
Introduction
🌟 Have you ever wondered how a tiny pill can be a game-changer in your fight against high cholesterol? With the hustle and bustle of professional life, Indian professionals in their 30s, 40s, and 50s often find themselves grappling with elevated cholesterol levels. This blog is your guiding star in the vast sky of cholesterol management, especially focusing on medications like Atorvastatin and other cholesterol-lowering drugs.
In this easy-to-understand guide, we dive into the world of cholesterol – distinguishing the good (HDL) from the bad (LDL) and how they impact your heart health. Just like a well-oiled machine needs the right balance to function smoothly, your body needs a balance of these cholesterol types for optimal health. We explore the role of statins, the most commonly prescribed cholesterol medications, in keeping this balance.
Did you know that statins can reduce LDL cholesterol by 20-60%? This blog will walk you through the effectiveness, potential side effects, and the importance of combining medication with lifestyle changes. It’s not just about popping a pill; it’s about a holistic approach to keeping your heart healthy and your life vibrant. 🌈❤️
Join us on this journey to demystify cholesterol medications and take control of your heart health. Let’s turn the tide against high cholesterol together!
Understanding Cholesterol: HDL vs. LDL
Cholesterol is an essential fat found in the blood that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. However, high cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues. To better understand cholesterol, we need to differentiate between two main types: high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
HDL Cholesterol:
HDL cholesterol, often referred to as the “good” cholesterol, plays a crucial role in maintaining heart health. It acts as a scavenger, picking up excess cholesterol from the blood vessels and transporting it back to the liver for disposal. By removing cholesterol buildup, HDL prevents arteries from becoming clogged and reduces the risk of heart disease.
LDL Cholesterol:
LDL cholesterol, on the other hand, is known as the “bad” cholesterol. It is responsible for transporting cholesterol from the liver to the body’s cells. When LDL levels are too high, it can lead to the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries, resulting in plaque formation. This can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
Managing LDL cholesterol levels is crucial for maintaining heart health and reducing the risk of heart disease. An optimal balance between HDL and LDL cholesterol is necessary for overall well-being.
Comparison of HDL and LDL Cholesterol
| Cholesterol Type | Function | Impact on Heart Health |
| HDL Cholesterol (Good Cholesterol) | Removes excess cholesterol from the blood vessels | Reduces the risk of heart disease |
| LDL Cholesterol (Bad Cholesterol) | Transports cholesterol to body cells | Increases the risk of heart disease |
By focusing on maintaining healthy levels of HDL and LDL cholesterol, individuals can take significant steps towards protecting their heart health and lowering the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions.
Beyond the Boardroom: Prashant’s Path to Heart Wellness
Part – 1
In the sprawling metropolis of Delhi, where the old and new converge in a symphony of chaos and beauty, Prashant, a 42-year-old marketing director, thrived amidst the cacophony. His days were a blur of meetings, pitches, and the relentless pursuit of success in the city’s competitive corporate landscape.
Prashant’s home was a quiet haven in the suburbs, shared with his wife and their two teenage children. Despite his demanding career, he was a devoted family man, balancing his professional ambitions with his role as a loving husband and father. However, Prashant’s emotional intelligence, which made him a star at work and a pillar at home, did not extend to his personal health.
Statins: The Most Commonly Prescribed Cholesterol Medications
When it comes to managing cholesterol, statins are the go-to medications. These widely prescribed drugs are highly effective in reducing LDL cholesterol levels and lowering the risk of heart attack and stroke. Statins work by inhibiting the production of cholesterol in the liver, thereby preventing the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
Examples of commonly used statins include:
- Atorvastatin
- Simvastatin
- Rosuvastatin
It’s important to note that statins are typically prescribed along with lifestyle modifications, such as a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise. Your doctor will determine the appropriate statin and dosage based on your cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health.
Effectiveness of Statins
Statins have been extensively studied and have consistently shown their ability to lower LDL cholesterol levels. In fact, they are regarded as the gold standard in cholesterol-lowering medication. Research has demonstrated that statins can reduce LDL cholesterol by an average of 20-60% depending on the statin used and the initial cholesterol levels.
