous chest compressions until professional help arrives. Remember, every minute counts during a heart attack, so don’t hesitate to take action.
Here are the steps for performing manual chest compressions:
- Begin by placing the heel of one hand in the center of the person’s chest, between the nipples.
- Place your other hand on top, interlocking your fingers.
- Position yourself directly above the person’s chest.
- With straight arms, use your upper body weight to press down firmly and quickly, aiming for a compression depth of about 2 inches.
- Allow the chest to fully recoil between compressions.
- Continue performing chest compressions at a rate of around 100-120 compressions per minute.
While CPR can provide temporary support during a heart attack, it’s crucial to get professional medical help as soon as possible. Emergency medical services (EMS) should always be contacted to ensure the person receives the necessary medical treatment.
Medical Treatment for Heart Attacks
When emergency medical services arrive, they will take over the care of a person experiencing a heart attack. In the hospital, various medical treatments may be administered to stabilize the condition and restore blood flow to the heart.
The treatment plan for a heart attack will be individualized based on the person’s condition and the severity of the heart attack. The goal of treatment is to minimize damage to the heart muscle and prevent future heart attacks.
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in heart attack treatment. They are used to:
- Dissolve blood clots: Thrombolytic medications, also known as clot-busters, are administered to dissolve the blood clot that is blocking the coronary artery and causing the heart attack.
- Reduce pain and discomfort: Analgesics are prescribed to relieve chest pain and discomfort associated with a heart attack.
- Lower blood pressure and heart rate: Medications such as beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors are used to reduce the workload on the heart and improve blood flow.
- Prevent blood clot formation: Antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications are prescribed to prevent the formation of new blood clots and reduce the risk of future heart attacks.
In addition to these medications, other drugs may be given to manage underlying conditions such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, which can contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
Percutaneous coronary intervention, also known as angioplasty, is a mechanical method of restoring blood flow to the heart. During this procedure, a thin tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in the arm or groin and threaded to the blocked coronary artery.
Once the catheter reaches the site of the blockage, a balloon at the tip is inflated to widen the narrowed or blocked artery, improving blood flow. In some cases, a stent, which is a small metal mesh tube, may be placed in the artery to keep it open and prevent further blockages.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Coronary artery bypass grafting is a surgical procedure that involves creating new pathways for blood to bypass blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. In this procedure, a healthy blood vessel, usually taken from the leg, arm, or chest, is grafted onto the coronary artery below the blockage.
CABG is typically recommended for individuals with multiple blockages or blockages in critical areas of the heart that cannot be effectively treated with PCI. This surgical intervention aims to improve blood flow to the heart and relieve symptoms of angina.
Following heart attack treatment, ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are essential to prevent future heart attacks and manage any underlying conditions. It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers and follow their recommendations for a successful recovery.
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Medications | Various medications are administered to dissolve blood clots, reduce pain and discomfort, lower blood pressure and heart rate, and prevent future blood clot formation. |
| Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) | A mechanical method of restoring blood flow to the heart by inserting a catheter with a balloon or stent to widen narrowed or blocked arteries. |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) | A surgical procedure that involves creating new pathways for blood to bypass blocked coronary arteries using grafts from other blood vessels. |
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack and seeking prompt medical care is crucial for a positive outcome. It’s important to be aware of the common symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath, as well as the atypical symptoms that can occur in women. When experiencing these symptoms, it’s crucial to take immediate action by calling 911 as it can save lives.
Prevention plays a vital role in reducing the risk of heart attacks. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is key, which includes regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and achieving a healthy weight. These lifestyle choices can significantly lower the chances of experiencing a heart attack. Additionally, regular check-ups with healthcare providers and managing underlying conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes are important for maintaining heart health.
By prioritizing heart health and making positive changes in your lifestyle, you can lead a longer and healthier life. Early detection of heart attack symptoms, coupled with preventive measures, can make a significant difference in your overall well-being. Remember, your heart health is in your hands, so take charge today and embrace a healthy lifestyle to protect your heart.

