
Introduction
Did you know that heart attacks are no longer just a concern for the elderly? Surprisingly, this alarming health issue is increasingly affecting younger individuals, including those in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. 🚨 Imagine a ticking time bomb, hidden yet potentially devastating – this is the reality of heart health in today’s fast-paced world.
In this blog, we delve into the rising trend of heart attacks among young people, particularly in India. We’ll explore the various factors contributing to this worrying phenomenon, such as sedentary lifestyles, stress, unhealthy eating habits, and more. 🏥 Statistics reveal a startling 2% annual increase in heart attack cases among adults under 40 since 2006. This data underscores the urgency of addressing heart health proactively.
Our goal is to equip you, the busy Indian professional, with knowledge and practical tips to safeguard your heart. From understanding the causes and recognizing symptoms to adopting heart-healthy diets and lifestyles, this blog is your guide to preventing heart attacks at a younger age. Let’s embark on this journey towards a healthier heart together! 💪🏼🍏
Understanding the Rise of Heart Attacks in Youths
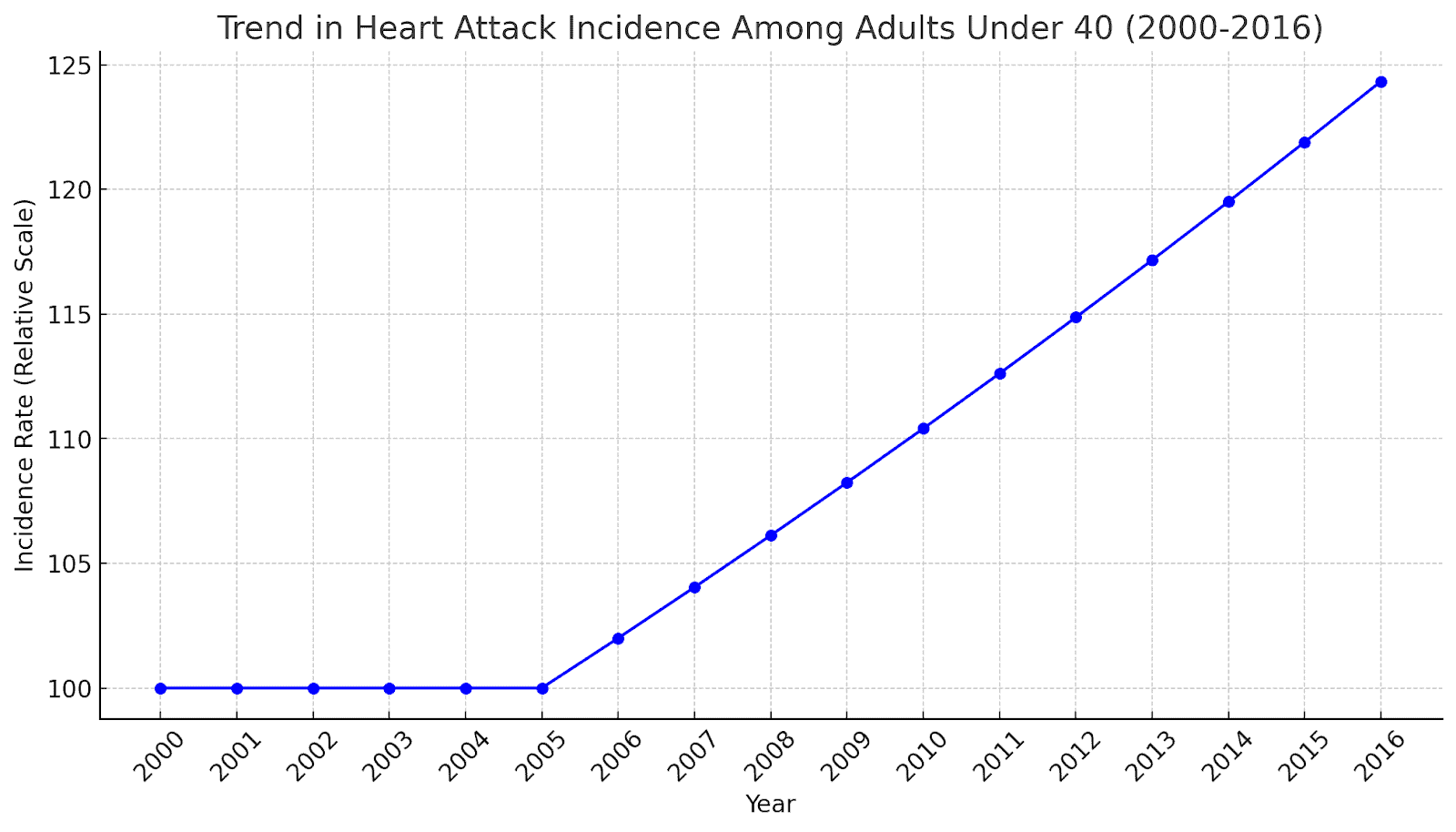
The line graph represents the trend in heart attack incidence among adults under 40 from 2000 to 2016:
- The years 2000 to 2005 show a stable incidence rate, as represented by the flat line in the graph’s initial segment.