Besides lowering LDL cholesterol, statins have other beneficial effects on heart health. They can stabilize plaque in the arteries, reduce inflammation, and improve the function of the blood vessel lining. All these factors contribute to reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
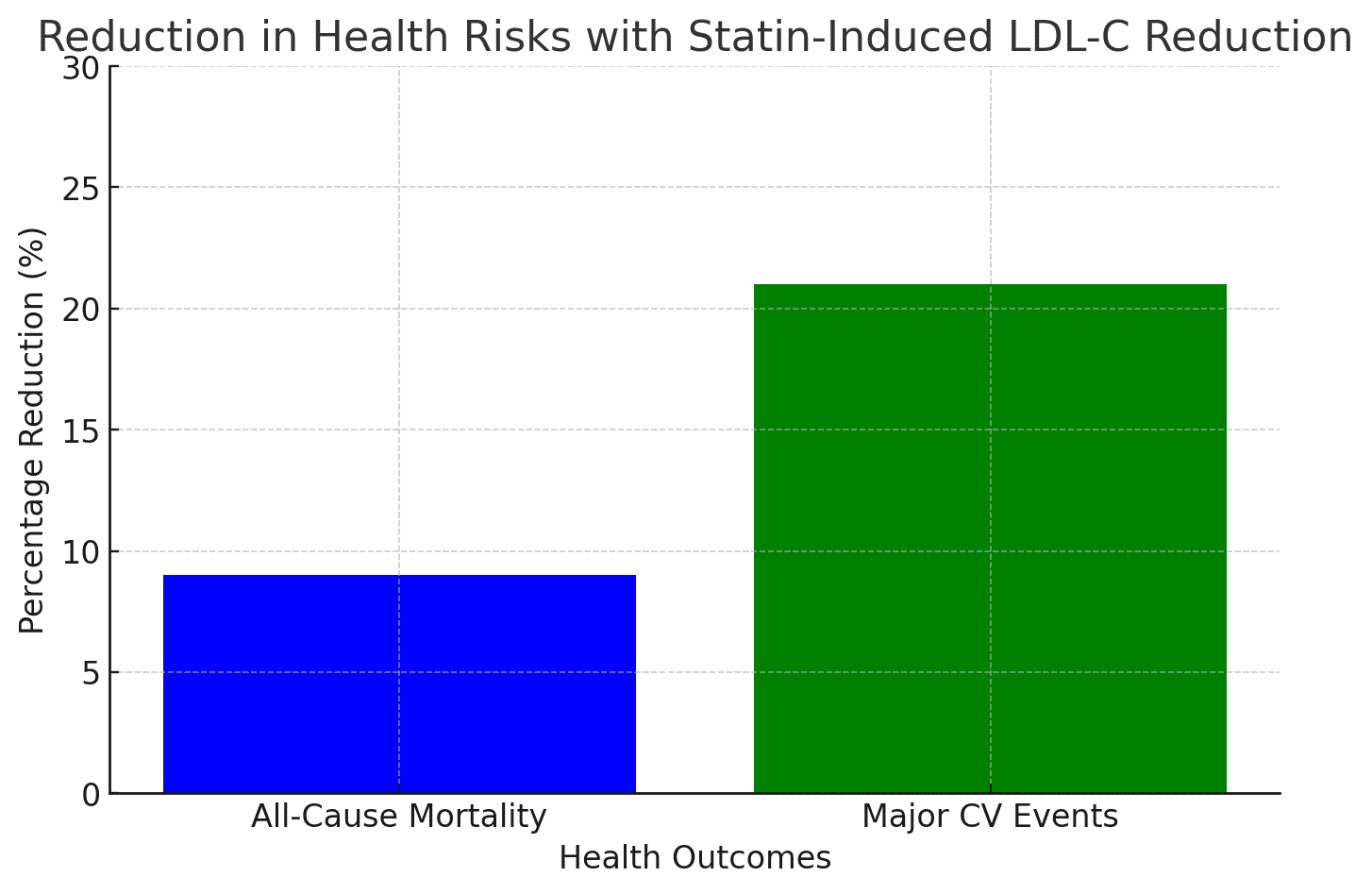
The bar chart is showing the effects of statin-induced reduction in LDL-C (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). The chart illustrates two key outcomes:
- All-Cause Mortality: There’s a 9% reduction in all-cause mortality.
- Major Cardiovascular (CV) Events: There’s a 21% reduction in the incidence of major Cadiovascular events.
Potential Side Effects

While statins are generally safe and well-tolerated, they can have side effects. Common side effects include muscle aches, liver enzyme elevations, and digestive issues. However, these side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own. Rarely, statins can cause more serious side effects such as muscle breakdown, liver problems, and increased blood sugar levels. It’s important to discuss any concerns or symptoms with your healthcare provider.
In rare cases, statins may interact with other medications, so it’s crucial to inform your doctor about all the medications you are taking. They will ensure that the prescribed statin is safe and suitable for you.
“Statins are a key component in the management of high cholesterol. They not only lower LDL cholesterol but also have additional cardiovascular benefits. By working closely with your doctor, you can determine the statin that best suits your individual needs and experience the benefits of improved heart health.”
Beyond the Boardroom: Prashant’s Path to Heart Wellness
Part – 2
Convinced that his youth and active job kept him healthy, Prashant ignored the subtle warnings his body sent him. “I’m too busy to worry about diet and exercise,” he’d argue, brushing aside his wife’s concerns about his health. This denial was his shield against the reality of his sedentary lifestyle and his fondness for rich, indulgent foods.
The wake-up call came during an annual health check-up, a corporate mandate he’d always deemed a formality. Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol—the dangerous kind that clogs arteries and invites heart disease—were a red flag he couldn’t ignore. The consequence of his years of neglect stared back at him from the lab results, a silent yet potent threat to his dreams and family life.
Prashant’s darkest moment wasn’t the diagnosis itself but the fear that he might not be there to see his children grow up, to celebrate anniversaries with his wife, or to enjoy the fruits of his labor. The thought of his family navigating life without him was a reality check more potent than any boardroom challenge.
Bile Acid Sequestrants: Supporting LDL Cholesterol Reduction
Bile acid sequestrants are powerful medications that aid in lowering LDL cholesterol levels. These medications work by binding to bile in the intestines, leading to a reduction in cholesterol absorption and promoting its elimination from the body. By preventing cholesterol reabsorption, bile acid sequestrants play a crucial role in supporting overall cardiovascular health.
These medications are often used in combination with statins to achieve further reduction in LDL cholesterol levels. When used together, bile acid sequestrants complement the effects of statins, resulting in improved cholesterol control. Examples of commonly prescribed bile acid sequestrants include colesevelam and cholestyramine.
It is important to note that triglyceride levels may increase with the use of bile acid sequestrants. Therefore, these medications are primarily recommended for individuals who have elevated LDL cholesterol levels and normal triglyceride levels. To ensure optimal cholesterol management, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors: Blocking Cholesterol Intake
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors, such as ezetimibe, play a key role in managing cholesterol levels by preventing the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines. These inhibitors are especially beneficial for individuals with high LDL cholesterol levels.
Ezetimibe has a modest effect on reducing LDL cholesterol levels and can also increase HDL cholesterol levels, which is often referred to as the “good” cholesterol. By blocking the absorption of cholesterol, ezetimibe helps lower overall cholesterol levels and promotes heart health.
Ezetimibe can be used alone or in combination with statins, which are another type of cholesterol-lowering medication, to further lower cholesterol levels. When combined with statins, ezetimibe enhances their effectiveness in reducing LDL cholesterol and improving cardiovascular health.
If you are concerned about your cholesterol levels, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for you. They can assess your individual needs and discuss the potential benefits and risks of using cholesterol absorption inhibitors like ezetimibe.
Benefits of Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors:
- Reduces LDL cholesterol levels
- Potentially increases HDL cholesterol levels
- Can be used alone or in combination with statins
- Efficacy in lowering cholesterol levels
| Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitor | Main Function | Typical Dosage | Common Brand Names |
| Ezetimibe | Prevents cholesterol absorption in the intestines | 10 mg daily | Zetia, Ezetrol, Ezecard |
Niacin: Boosting HDL and Lowering LDL
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is a valuable tool in improving your cholesterol levels. It has the ability to increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, which is often referred to as the “good” cholesterol, and lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as the “bad” cholesterol. Additionally, niacin can help reduce triglyceride levels, which are another type of fat found in the blood.
Prescription-strength niacin is typically recommended for individuals who cannot tolerate statin therapy or require additional help in managing their cholesterol levels. It is available under brand names such as Niacor and Niaspan.
Niacin works by affecting the production of lipoproteins, which are responsible for transporting cholesterol in the bloodstream. By increasing HDL cholesterol and decreasing LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, niacin helps maintain a healthier cholesterol profile that is beneficial for heart health.
Please note that niacin should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as it can have side effects such as flushing, itching, and increased liver enzymes. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and monitor your response to niacin therapy.
PCSK9 Inhibitors: Medicine Targeting LDL Cholesterol
PCSK9 inhibitors are a newer class of cholesterol medications that specifically target LDL cholesterol levels to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease. These inhibitors work by inactivating PCSK9, a protein that prevents the clearance of cholesterol from the blood. By inhibiting PCSK9, these medications help lower LDL cholesterol levels, which is essential for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health.