- Starting from 2006, there is a 2% annual increase in the incidence rate, illustrated by the upward trend in the graph.
The Banker’s Heartbeat: Part 1
In the bustling heart of Mumbai, where the skyline kissed the heavens, lived Nikhil, a 38-year-old investment banker. His life was a whirlwind of numbers and deals, a dance of digits that never seemed to end.
Nikhil was the epitome of success in his crisp suits and shiny shoes, but his lifestyle was far from healthy. Long hours at the office, fast food, and minimal exercise were his constants. He lived with his wife and young son, who often complained about his absence at home. Despite his emotional intelligence, he brushed off their concerns, believing that providing for them was his primary role.
Adopting Healthy Heart Diets for Youths
Embracing a heart-healthy diet is crucial for young people to mitigate cardiovascular risk factors and promote overall heart health. By incorporating the following dietary habits, you can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and maintain a healthy heart:
- Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your daily meals. These nutrient-rich foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health.
- Opt for whole grains such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oats. These provide dietary fiber and essential nutrients that contribute to a healthy heart.
- Incorporate legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and beans into your diet. They are excellent sources of plant-based protein, fiber, and key minerals that promote heart health.
- Include a variety of nuts and seeds in your snacks or meals. They contain heart-healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health.
- Choose unsaturated fats over saturated and trans fats. Incorporate sources of unsaturated fats such as olive oil, avocados, fatty fish, and nuts into your meals.
- Limit consumption of processed foods that are often high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, and sodium.
- Monitor your salt intake and use herbs and spices to add flavor to your meals instead.
- Include lean sources of protein such as skinless poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu, which provide essential nutrients without adding excessive saturated fats.
- Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Opt for water over sugary beverages.
- Practice mindful eating by paying attention to your hunger and fullness cues. Avoid distractions while eating and savor each bite.
- Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants like berries, dark chocolate, and green tea. Antioxidants help protect against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of heart disease.
By adopting these heart-healthy dietary habits, you can take control of your heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease. Remember, small changes in your eating habits can have a big impact on your cardiovascular well-being.
Common Causes of Heart Attacks in Young People
Heart attacks can occur in young people due to various factors. Poor lifestyle habits such as excessive drinking, smoking, and being overweight can significantly contribute to the risk of myocardial infarction. Chronic stress, hypertension, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle also increase the likelihood of a heart attack. Substance abuse, including drug and alcohol misuse, can further elevate the risk. Additionally, having a family history of heart disease puts individuals at a greater susceptibility to heart attacks at a young age.
Understanding the common causes of heart attacks in young people is crucial in raising awareness and implementing preventive measures to protect cardiovascular health. By addressing these risk factors and adopting a healthier lifestyle, the risk of heart attacks in young individuals can be significantly reduced.
Risk Factors for Heart Attacks in Young People
| Causes | Risk Level |
| Poor Lifestyle Habits (excessive drinking, smoking, and overweight) | High |
| Chronic Stress | Moderate |
| Hypertension | Moderate |
| Diabetes | Moderate |
| Sedentary Lifestyle | Moderate |
| Substance Abuse | Moderate |
| Family History of Heart Disease | High |
It is important for young individuals to recognize the impact of these causes and take proactive steps to mitigate the risk of heart attacks. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, maintaining an appropriate weight, and keeping regular medical check-ups, the probability of experiencing a heart attack can be significantly reduced.
The Banker’s Heartbeat: Part 2
His mental frame was simple: work hard now, enjoy life later. This mantra drove him, even as he ignored the mild chest pains and bouts of breathlessness. He attributed these to stress and lack of sleep, never considering they could be signs of something more sinister.
One evening, as he was leaving the office, Nikhil felt a sharp pain in his chest. He collapsed, clutching his heart. This was his darkest moment, lying on the cold, hard pavement, the city’s lights blurring above him.
Diagnosing and Treating Heart Attacks in Young People
To diagnose a heart attack, medical professionals rely on a patient’s medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. The initial step is to gather information about the patient’s medical history, including any previous cardiac issues, family history of heart disease, and risk factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and sedentary lifestyle. Understanding the patient’s medical history helps in assessing the likelihood of a heart attack and determining appropriate diagnostic tests and treatment options.
In addition to medical history, physical examination plays a crucial role in diagnosing a heart attack in young individuals. The vital signs, including blood pressure and pulse rate, are evaluated to identify any abnormalities that may indicate cardiac distress. Any symptoms reported by the patient, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, are carefully noted and investigated further.
To confirm the diagnosis, several diagnostic tests are performed. Electrocardiography (ECG) is a commonly used test to record the electrical activity of the heart and detect any abnormalities. Echo cardiography, also known as an echocardiogram, is another valuable test that uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart’s structure and functioning. These tests help in evaluating the extent of damage to the heart muscle and identifying if a heart attack has occurred.
Additionally, a troponin test is conducted to measure the levels of troponin, a protein released into the blood when the heart muscle is damaged. Elevated troponin levels indicate a heart attack.
Quick and accurate diagnosis is critical when dealing with heart attacks in young people. Gathering the patient’s medical history, conducting a thorough physical examination, and performing diagnostic tests help healthcare professionals make an informed diagnosis.
Once a heart attack is diagnosed, prompt treatment is essential to minimize damage and prevent complications. The primary treatment option for heart attacks in young individuals is urgent coronary angioplasty. This procedure involves opening the blocked or narrowed arteries using a balloon-tipped catheter, followed by the placement of a stent to keep the artery open. This helps restore blood flow to the heart muscle.
In addition to urgent coronary angioplasty, medications play a crucial role in the treatment of heart attacks. Blood thinners, such as aspirin and antiplatelet drugs, help prevent clot formation and reduce the risk of further blockages. Pain relievers, such as nitroglycerin, help alleviate chest pain and discomfort. Medications to dissolve clots may also be administered to restore blood flow more quickly.
The specific medications prescribed may vary based on individual factors such as the extent of the heart attack, underlying health conditions, and the patient’s response to treatment.
Immediate medical attention is crucial for young individuals experiencing a heart attack. The sooner the diagnosis is made and appropriate treatment initiated, the better the chances of a positive outcome and a faster recovery.
Preventing Heart Attacks in Young People
Preventing heart attacks in young people is crucial for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health. By implementing a range of lifestyle modifications and adopting healthy habits, you can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease. Here are some key preventive measures:
- Adopting a Balanced Diet: A well-rounded, balanced diet is the foundation for heart health. Focus on consuming a variety of nutritious foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Incorporate fiber-rich foods to support digestion and reduce cholesterol levels.
- Reducing Sodium Intake: Excess sodium can contribute to high blood pressure, placing strain on the heart. Limit your consumption of processed foods, fast food, and canned goods, as they are often high in sodium. Opt for fresh, homemade meals with minimal added salt.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping tabs on your blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals at risk of developing diabetes. Uncontrolled blood sugar can increase the likelihood of heart disease. Maintain a healthy weight, limit refined sugars and carbohydrates, and follow a diabetes management plan if necessary.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking damages your blood vessels and can significantly increase the risk of heart attacks. Seek support and resources to quit smoking, such as nicotine replacement therapies, counseling, or support groups.
- Maintaining an Active Lifestyle: Regular physical activity is essential for overall heart health. Engage in moderate-intensity exercises such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing for at least 150 minutes per week. Find activities you enjoy to stay motivated.
- Understanding Family Heart History: Knowing your family’s heart history can offer insight into your own risk factors. If there is a history of heart disease, work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized prevention plan.
- Managing Stress: Chronic stress has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, seeking social support, or trying relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts strain on the heart and increases the risk of heart attacks. Aim for a healthy weight range by adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity.
“Preventing heart attacks in young people starts with adopting a balanced diet, reducing sodium intake, monitoring blood sugar levels, quitting smoking, and maintaining an active lifestyle.”
Incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine can provide long-term benefits for your heart health. Remember, small changes can make a significant difference in reducing the risk of heart attacks. Prioritize your cardiovascular well-being and make proactive choices to protect your heart.
The Banker’s Heartbeat: Part 3
Rushed to the hospital, Nikhil was confronted with the truth by Dr. Mehta, a cardiologist. “You’ve had a minor heart attack,” the doctor said gravely. “Your lifestyle is not just harming your health; it’s risking your life.”
The words hit Nikhil like a ton of bricks. He realized his mistakes – his neglect of health for wealth. Lying in the hospital bed, he reflected on his life choices. He decided to change, not just for himself, but for his family.