Two examples of PCSK9 inhibitors are alirocumab and evolocumab. These medications are available in injectable form and are typically used in combination with other cholesterol-lowering drugs, such as statins, to provide greater reduction in the levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Studies have shown that PCSK9 inhibitors effectively lower LDL cholesterol levels and can even be used as an alternative for patients who cannot tolerate statin therapy. By achieving significant LDL cholesterol reduction, PCSK9 inhibitors contribute to reducing the overall risk of heart disease and cardiovascular events.
| Medication | Route of Administration | Dosage Frequency |
| Alirocumab | Subcutaneous injection | Every 2 weeks |
| Evolocumab | Subcutaneous injection | Every 2 weeks or monthly |
It is important to note that PCSK9 inhibitors are typically prescribed for individuals with high LDL cholesterol levels and an increased risk of heart disease, despite other treatment methods. These medications are administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional and may be used in combination with lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, for optimal cardiovascular health.
Beyond the Boardroom: Prashant’s Path to Heart Wellness
Part – 3
The path to recovery began with a visit to Dr. Singh, a cardiologist known for his expertise and empathy. Alongside Aarti, a friend who had navigated her health journey, Prashant embarked on a new chapter. Dr. Singh introduced him to statin therapy, a proven method to lower LDL cholesterol and protect the heart. With Aarti’s encouragement, Prashant also embraced lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Prashant’s journey from denial to proactive health management was a testament to the power of medical intervention and personal responsibility. His story became a message of hope and action for his peers, a reminder that health is a gift that requires attention and care.
ACL Inhibitors: Decreasing Liver Cholesterol Production
ACL inhibitors, such as bempedoic acid, are medications that work by blocking an enzyme in the liver responsible for cholesterol production. By inhibiting this enzyme, ACL inhibitors effectively reduce the production of cholesterol in the liver, leading to lower LDL cholesterol levels.
Bempedoic acid, a widely used ACL inhibitor, has been shown to be effective in lowering LDL cholesterol. It works by targeting the liver specifically, where most cholesterol is produced. By decreasing liver cholesterol production, bempedoic acid helps to manage high cholesterol levels.
What sets ACL inhibitors apart is their ability to be used in combination with other cholesterol-lowering drugs for better efficacy. When used in combination, these medications provide a comprehensive approach to cholesterol management.
ACL Inhibitors vs. Other Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
When compared to other cholesterol-lowering medications, ACL inhibitors offer unique benefits. While statins, bile acid sequestrants, and cholesterol absorption inhibitors primarily target cholesterol uptake and circulation, ACL inhibitors focus on decreasing cholesterol production in the liver.
This focused approach not only helps lower LDL cholesterol levels but also offers an alternative for individuals who may not tolerate or respond well to other medications. It provides an additional option for managing cholesterol levels, including low density lipoprotein cholesterol, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular issues.
| Cholesterol-Lowering Medications | Target Mechanism of Action |
| Statins | Inhibit cholesterol production in the liver |
| Bile Acid Sequestrants | Prevent cholesterol absorption in the intestines |
| Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors | Inhibit cholesterol absorption in the intestines |
| ACL Inhibitors | Block liver cholesterol production |
By understanding the different mechanisms of action, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment plans to best suit the individual needs of patients. This personalized approach ensures optimized cholesterol management for better overall cardiovascular health.
ACL inhibitors such as bempedoic acid offer a new perspective in cholesterol management. By selectively targeting liver cholesterol production, these medications provide an effective option for individuals who require additional support in lowering their LDL cholesterol levels.
Beyond the Boardroom: Prashant’s Path to Heart Wellness
END
As he shared his experience, Prashant posed a question that resonated with many: “What are we waiting for?” It was an invitation to prioritize health, to embrace the science of medicine like statin therapy, and to make choices that ensure a longer, happier life.
The message was clear: taking action against high cholesterol is not just a personal choice but a commitment to oneself and loved ones, a step towards a healthier heart and a future filled with possibilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, medication plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels, especially for individuals who do not achieve desired results through diet and lifestyle changes alone. By incorporating the use of statins, bile acid sequestrants, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, niacin, PCSK9 inhibitors, and ACL inhibitors, it is possible to effectively lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
When considering medication for cholesterol management, it is essential to consult with your doctor. They can help determine the most appropriate medication for your specific needs and discuss potential side effects or interactions. It is important to note that medication is not a standalone solution and should be used in conjunction with a healthy lifestyle for optimal cholesterol control.