Heart Attack Risk Factors in Young People
In order to prevent heart attacks in young individuals, it is crucial to understand the risk factors that contribute to this health concern. By recognizing these factors and taking proactive steps to modify them, the risk of heart attacks can be significantly reduced.
Type 2 Diabetes: Individuals with type 2 diabetes are at a higher risk of heart attacks due to the effects of high blood sugar on the blood vessels and heart.
Tobacco Use: Smoking and tobacco use are known to increase the risk of heart disease. The chemicals in tobacco can damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to a higher likelihood of experiencing a heart attack.
Substance Abuse: The abuse of substances such as drugs and alcohol can have detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart attacks in young people.
Family History: Having a family history of heart disease, especially at a young age, is a significant risk factor. Genetics can play a role in predisposing individuals to heart attacks.
Genetic Risk: Certain genetic factors can make individuals more susceptible to heart attacks. Understanding one’s genetic risk can help in taking preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack.
High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure, also known as hypertension, puts added stress on the heart and increases the risk of heart attacks in young people.
Waist Circumference: Excess abdominal fat, indicated by an unhealthy waist circumference, can contribute to the development of heart disease and increase the risk of heart attacks.
Unhealthy BMI: Having a body mass index (BMI) that falls into the overweight or obese category is associated with a higher risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
Recognizing these heart attack risk factors is the first step towards prevention. Taking proactive measures to address these factors, such as managing diabetes, quitting smoking, seeking help for substance abuse, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks in young individuals.
Tips for Maintaining Heart Health in Young People

To maintain a healthy heart, there are several essential tips that young people should follow. By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of heart attacks and promote overall cardiovascular well-being.
1. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, most days of the week. Exercise helps strengthen the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for heart health. Be mindful of your calorie intake and focus on consuming whole, nutritious foods. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your diet. Avoid excessive consumption of processed and sugary foods, which can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of heart disease.
3. Consume Nutritious Foods
A heart-healthy diet plays a vital role in preventing heart attacks. Opt for foods that are low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. Include foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables. Choose lean proteins, such as poultry, fish, and plant-based sources. These dietary choices help lower cholesterol levels, maintain healthy blood pressure, and improve overall heart function.
4. Manage Stress
Stress can negatively impact heart health. Implement stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in activities you enjoy. Adequate sleep and maintaining a healthy work-life balance are also important for stress reduction. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks.
5. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. If you smoke, it’s crucial to quit as soon as possible. Seek support from healthcare professionals or join smoking cessation programs to increase your chances of successfully quitting. Quitting smoking improves heart health and reduces the risk of heart attacks.
6. Be Aware of Family Heart History
Knowing your family’s heart history is essential for understanding your own risk factors. Certain heart conditions and risk factors, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, can run in families. Share this information with your healthcare provider so they can help assess and manage your cardiovascular risk effectively.
By following these heart health tips, you can protect your heart and reduce the risk of heart attacks. It’s never too early to prioritize your cardiovascular well-being and make positive lifestyle changes for a healthier future.
The Banker’s Heartbeat: END
With Dr. Mehta’s guidance and support from his friend, Vivek, Nikhil embarked on his journey to recovery. He adopted a healthier diet, started exercising, and made time for his family. His transformation was not just physical but mental and emotional.
As he sat on his balcony one evening, watching the sunset, Nikhil realized the true wealth in life was health and family. He had learned his lesson the hard way, but he was grateful for the second chance.
“Remember, it’s never too late to change. How will you protect your heart today?”
Conclusion
The rising concern of heart attacks in young people highlights the need to prioritize heart health. By making lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits, you can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks.
Prevention is key, and it starts with regular exercise to keep your heart strong and healthy. Engaging in physical activities that you enjoy, such as jogging, cycling, or swimming, can make a significant difference in your heart health.
In addition, making healthy dietary choices is crucial. Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid processed foods and limit your intake of salt and saturated fats. By fueling your body with nutrient-dense foods, you can support your heart’s well-being.
Stress management is another essential aspect of maintaining a healthy heart. Find healthy coping mechanisms, such as practicing mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in activities that bring you joy and relaxation. By managing stress, you can protect your heart from the damaging effects of chronic stress.
Lastly, it’s important to identify and modify risk factors that contribute to heart attacks. Regularly monitor your blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and consult with a healthcare professional to address any concerns. If you smoke, quitting is one of the most significant steps you can take to protect your heart.
In conclusion, taking care of your heart at a young age is crucial for long-term heart health. By implementing lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, stress management, and risk factor modification, you can greatly reduce the risk of heart attacks and ensure a healthier future.
Key Takeaways:
- Heart attacks are no longer limited to older individuals; teenagers and young people are also at risk.
- Inactivity, stress, smoking, drinking, diabetes, hypertension, and obesity contribute to the rise of heart attacks among young people.
- A heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and preventive measures can help reduce the risk of heart attacks in teenagers.
- Early detection and prompt medical attention are crucial in diagnosing and treating heart attacks in young individuals.
- Understanding the risk factors and adopting a proactive approach to heart health can help prevent heart attacks in young people.
FAQ Section on Recognizing and Preventing Heart Attacks among Young People
A: Major risk factors for cardiac arrest among young people include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congenital heart abnormalities, heart rhythm disorders, and previously undiagnosed heart conditions.
A: While heart attacks are less common in adolescents compared to adults, they can still occur, especially in those with underlying heart conditions or genetic predispositions.
A: The key symptoms of a heart attack in teenagers may include chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting, or palpitations. It’s important to seek medical attention if these symptoms occur.
A: Early signs of a heart problem in young individuals may include experiencing chest pain during physical activity, feeling lightheaded or dizzy during exercise, or having a family history of heart disease. Regular check-ups with a cardiologist can also help identify any potential issues.
A: Preventive measures include promoting regular physical activity, educating about the signs of heart problems, encouraging healthy lifestyle choices, and conducting screenings for underlying heart issues in young individuals, especially those involved in sports or intense physical activities.
A: Sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of sudden cardiac death in young individuals due to the potential development of underlying heart issues, as physical inactivity contributes to cardiovascular disease risk factors.
A: Lowering the risk involves promoting physical activity, educating about healthy lifestyle choices, conducting regular screenings for heart issues, and raising awareness about the signs and symptoms of heart problems, especially among those at higher risk.
A: Underlying heart conditions that may lead to sudden cardiac death include genetic heart disorders, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, heart rhythm abnormalities, structural defects in the heart, and certain coronary artery abnormalities.
A: Adolescents can reduce their risk of experiencing a heart attack by maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, managing stress, and seeking regular medical check-ups to monitor their heart health.
A: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can significantly increase the risk of developing heart disease and experiencing a heart attack among young individuals, emphasizing the importance of early detection and management of this condition.
A: Sudden cardiac arrest is a sudden loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness, often caused by an electrical disturbance in the heart. It differs from a heart attack, which occurs when blood flow to a section of the heart becomes blocked.
A: Adolescents can lower the risk of sudden cardiac death by staying physically active, eating a healthy diet, avoiding smoking and drug abuse, managing stress, and getting regular check-ups with a cardiologist.
A: Yes, some specific risk factors for sudden cardiac death in young athletes include certain genetic heart conditions, underlying heart rhythm abnormalities, and a history of fainting during exercise or activity.
A: Preventing sudden cardiac death among adolescents involves raising awareness about heart health, providing access to CPR training and AEDs in schools and sports facilities, and conducting regular heart screenings for young athletes.
A: Physical activity plays a crucial role in preventing heart attacks among adolescents by promoting cardiovascular health, maintaining a healthy weight, and reducing the risk of developing heart disease.
A: While relatively rare, heart attacks can occur in teenagers, and it’s important to recognize the symptoms and risk factors to ensure prompt medical attention and intervention.
A: It’s important for parents and educators to be aware of early heart attack symptoms in adolescents, including chest discomfort, shortness of breath, and fainting, and to seek medical attention if any concerning symptoms arise.
A: To prevent sudden cardiac death in young people, it’s crucial to promote physical activity, encourage regular heart screenings, and raise awareness about the risks of heart issues among adolescents.
A: Sudden cardiac arrest among young individuals can be caused by underlying heart rhythm abnormalities, congenital heart conditions, and certain genetic or hereditary factors.
A: Lowering the risk of a heart attack in adolescents involves promoting healthy lifestyle choices, educating about the importance of regular exercise, and addressing any underlying heart issues promptly.
A: Raising awareness about heart issues among young individuals can involve organizing educational campaigns in schools, implementing heart health programs, and collaborating with healthcare professionals and organizations to spread the word about prevention and symptoms recognition.
A: You can find resources on preventing heart attacks among adolescents through reputable healthcare organizations, such as the American Heart Association, and by seeking information from cardiologists and heart institutes.
A: Supporting young individuals in understanding the risks and symptoms of heart issues can be achieved through open discussions, providing access to educational materials, and encouraging them to seek medical attention if they experience any concerning symptoms.