Remember, lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, regular exercise, and weight management also play a significant role in managing cholesterol levels. By making these positive lifestyle changes alongside medication, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining better heart health and overall well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- Cholesterol control is necessary for maintaining heart health.
- Diet and lifestyle adjustments are essential, but medication may be required for some individuals.
- Drinks and oral drops can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Medications like statins, bile acid sequestrants, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, niacin, PCSK9 inhibitors, and ACL inhibitors effectively lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Consult with your doctor to determine the most appropriate medication for your specific needs.
Q: What is the purpose of atorvastatin and other cholesterol-lowering medications?
A: The purpose of atorvastatin and other cholesterol-lowering medications is to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in the blood, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Q: How do cholesterol-lowering medications work?
A: Cholesterol-lowering medications, such as atorvastatin, work by blocking the enzyme in the liver that is responsible for producing cholesterol. This helps lower the levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood.
Q: Who can benefit from taking cholesterol-lowering medications?
A: Individuals with high cholesterol levels, familial hypercholesterolemia, and those at high risk for cardiovascular disease can benefit from taking cholesterol-lowering medications to help manage their cholesterol levels.
Q: Are there any side effects associated with cholesterol-lowering medications?
A: While cholesterol-lowering medications are generally well-tolerated, some potential side effects may include muscle pain, liver function abnormalities, and an increased risk of diabetes. It’s important to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
Q: Can cholesterol-lowering medications be used as a sole treatment for high cholesterol?
A: Cholesterol-lowering medications are often used in conjunction with lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, to effectively lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Q: How long does it take for cholesterol-lowering medications to show results?
A: The effects of cholesterol-lowering medications, including atorvastatin, may be seen within a few weeks, but it may take several months to achieve optimal cholesterol levels. Individual responses may vary.
Q: What should I do if I miss a dose of my cholesterol-lowering medication?
A: If you miss a dose of your cholesterol-lowering medication, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule.
Q: Can cholesterol-lowering medications be taken with other medications?
A: It’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all medications, including over-the-counter and herbal supplements, that you are taking, as some medications may interact with cholesterol-lowering medications.
Q: Can cholesterol-lowering medications be used in children?
A: Cholesterol-lowering medications, including atorvastatin, may be prescribed for children with familial hypercholesterolemia or other specific conditions, but their use in children should be carefully monitored by a healthcare provider.
Q: What lifestyle changes can complement the use of cholesterol-lowering medications?
A: Lifestyle changes, such as following a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress, can complement the use of cholesterol-lowering medications to effectively lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Q: How do cholesterol-lowering medications like Atorvastatin help manage high cholesterol levels?
A: Cholesterol-lowering medications such as Atorvastatin, along with other drugs, are beneficial in controlling cholesterol levels, particularly for individuals with conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia or those at risk of heart disease. These medications effectively reduce LDL cholesterol and can also lower triglyceride levels while increasing HDL cholesterol levels.
Q: What are some common side effects associated with taking statins for cholesterol management?
A: While statins like Atorvastatin are generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects such as muscle pain or weakness, liver function abnormalities, digestive issues, and rarely, an increased risk of diabetes. It’s essential for patients taking statins to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider to ensure the most suitable treatment and monitor any potential side effects.
Q: Can Atorvastatin and other cholesterol-lowering medications be used to treat high blood cholesterol in adults?
A: Yes, Atorvastatin and other cholesterol-lowering medications are commonly prescribed to individuals with high blood cholesterol, particularly those at risk of cardiovascular disease. These medications are an essential part of managing blood cholesterol levels and have been endorsed by organizations such as the American Heart Association and the National Cholesterol Education Program.
Q: How can one safely lower their cholesterol with the help of medications to lower LDL cholesterol?
A: To safely lower cholesterol with the help of medications, it’s important to follow the guidance of a healthcare professional. This includes taking the prescribed medication as directed, monitoring and managing any potential side effects, and engaging in lifestyle changes such as a heart-healthy diet and regular physical activity to complement the medication’s effects.
Q: What role does Atorvastatin play in the management of blood cholesterol in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia?
A: Atorvastatin, along with other cholesterol-lowering medications, plays a significant role in managing blood cholesterol levels in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. These medications are essential in reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications associated with this genetic condition and are commonly integrated into treatment plans for affected individuals.
Q: Are there any dietary considerations while taking medications to lower LDL cholesterol?
A: While taking medications to lower LDL cholesterol, it’s advisable to follow a heart-healthy diet as recommended by healthcare professionals. This may involve reducing saturated and trans fats, increasing intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limiting cholesterol-rich foods to complement the cholesterol-lowering effects of the prescribed medication.
Q: Can cholesterol-lowering medications impact liver function tests?
A: Cholesterol-lowering medications, including Atorvastatin and other statins, may affect liver function tests in some individuals. Periodic monitoring of liver function is typically recommended while taking these medications to ensure early detection of any potential abnormalities and to adjust the treatment plan if needed.
Q: What is the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and how do cholesterol-lowering medications contribute to it?
A: The primary prevention of cardiovascular disease encompasses measures taken to mitigate the risk of developing heart-related complications. Cholesterol-lowering medications, such as Atorvastatin, play a crucial role in this by effectively lowering LDL cholesterol levels, which is a key risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and enhancing overall cardiovascular health.
Q: How can medications to lower LDL cholesterol impact overall cholesterol levels in individuals?
A: Medications to lower LDL cholesterol, including Atorvastatin and other statins, can have a significant impact on overall cholesterol levels by specifically targeting the reduction of LDL cholesterol in the blood. This approach contributes to a more balanced lipid profile and helps in reducing the overall risk of cardiovascular disease and related complications.
Q: How can I lower my cholesterol?
A: You can lower your cholesterol by making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight. Additionally, your doctor may prescribe cholesterol-lowering medications, such as atorvastatin, to help lower your cholesterol levels.
Q: What is atorvastatin and how does it work to lower cholesterol?
A: Atorvastatin is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called statins. It works by blocking an enzyme in the liver that is responsible for producing cholesterol. By inhibiting the production of cholesterol, atorvastatin helps lower the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in the blood.
Q: Can atorvastatin help lower both LDL and non-HDL cholesterol?
A: Yes, atorvastatin is effective in lowering both LDL cholesterol and non-HDL cholesterol. Non-HDL cholesterol includes all the “bad” cholesterol in the blood, which can contribute to the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Q: Are there any side effects associated with atorvastatin therapy?
A: Like any medication, atorvastatin may cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include muscle pain, weakness, and an increased risk of diabetes due to the amount of cholesterol reduced. It’s important to discuss any concerns or potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
Q: Can atorvastatin be used in patients with type 2 diabetes?
A: Yes, atorvastatin can be used in patients with type 2 diabetes to help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. However, it’s essential to discuss your medical history and any existing conditions with your doctor before starting atorvastatin therapy.
Q: How long does it take for atorvastatin to start lowering cholesterol levels?
A: Atorvastatin may start to lower cholesterol levels within a few weeks of starting the medication. However, the full effects on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol levels may take several weeks to months to become evident. It’s important to continue taking the medication as prescribed by your doctor.
Q: What should I do if I experience side effects after taking a statin?
A: If you are experiencing side effects from statin therapy, it is important to discuss this with your healthcare provider. They may adjust the dosage, switch to a different statin, or provide alternative treatment options.
Q: Can atorvastatin be used to treat high levels of dietary cholesterol?
A: Atorvastatin is primarily used to lower levels of cholesterol produced by the body, rather than dietary cholesterol consumed through food. It is essential to focus on dietary and lifestyle changes in addition to medication to effectively manage cholesterol levels.
Q: Is atorvastatin approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for cholesterol lowering?
A: Yes, atorvastatin has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of high cholesterol and to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. It has been shown to be effective in lowering LDL cholesterol and improving overall lipid profiles.
Q: Can statins be used in patients with fatty liver disease?
A: Statins can be used in patients with fatty liver disease, but careful monitoring of liver enzymes and overall liver health is important during statin therapy.
Q: Can atorvastatin be taken alongside other cholesterol-lowering medications?
A: In some cases, atorvastatin may be prescribed in combination with other cholesterol-lowering medications to achieve optimal results. However, the use of multiple cholesterol-lowering medications should be carefully monitored by a healthcare professional to minimize potential interactions and side effects.
Q: What should I do if I have liver disease and need to lower my cholesterol?
A: If you have liver disease, it’s crucial to discuss the use of atorvastatin or any other cholesterol-lowering medications with your healthcare provider. Certain liver conditions may require special considerations when using these medications, and your doctor can provide guidance on the most suitable options for managing your cholesterol levels.
Q: Do statins cause drug interactions?
A: Statins have the potential to interact with other medications, so it’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications and supplements you are taking to avoid any potential drug interactions.
